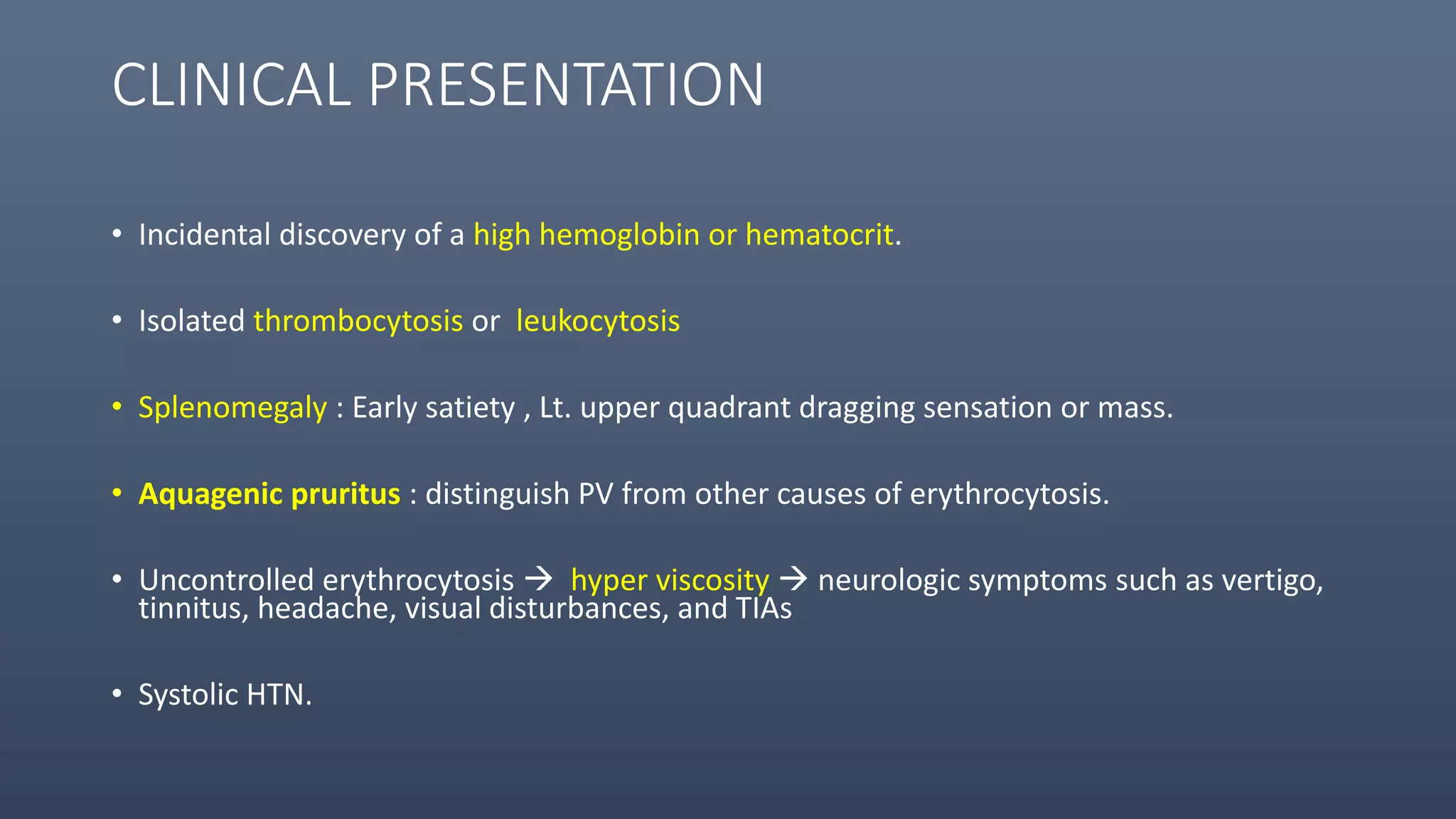
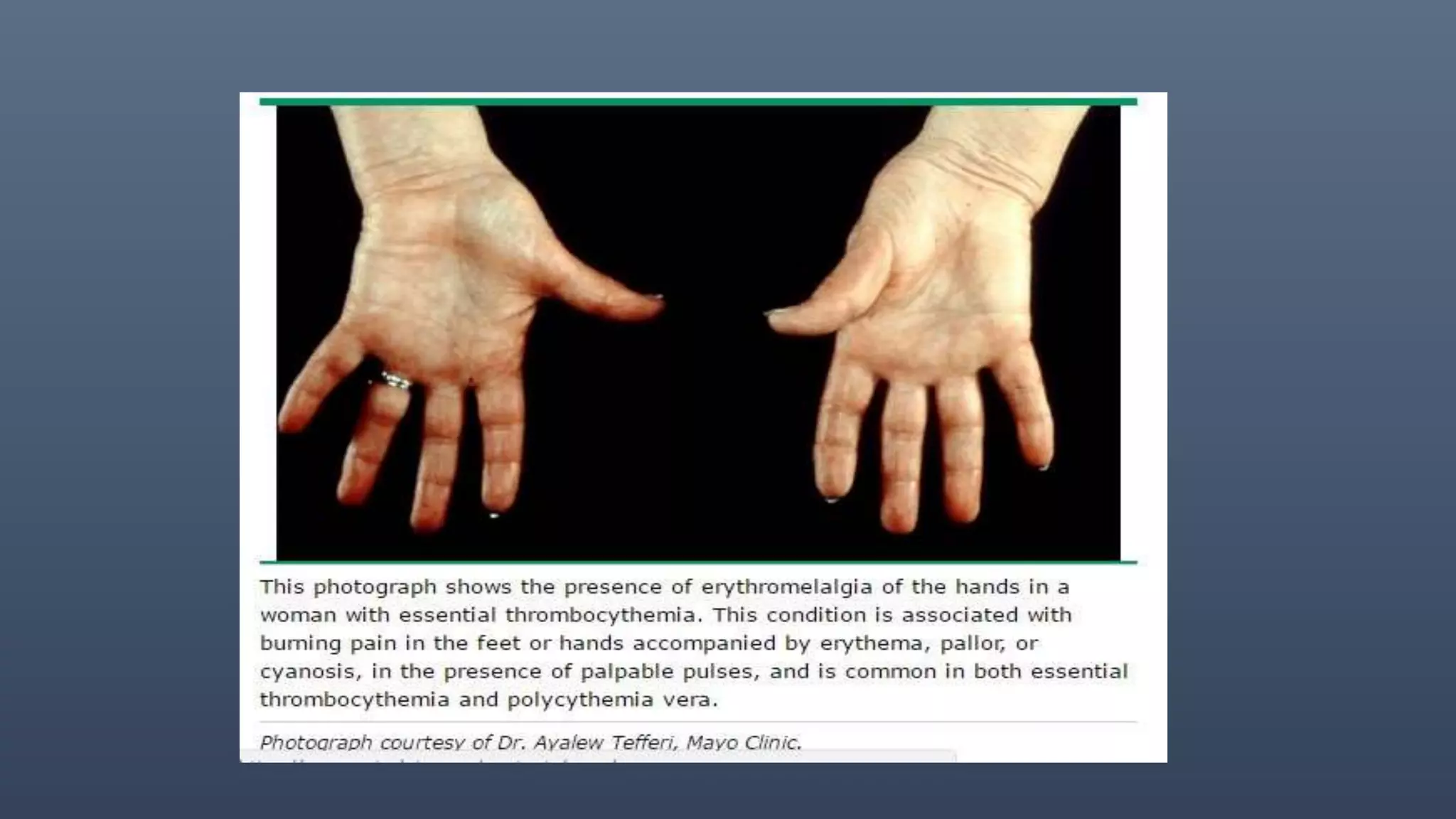
1. Polycythemia vera (PV) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by an overproduction of red blood cells without an identifiable stimulus. It commonly presents with erythrocytosis, splenomegaly, thrombosis, and pruritus.
