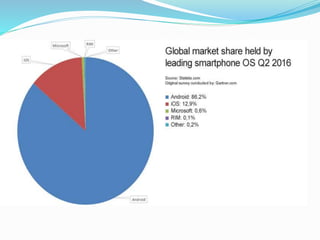
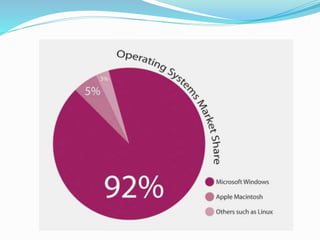
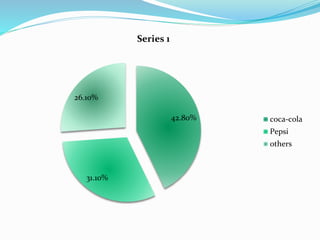
This document discusses oligopoly, which is a market structure with a few large firms that dominate the industry. It defines oligopoly and lists its key characteristics. It then describes the different types of oligopoly including pure/perfect, differentiated, collusive, non-collusive, open, and closed oligopolies. Barriers to entry in oligopolies are also outlined. Several real-world examples of oligopolistic industries are provided such as smartphones, computers, music, automobiles, soft drinks, airlines, and supermarkets. The document concludes by mentioning two models used to explain oligopoly behavior: the kinked demand model and price leadership model.