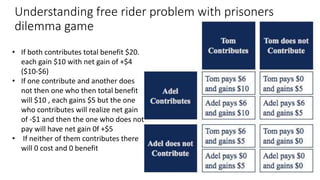
Public goods are non-rival and non-excludable goods. They have characteristics of non-excludability, meaning once produced their benefits cannot be confined only to those who pay. They are also non-rival, so one person's consumption does not diminish another's. Examples include national defense, street lights, and fresh air. Private markets often underprovide public goods due to free-rider problems, where people can benefit without paying. This leads to underprovision. The government can more efficiently provide public goods by charging for them through taxes to avoid these issues.