This document discusses viruses associated with lymphoma. It focuses on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) which is present in tumor cells of some lymphomas. EBV infects B cells and can immortalize them in vitro, expressing genes that drive proliferation. While EBV infection is common, only a small subset develops lymphoma, showing lymphomagenesis requires additional factors. EBV is strongly associated with several lymphoma subtypes, variably associated with others, and rarely associated with some. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder is often EBV-associated due to immunosuppression allowing infected B cells to proliferate.
![1245
C H A P T E R 82
VIRUS-ASSOCIATED LYMPHOMA
Jennifer A. Kanakry and Richard F. Ambinder
There are five well-characterized human viruses that are generally
accepted as important in lymphomagenesis (Table 82-1). These
viruses may infect tumor cells (or their progenitors) or may act at a
distance. The genomes of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Kaposi sarcoma–
associated herpesvirus (KSHV, also known as human herpesvirus 8
[HHV-8]), and human T-lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1) are present
in tumor cells. The viral genes expressed in tumor cells modulate
cellular metabolism, proliferation, and cell death. In contrast, the
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) genome is generally not
detected in tumor cells. Whether hepatitis C virus (HCV) genomes
are present in lymphoma cells remains a subject of controversy.
Although viral infection plays a role in the pathogenesis of some
lymphomas, lymphomagenesis is unusual. Only a small subset of
infected people develops lymphoma. Furthermore, although primary
viral infection may be followed by lymphomagenesis within days or
weeks in exceptional circumstances, most lymphomas arise years or
decades after primary infection. Indeed the term adult in adult T-cell
leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) reflects the time lag between HTLV-1
infection in infancy and the evolution to malignancy. Geography and
associated environmental exposures, host genetic factors, and immune
status all modify risk.
Aspects of the biology and epidemiology of each of these viruses
and their relationship with lymphomagenesis are reviewed. In addi-
tion, clinically important and distinctive features of diagnosis and
treatment of the associated lymphomas are presented.
EPSTEIN-BARR VIRUS
Viral Biology
EBV is a gammaherpesvirus transmitted mainly through saliva.1,2
After primary infection, some of the infected cells are driven to pro-
liferate and thereby spread infection throughout the B-cell compart-
ment. Ultimately, in the normal host, there is an immune response
that controls infection and eradicates virus-infected proliferating
cells. Thereafter the viral genome is harbored mainly in resting
memory B lymphocytes that persist for life. These B cells that harbor
virus elude immune surveillance in part because of their very restricted
viral gene expression such that few viral antigens are presented. Occa-
sionally there is activation of viral lytic gene expression (at least in
some instances this occurs in concert with plasma cell differentiation)
leading to production of infectious virions that may infect other B
cells. T cell–mediated immune function keeps such proliferation in
check.3
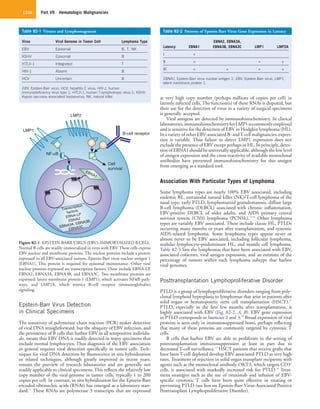
In vitro EBV immortalizes B cells such that they grow indefinitely
as lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) (Fig. 82-1). LCLs are tumorigenic
in immunodeficient mice. In LCL, viral genomes are present as cir-
cular double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) episomes within
the nucleus. The viral proteins required for immortalization include
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA1), a sequence-specific
DNA-binding protein important in the maintenance of the viral
episome; EBNA2, a transcription factor that has many effects similar
to those of activated Notch receptors; and latent membrane protein-1
(LMP1), a constitutively activated member of the tumor necrosis
factor (TNF) receptor superfamily, which most closely resembles
CD40.4
LMP1 activates the nuclear factor kappa-B (NFκB) pathway,
which modulates cell proliferation and apoptosis.5
Several other EBV
proteins are also required for immortalization. Although EBV immor-
talization of B cells in vitro may offer some insights into tumorigen-
esis, some caution is required in using LCL as a tumor model. Most
EBV tumors, including tumors of B-lineage cells, do not express
many of the viral genes required for lymphocyte immortalization.
The only tumors that express the full complement of viral proteins
required for immortalization are those that arise in the most pro-
foundly immunocompromised patients (organ or hematopoietic
transplant recipients, patients with congenital immunodeficiency, or
patients with far advanced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
[AIDS]). Thus in posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder
(PTLD), tumor cells may resemble LCL in expressing many viral
latency genes in association with normal karyotype (and few muta-
tions of the cellular genome). It has been suggested that there is an
inverse relationship between cellular mutations and viral gene expres-
sion in tumors.6
EBV gene expression may directly drive proliferation or inhibit
apoptotic pathways as illustrated by lymphocyte immortalization.
