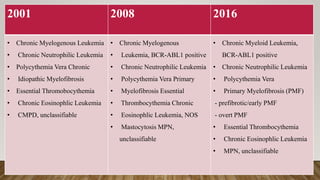
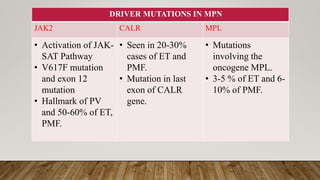
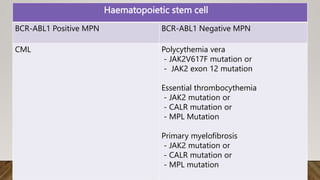
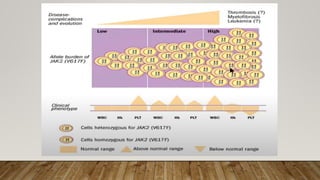
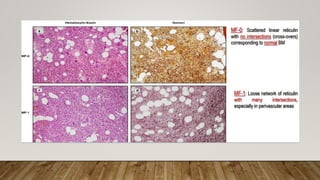
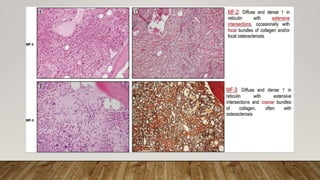
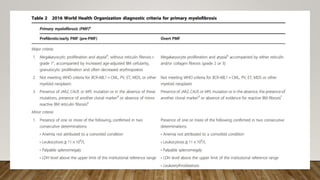
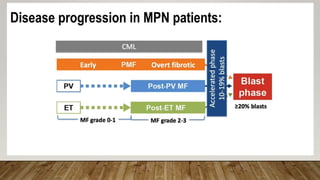
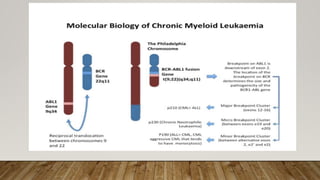
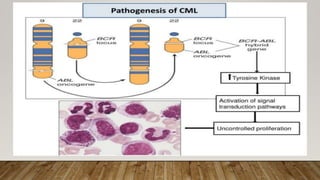
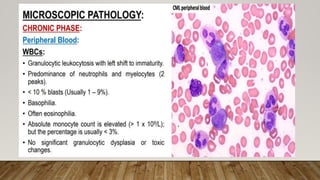
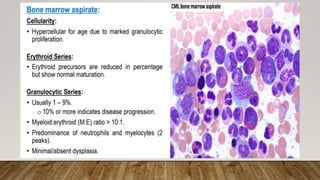
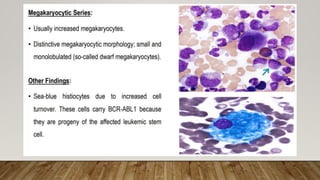
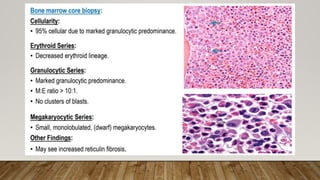
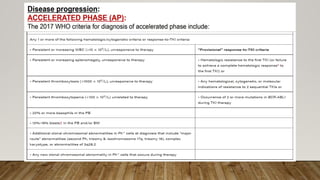
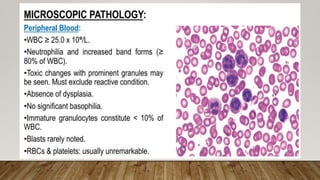
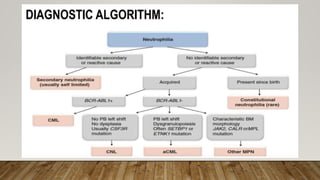
The document summarizes the latest 2016 WHO classification of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), which are clonal hematological disorders characterized by increased proliferation of myeloid lineages in bone marrow. Some key changes in the 2016 classification include revising the diagnostic criteria for accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia, including CSF3R mutations for chronic neutrophilic leukemia, lowering the hemoglobin threshold for polycythemia vera, adding CALR and MPL mutations to criteria for essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis, further clarifying criteria for prefibrotic vs overt primary myelofibrosis, and removing mastocytosis. The classification provides comprehensive and practical diagnostic guidelines for clinicians.