Embed presentation
Downloaded 121 times





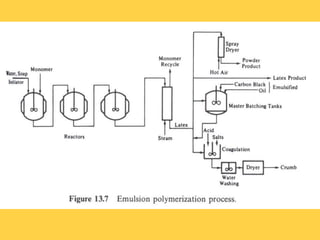


Emulsion polymerization is a process where droplets of monomer are emulsified in water using surfactants. Common ingredients include 100 parts monomer, 180 parts water, 2-5 parts acid soap, and 0.1-0.5 parts water-soluble initiator. During the process, monomers inside micelles decrease as the growing polymer particle absorbs them. Unreacted monomers diffuse to other micelles and particles to continue the reaction. Polymers produced via emulsion polymerization include synthetic rubbers like styrene-butadiene rubber and plastics like polyvinyl chloride and polystyrene.






