Embed presentation




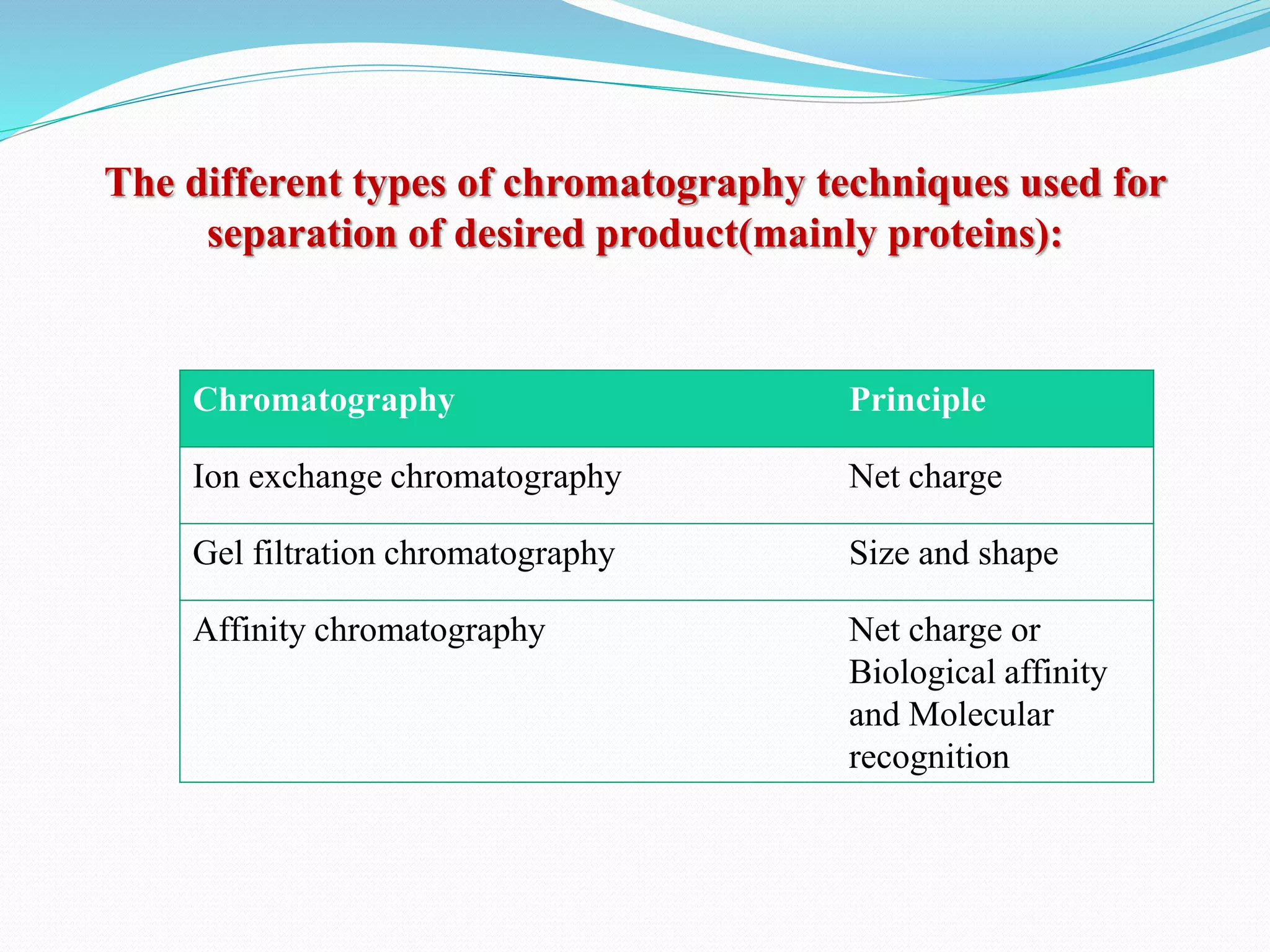

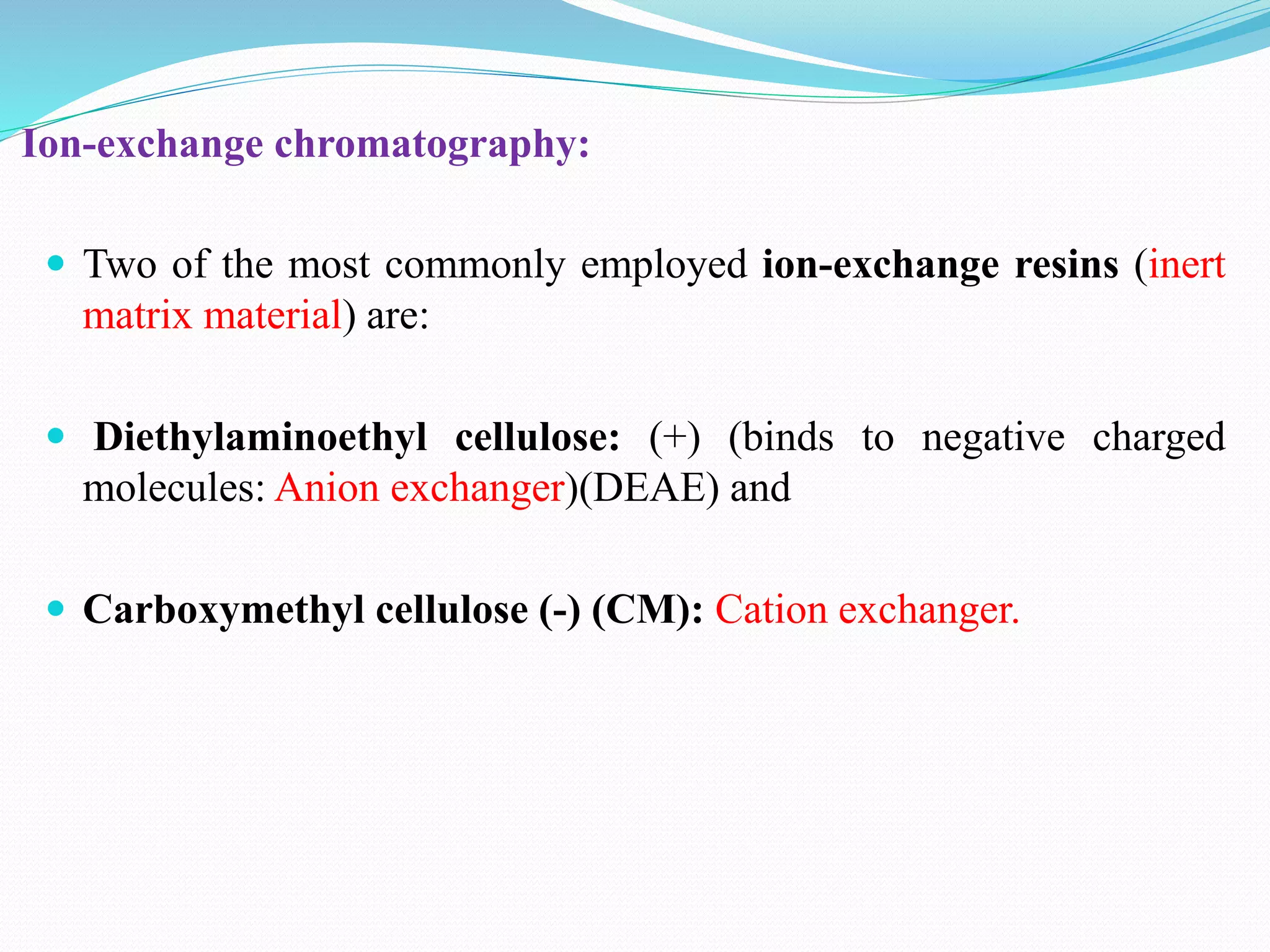
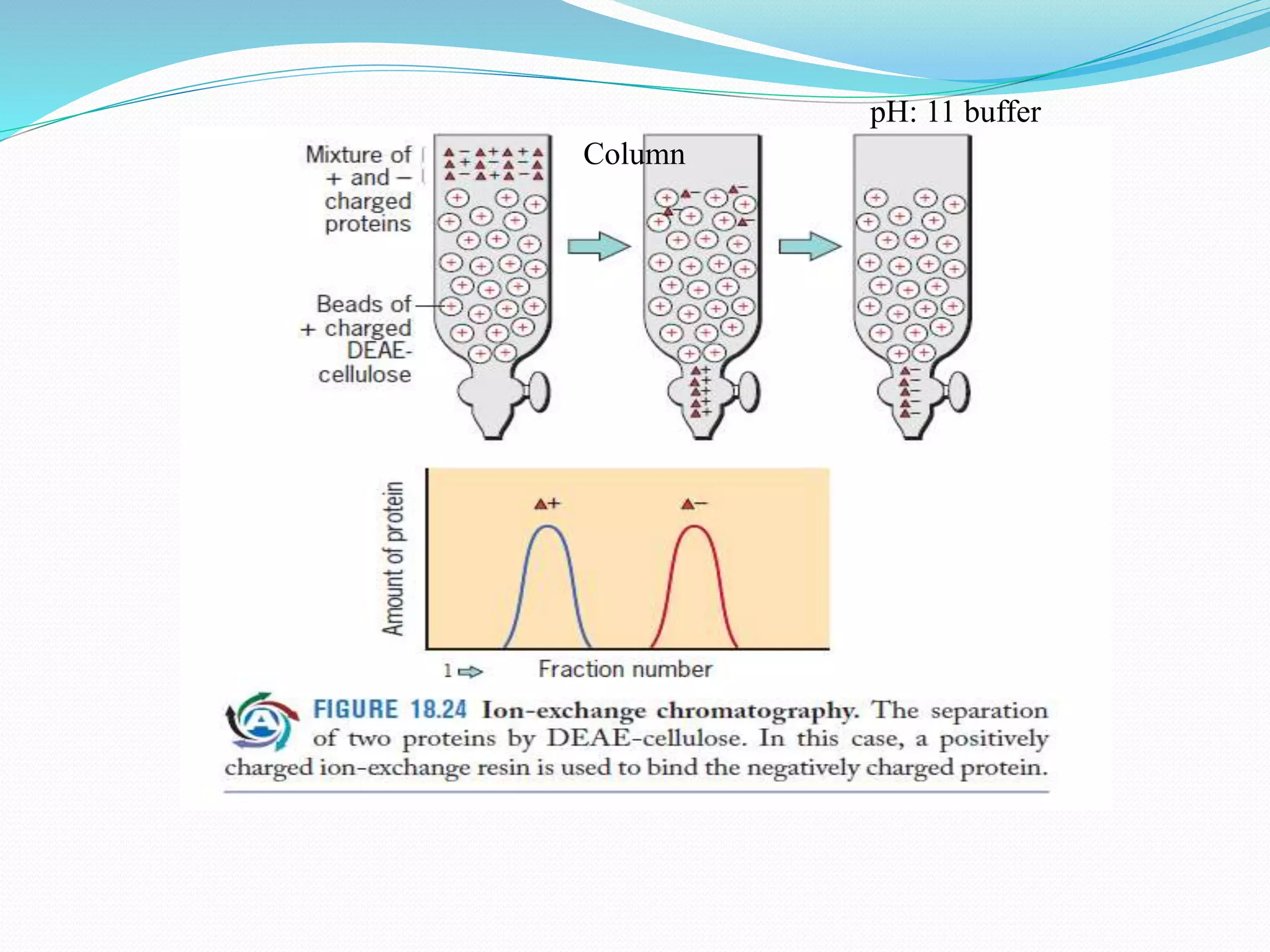




