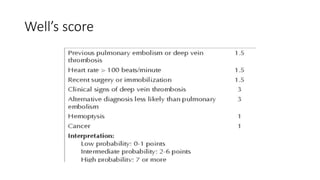
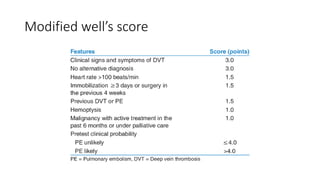
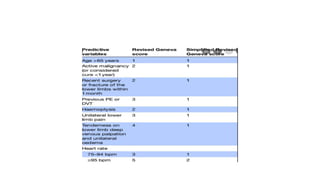
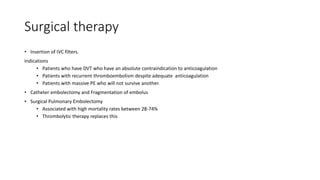
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a significant obstruction in the pulmonary arteries that results from thrombus originating in the venous system, primarily due to deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It poses a substantial global health burden, with an estimated 100,000 deaths annually in the U.S. and an array of clinical features varying from chest pain and dyspnea to circulatory collapse, necessitating prompt diagnosis and management such as anticoagulation and possibly thrombolytic therapy.











![• Pulmonary infarction (interruption of pulmonary artery blood flow
leading to ischemia of lung tissue, sometimes represented by a
pleural-based [peripherally located], often wedge-shaped pattern on
chest x-ray [Hampton hump] or other imaging modalities) occurs in <
10% of patients diagnosed with PE. This low rate has been attributed
to the dual blood supply to the lung (ie, bronchial and pulmonary).
Generally, pulmonary infarction is due to smaller emboli that become
lodged in more distal pulmonary arteries and is nearly always
completely reversible; pulmonary infarction is recognized early, often
before necrosis occurs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonaryembolism-240529232232-2350e25a/85/Pulmonary-embolism-slide-presentation-pptx-13-320.jpg)