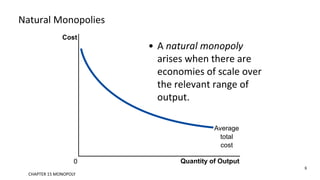
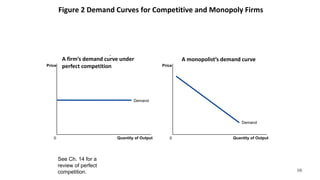
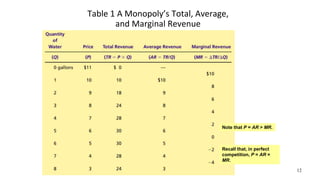
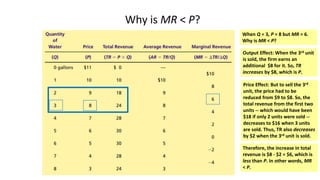
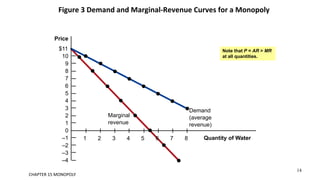
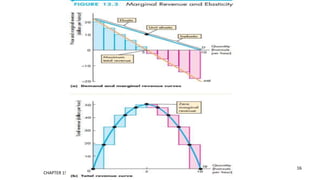
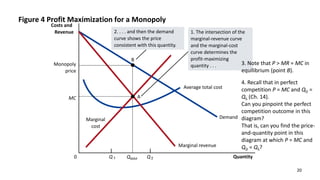
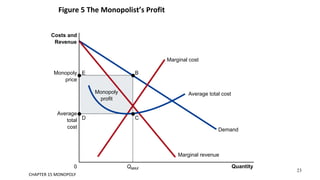
This document discusses monopolies and how they make production and pricing decisions. It defines a monopoly as a firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes. Monopolies can arise due to barriers to entry, which include owning a key resource, government restrictions, or large economies of scale. A monopoly faces a downward-sloping demand curve and is a price maker, unlike competitive firms which are price takers. A monopoly sets its profit-maximizing quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, and then sets the price on the demand curve consistent with that quantity, which is above marginal cost.