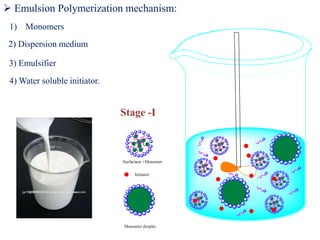
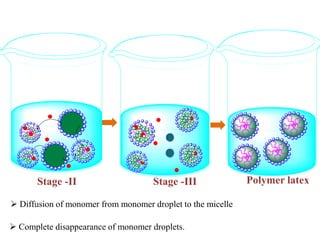
Emulsion polymerization involves radical chain polymerization where monomers are dispersed as droplets in water and polymerize within micelles. It allows for high molecular weight polymers to form at high reaction rates. The process involves four main components: 1) monomers, 2) a dispersion medium (water), 3) an emulsifier, and 4) a water-soluble initiator. Polymerization occurs only within the micelles. The mechanism proceeds in three stages: initiation within the micelles, monomer diffusion into particles as conversion increases, and consumption of monomer droplets. Emulsion polymerization produces polymer latex particles and addresses heat transfer and viscosity issues relative to other polymerization methods.