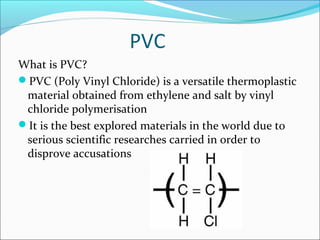
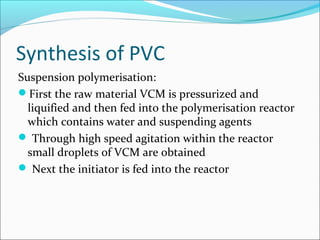
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a versatile thermoplastic material produced through the polymerization of ethylene and salt with vinyl chloride. It is synthesized through suspension polymerization where vinyl chloride monomer droplets are formed and polymerized in a reactor at 400-600°C. This produces PVC particles suspended in water that are then processed into a white powder. PVC has a wide range of applications, including use in construction materials, healthcare products like blood bags, electronic cables, automotive components, and sports equipment, due to its weather resistance, versatility between rigid and flexible forms, fire resistance, longevity, energy recovery potential, and recyclability.