However, viral gene expression may also perturb normal lymphocyte
biology. Thus LMP1 expression upregulates activation induced (cyti-
dine) deaminase expression, which facilitates somatic hypermutation
and immunoglobulin class switching.7
LMP1 expression may also be
important in the conversion of naive B-cells to post-germinal center
memory B-cells. LMP2A allows B-cells that lack normal immuno-
globulin expression to escape regulatory checkpoints and survive.8
Epidemiology of Viral Infection
EBV infection is ubiquitous. The vast majority of adults are infected
worldwide. Primary infection is most often asymptomatic, especially
when it occurs in childhood.9
Primary infection may be associated
with the syndrome of infectious mononucleosis. Symptomatic
primary infection occurs more frequently in older children and in
adults than in younger children. Other possible determinants of
symptomatic primary infection include genetic factors and possibly
the size of the viral inoculum.
Strain differences in EBV are well recognized.10
However, the
importance of these strain differences with regard to lymphomagen-
esis remains poorly understood. There is general agreement that the
Type 1 strain EBV is most common worldwide and in tumors. The
Type 2 strain virus has been identified in some African Burkitt lym-
phoma (BL) and in some AIDS-associated lymphoma. A-strain virus
is more efficient at lymphocyte immortalization in vitro and lym-
phomagenesis in mouse models. The two strains of virus differ mainly
in the EBNA2 gene, but differences are recognized in some other
viral proteins as well.11
Variations in the regulatory regions or coding
regions of a variety of other genes including EBNA1, LMP1, and
ZTA have been recognized and suggested to play a role in
lymphomagenesis.
A simple classification of latent viral gene expression recognizes
three patterns as shown in the Table 82-2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l3-140613130911-phpapp01/75/Linfomas-y-VIH-III-1-2048.jpg)



![Chapter 82 Virus-Associated Lymphoma 1253
whether infection of B cells plays any role in this process. A lym-
phoma cell line that produces infectious HCV has been reported.
Even in the absence of infection of B cells, interaction of the HCV
E2 protein with CD81 on B cells may drive B-cell proliferation or
lower the threshold for other B-cell stimuli to drive proliferation. Ig
signaling may be activated by Ig-virus complexes, and Toll-like recep-
tor 7 signaling may be activated by viral RNA. Finally, it is noted
that E2 binding triggers expression of activation-induced deaminase,
an enzyme that is important in generating somatic hypermutation
and that has also been implicated in mediating mutations thought to
play a role in DLBCL lymphomagenesis.77
Epidemiology of Viral Infection
and Associated Lymphoma
The association between HCV and lymphoma was first recognized
in patients with HCV-associated type II mixed cryoglobulinemia, an
autoimmune extrahepatic manifestation of HCV infection.79
There
followed demonstration of an increased risk for certain subtypes of
B-cell lymphoma (marginal zone lymphoma [MZL], lymphoplasma-
cytic lymphoma and to a lesser extent DLBCL in HCV-infected
patients).80-83
For example, in Taiwan the rate of chronic HCV infec-
tion in patients with NHL was 11%, 10-fold higher than in the
general Taiwanese population.84
Among HCV-infected patients with
lymphoma, nodal and splenic MZL, but not mucosa-associated lym-
phoid tissue (MALT) lymphomas, were increased. The HCV-
lymphoma association is more apparent in some countries than
others, with the association being established most clearly in Italy and
Japan. A multitude of studies in regions or countries where HCV
infection is less prevalent have failed to identify any association with
lymphoma.85-87
Further evidence in support of an etiologic relationship comes
from studies in which successful treatment of HCV was followed by
lymphoma regression.88
The most dramatic illustration comes from
patients with splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes treated
with ribavirin and interferon.
Certain HCV genotypes may confer increased risk for NHL, with
genotypes 2a/III and 2b/IV seen more frequently in the HCV-
seropositive patients that develop NHL.
Diagnostic Considerations
In contrast to EBV-, KSHV-, or HTLV-1–associated tumors, there is
no established role for studies demonstrating HCV nucleic acid or
protein in tumor cells. Thus serologic study and measurement of
HCV copy number are the only tools available for inferring an asso-
ciation. We recommend checking HCV serologic characteristics in
all patients with B-cell lymphomas most commonly associated with
chronic HCV infection.89
In addition, screening patients with chronic
HCV for a monoclonal gammopathy and cryoglobulinemia may be
of benefit to identify patients at highest risk for malignant transfor-
mation. Elevated serum γ-globulin levels have been found to be a
predictor of NHL among patients with type II mixed cryoglobuline-
mia.90
In patients who are HCV seropositive, we evaluate HCV RNA
in plasma.
