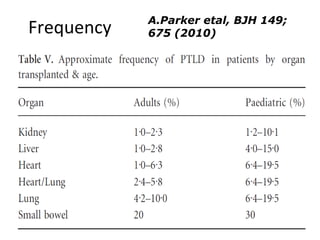
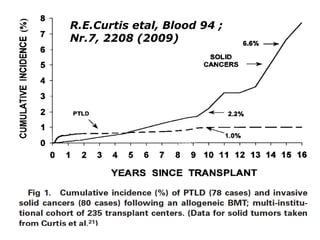
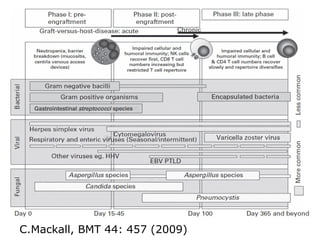
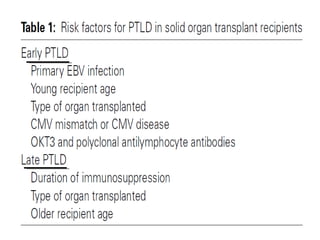
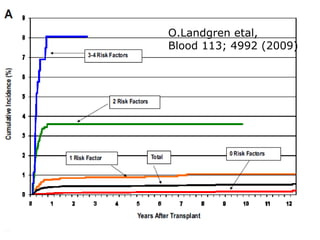
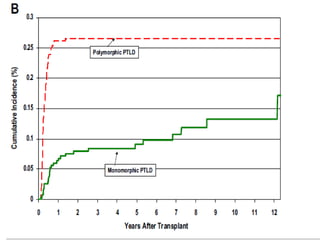
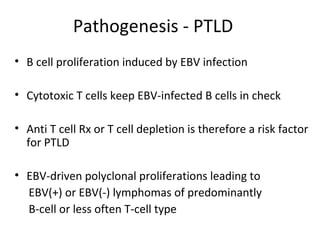
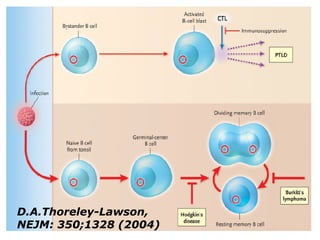
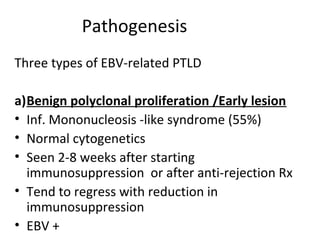
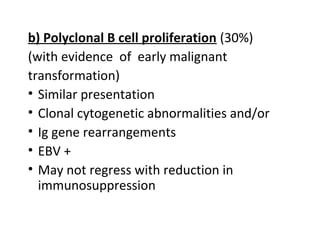
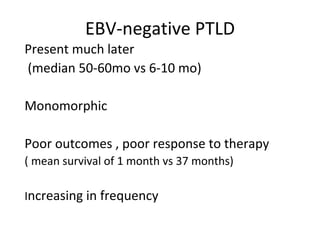
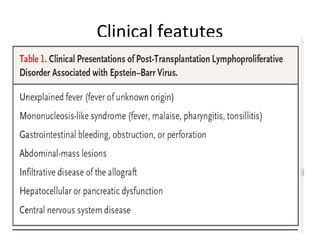
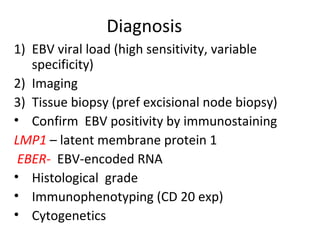
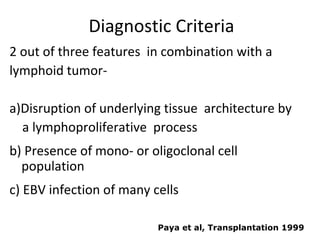
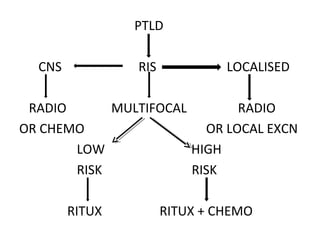
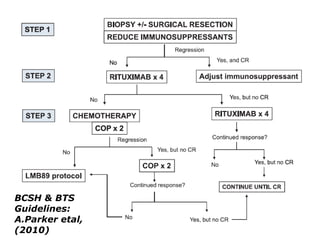
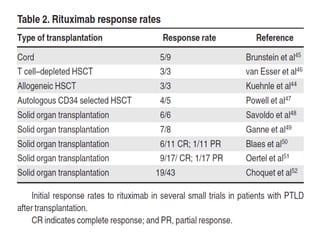
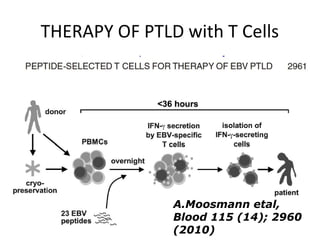
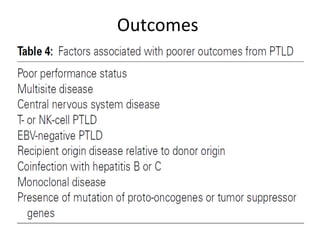
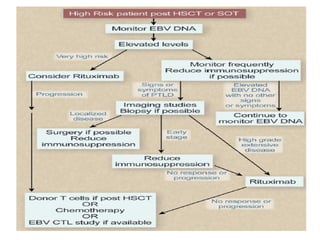
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is a lymphoid proliferation that occurs after solid organ or stem cell transplantation due to immunosuppression. It is caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection in B cells that is normally kept in check by cytotoxic T cells. PTLD ranges from benign early lesions to malignant monoclonal B cell proliferations and has an incidence of around 10% in solid organ transplant recipients. Diagnosis involves evaluating EBV viral load, imaging, and biopsy to detect EBV infection and lymphoid proliferation. Treatment depends on disease severity and includes reducing immunosuppression, antiviral drugs, surgery, rituximab, chemotherapy, and