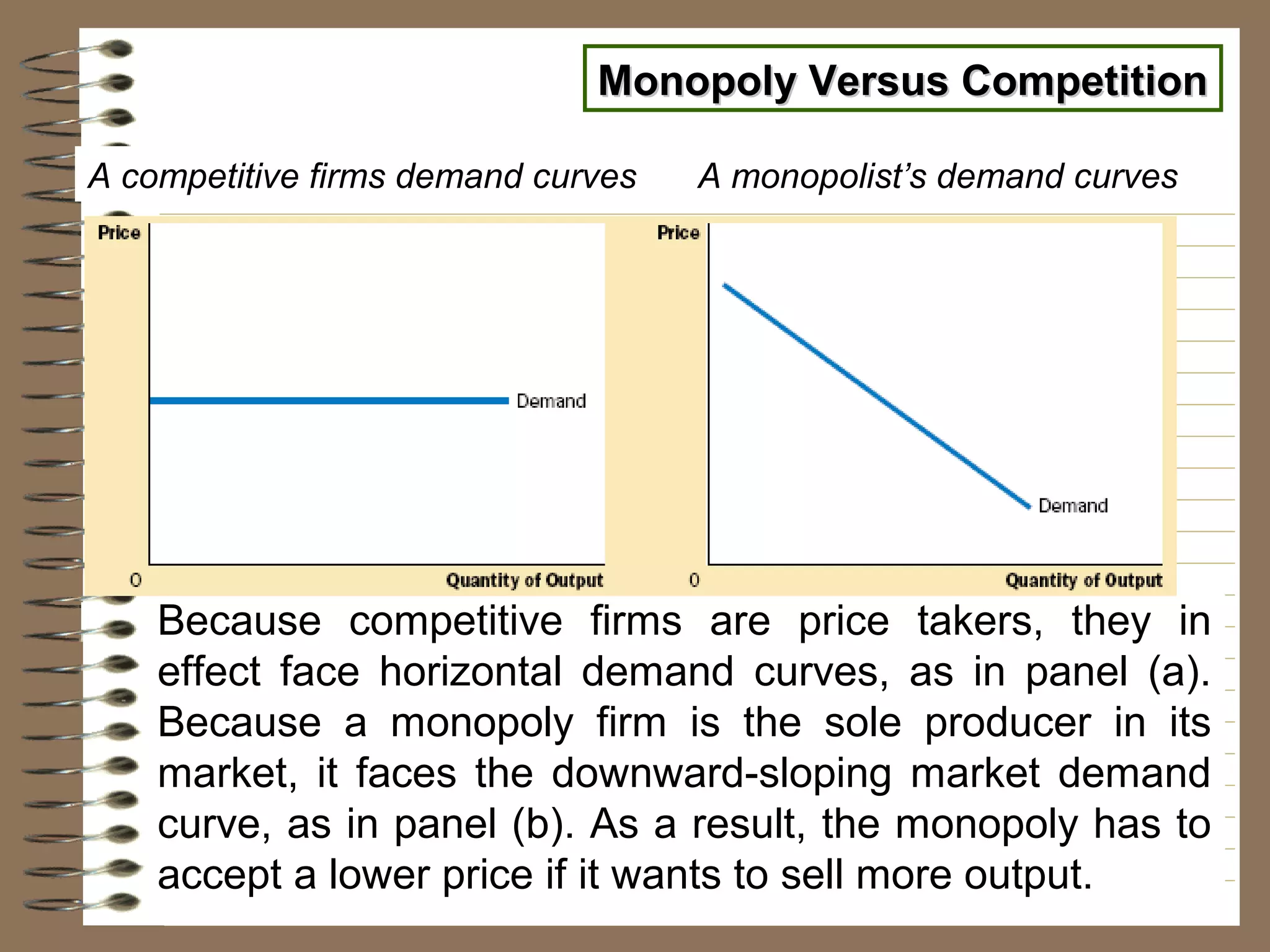
A pure monopoly exists when a single firm is the sole producer of a product with no close substitutes. A pure monopolist faces a downward-sloping demand curve and is a price maker. It controls total supply and has influence over price. Entry into the industry is blocked. A pure monopolist maximizes profits by producing at the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and setting the price on the demand curve corresponding to that quantity of output. This generally results in a smaller quantity and higher price than under perfect competition.