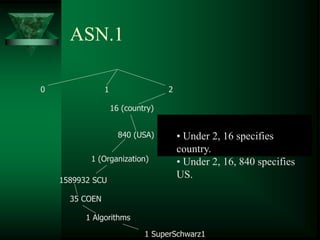
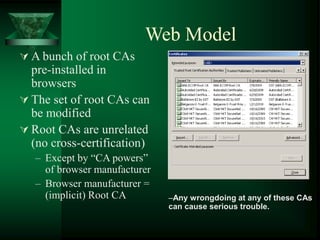
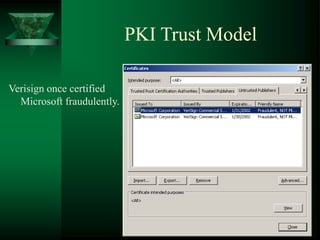
A certificate authority (CA) binds public keys to user identities through digital certificates. This establishes a public key infrastructure (PKI) based on asymmetric cryptography. However, a single CA cannot handle all public key queries, so certificate authority hierarchies are used with multiple levels of CAs. The X.509 standard defines the structure of digital certificates, including the issuer, validity period, subject, and signature.