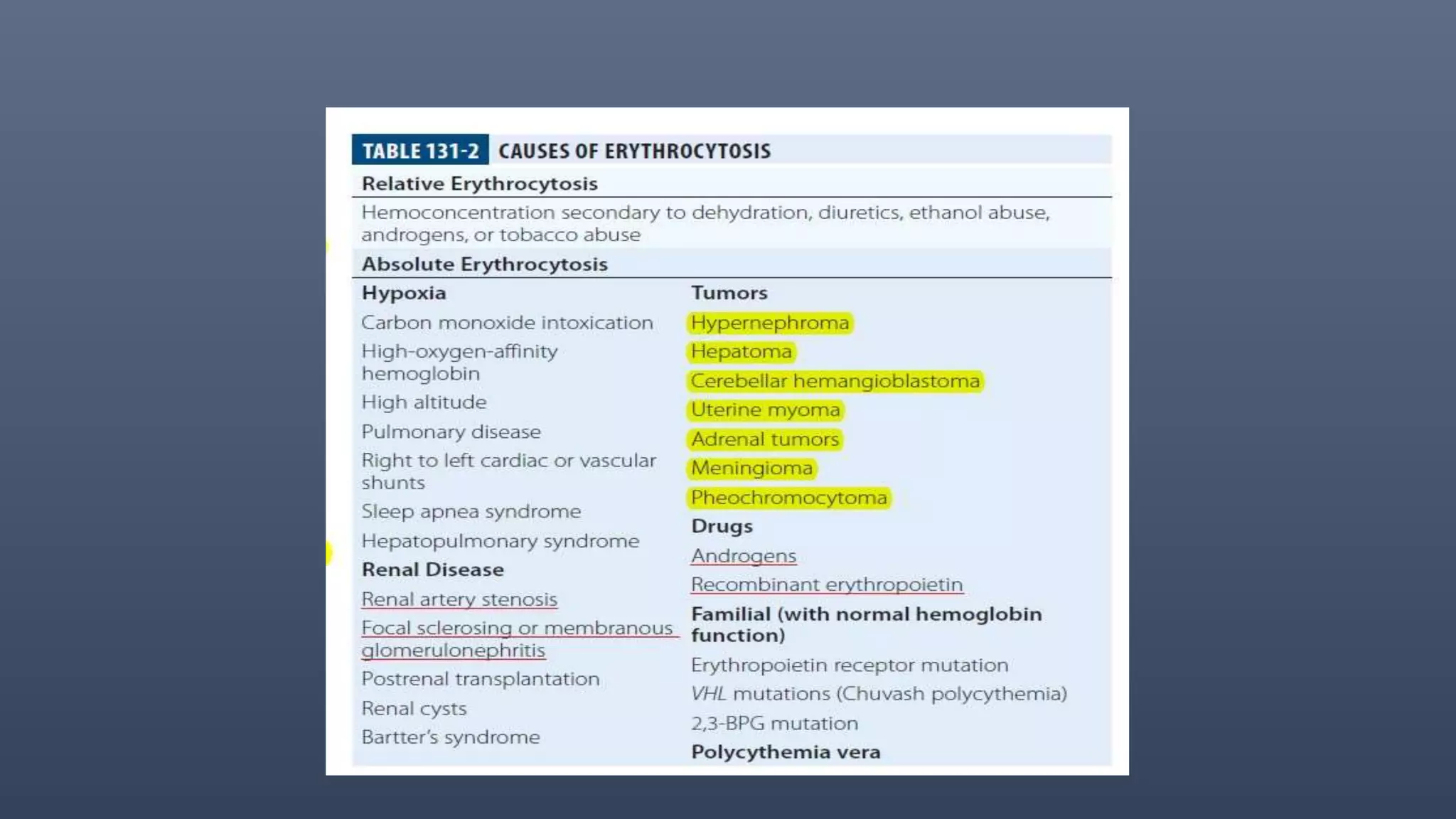
2. The main cause of PV is a mutation in the JAK2 gene, but some patients have mutations in exon 12. Diagnosis requires tests to distinguish absolute from relative erythrocytosis. Treatment focuses on phlebotomy and medications to control symptoms and prevent complications.
