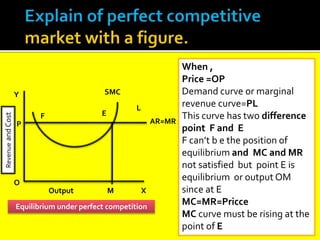
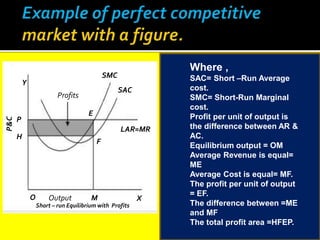
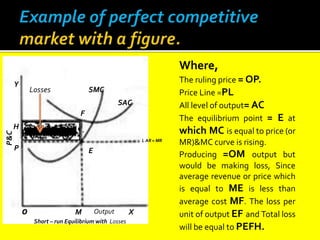
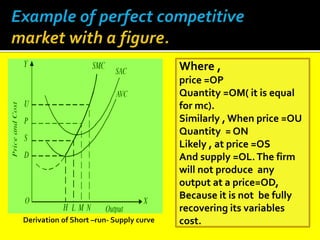
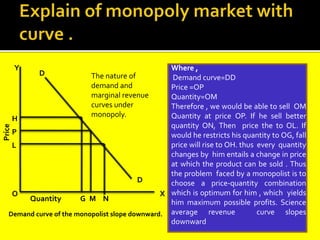
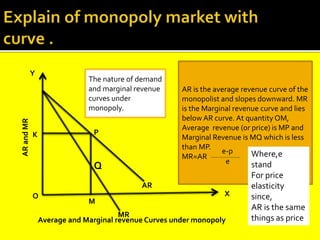
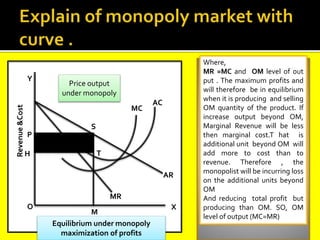
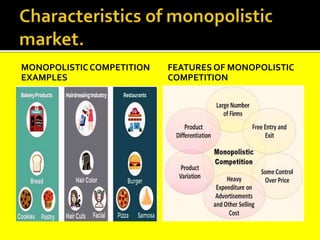
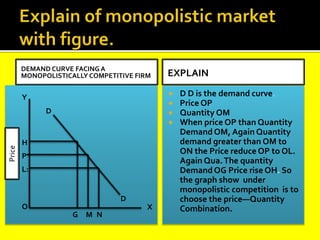
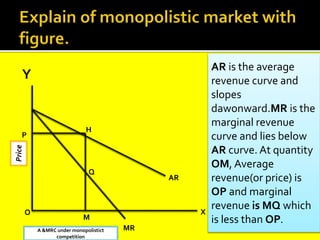
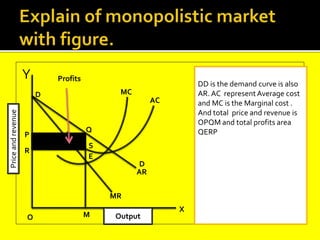
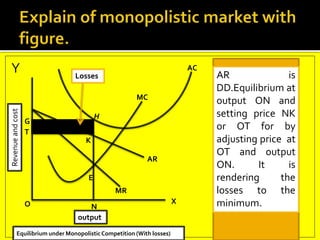
This document provides an overview of three market structures: perfect competition, monopoly, and monopolistic competition. It defines each market structure and lists their key characteristics. For each one, it also includes an example graph illustrating the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, average cost curve, and marginal cost curve. The document explains how firms determine equilibrium output and price under each market structure in order to maximize profits or minimize losses.