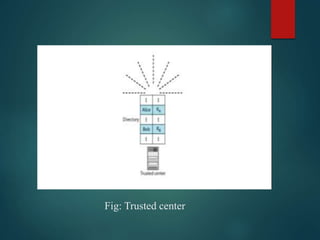
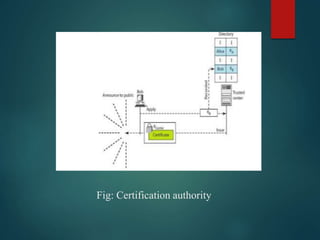
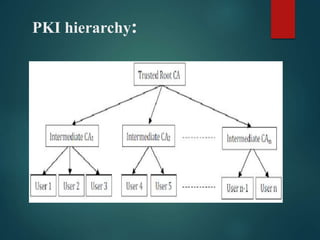
This presentation discusses various methods of public key distribution, including: public announcement; a trusted center directory; a controlled trusted center with timestamps; and a certification authority hierarchy using X.509 certificates. It describes how a public key infrastructure (PKI) establishes a hierarchical system of certification authorities to authenticate, manage and distribute digital certificates containing public keys.