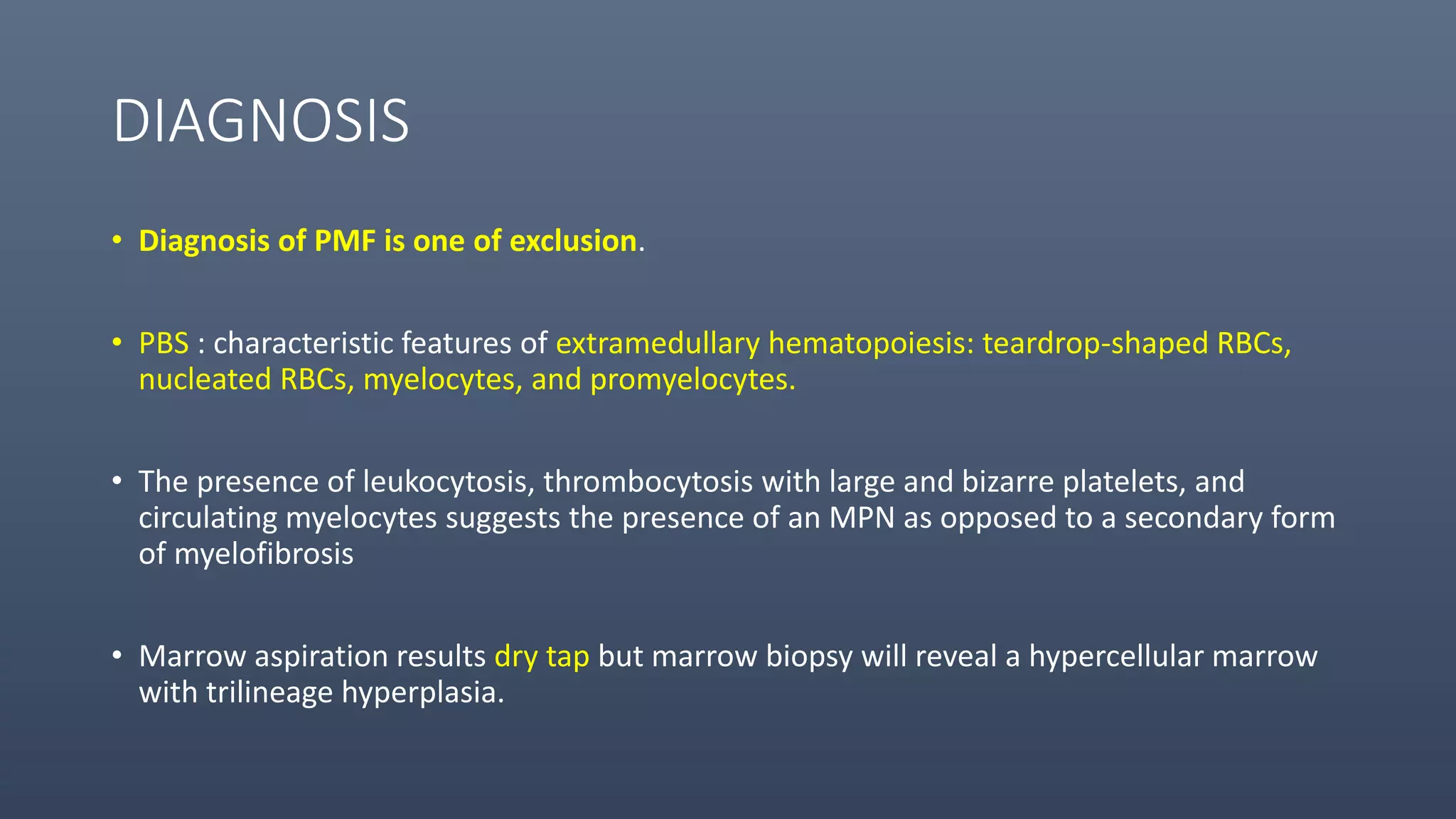
3. Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm involving clonal proliferation and