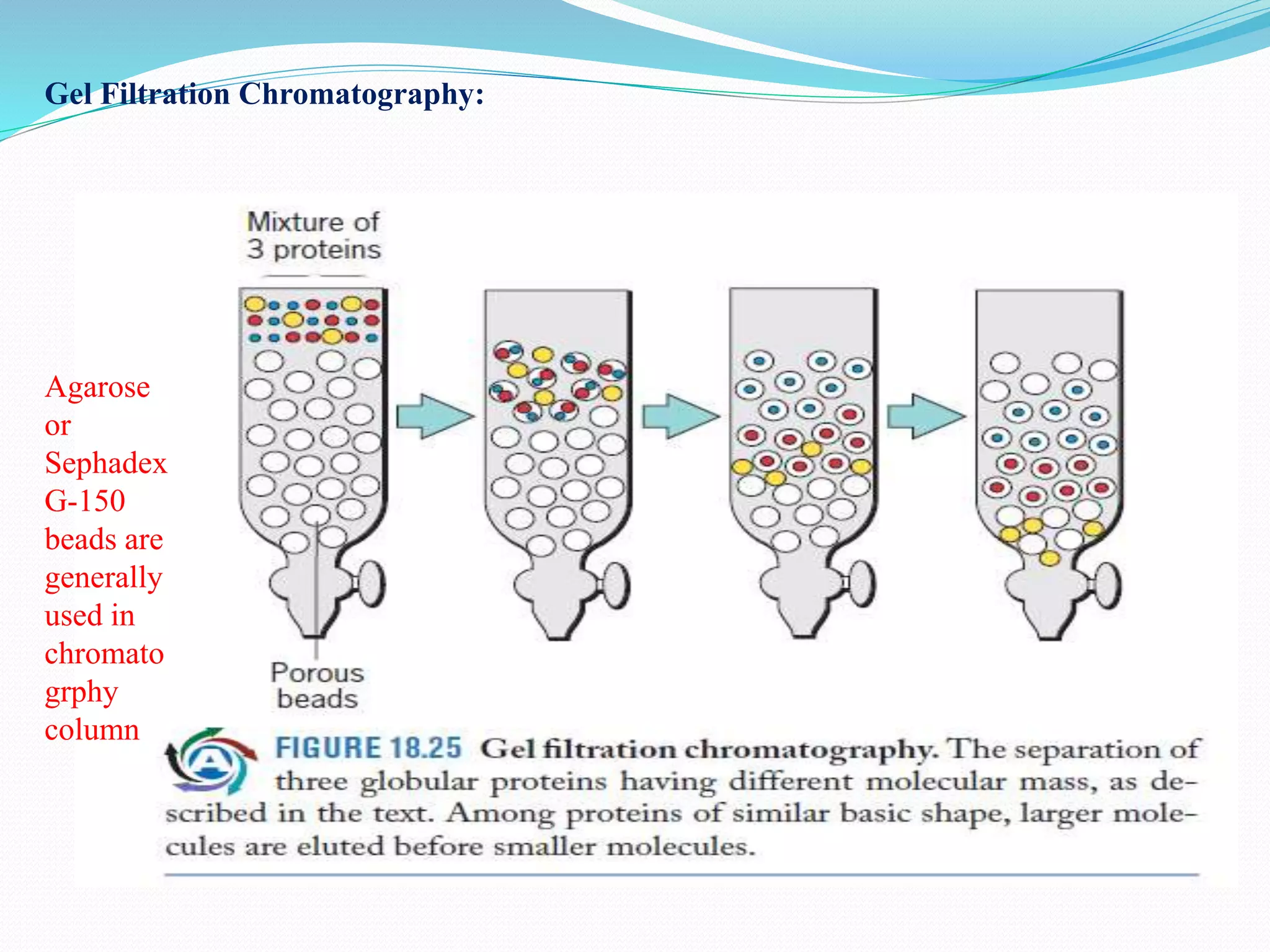
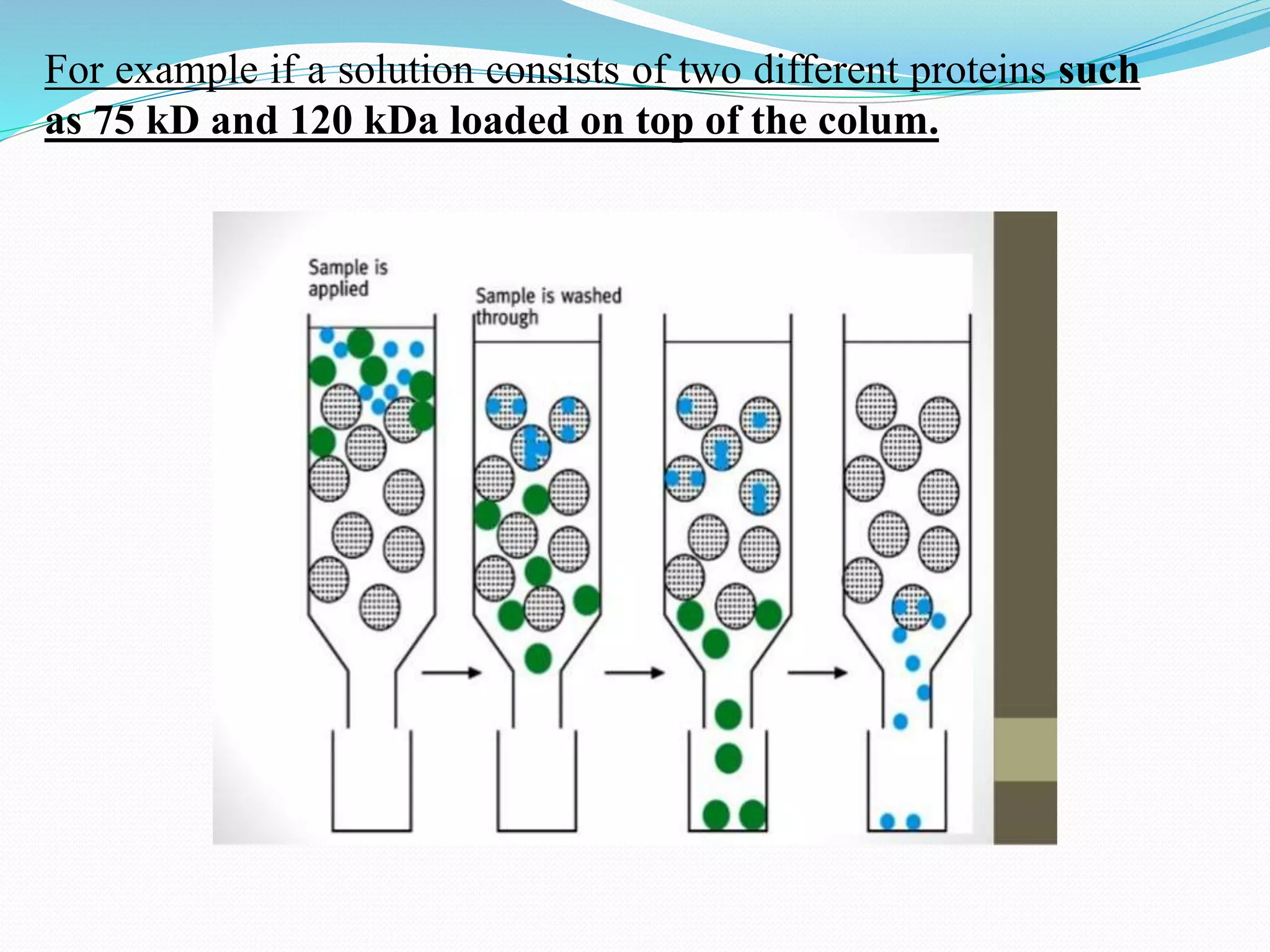




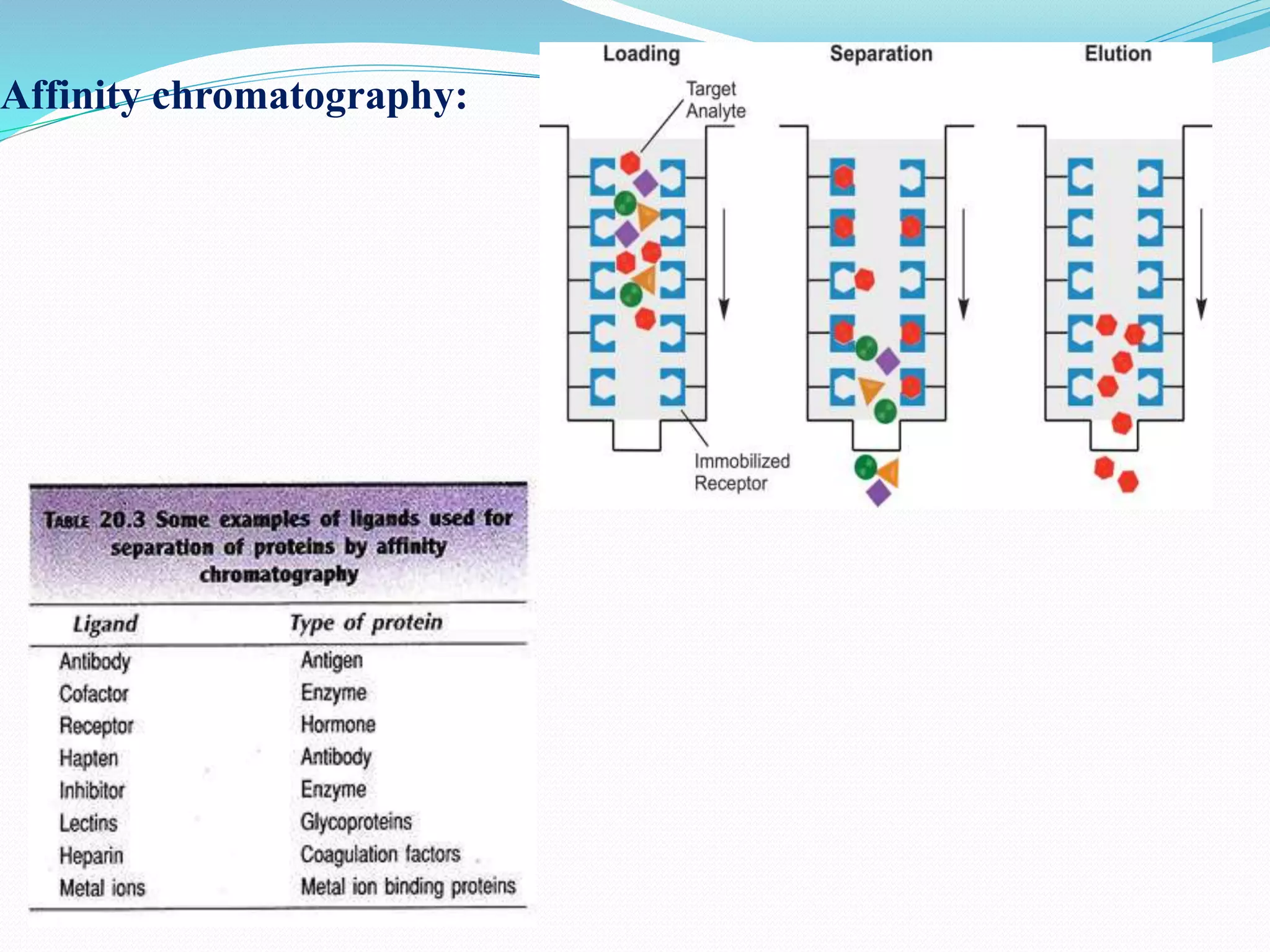













The document discusses various chromatography techniques used to purify biological products from fermentation, including ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, and affinity chromatography. It provides details on how each technique works, such as how ion exchange chromatography separates molecules based on surface charge using cation or anion exchangers, and how gel filtration chromatography separates proteins based on size as they diffuse in and out of gel beads of different porosity. The document also discusses formulation of biological products, including drying methods like spray drying and freeze drying which are used to produce stable dry powders.