Therapy
In patients with indolent lymphomas and untreated HCV infection,
antiviral treatment may obviate the need for cytotoxic chemotherapy
and should be considered as an initial therapeutic strategy. The
studies showing that antiviral therapy may lead to regression of HCV-
associated lymphomas involved treatment with ribavirin and inter-
feron. In the last year new antiviral agents have become available,
notably protease inhibitors specific for the HCV protease. Likelihood
of response to older therapy is a function of viral genotype, host
genetics (IL28R polymorphisms play a critical role in response to
chemotherapy dose adjustments. Ritonavir inhibits the clearance of
midazolam, phenytoin, and voriconazole and other agents metabo-
lized by the cytochrome P-450 CYP3A4 pathway.
Supportive Care
Although PJP prophylaxis is recommended only when the CD4+
count is less than 200 cells/mm3
for HIV patients not receiving
cytotoxic chemotherapy, prophylaxis is universally recommended for
HIV patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy. The following are
also commonly used: fungal prophylaxis with fluconazole; herpes
simplex and varicella prophylaxis with acyclovir, valacyclovir, or fam-
ciclovir; quinolone prophylaxis when neutrophil counts fall below
1000 cells/mm3
; and granulocyte growth factors.
Bone Marrow Transplantation in HIV Patients
Autologous bone marrow transplant has been successful in HIV-
seropositive NHL patients, with these patients having adequate stem
cell mobilization, nonrelapse mortality rates comparable to those for
HIV-negative patients, count recovery within 2 weeks of stem cell
rescue, and maintained control of HIV viral loads and CD4+
counts
after high-dose chemotherapy.73,74
There have also been successful
reduced-intensity allogeneic bone marrow transplants in HIV-
seropositive patients, making the possibilities for treating HIV
patients with NHL even more vast, even in those patients with
chemotherapy-resistant disease (see box on Autologous Bone Marrow
Transplant in an HIV-Seropositive Hodgkin Lymphoma Patient).75
HEPATITIS C VIRUS
Viral Biology and B-Lymphocyte Proliferation
HCV is an enveloped positive-strand RNA virus.76,77
Infection
involves interactions between E2, a viral structural protein with two
hypervariable regions, and a cellular protein CD81 present on hepa-
tocytes and B lymphocytes. A polyprotein is translated from viral
RNA and is cleaved by cellular and viral proteases, including NS3,
to yield proteins required for viral replication. The RNA-dependent
RNA polymerase that replicates the viral genome lacks proofreading
capacity, thus generating genetic heterogeneity among viral progeny.
Viral replication occurs predominantly in the liver, but some evidence
suggests that B cells may also be infected.
Chronic infection can be associated with mixed cryoglobulinemia,
a systemic vasculitis that results from clonal expansion of B cells
producing an IgM autoantibody against IgG, leading to deposition
of immune complexes on endothelial surfaces, resulting in inflamma-
tion.78
Several hypotheses have been advanced with regard to how
HCV might drive B-cell proliferation. There is controversy as to
Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant in an HIV-Seropositive Hodgkin
Lymphoma Patient
A 38-year-old human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–positive
patient with CD4+
count of 485 cells/mm3
is diagnosed with
classic Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and treated with doxorubicin
(Adriamycin), bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD),
achieving a complete remission. Two years later he presents with
retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy and is found on biopsy to have
relapsed HL. He is treated with salvage chemotherapy with com-
plete response, as well as good performance status and no active
infections. His HIV remains well controlled on antiretroviral
therapy. He is deemed an excellent candidate for high-dose
therapy and undergoes consolidation with autologous bone
marrow transplant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l3-140613130911-phpapp01/85/Linfomas-y-VIH-III-9-320.jpg)
![Part VII Hematologic Malignancies1254
Choi I, Tanosaki R, Uike N, et al: Long-term outcomes after hematopoietic
SCT for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: Results of prospective trials.
Bone Marrow Transplant 46:116, 2011.
Chuang SS, Liao YL, Chang ST, et al: Hepatitis C virus infection is signifi-
cantly associated with malignant lymphoma in Taiwan, particularly with
nodal and splenic marginal zone lymphomas. J Clin Pathol 63:595, 2010.
Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM, Landgren O, et al: Immunologic and virologic
predictors of AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the highly active
antiretroviral therapy era. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 54:78, 2010.
Epeldegui M, Hung YP, McQuay A, et al: Infection of human B cells with
Epstein-Barr virus results in the expression of somatic hypermutation-
inducing molecules and in the accrual of oncogene mutations. Mol
Immunol 44:934, 2007.
Evens AM, Roy R, Sterrenberg D, et al: Post-transplantation lymphoprolifera-
tive disorders: Diagnosis, prognosis, and current approaches to therapy.
Curr Oncol Rep 12:383, 2010.
Giordano TP, Henderson L, Landgren O, et al: Risk of non-Hodgkin lym-
phoma and lymphoproliferative precursor diseases in US veterans with
hepatitis C virus. JAMA 297:2010, 2007.
Guech-Ongey M, Simard EP, Anderson WF, et al: AIDS-related Burkitt
lymphoma in the United States: What do age and CD4 lymphocyte pat-
terns tell us about etiology and/or biology? Blood 116:5600, 2010.
Heslop HE, Slobod KS, Pule MA, et al: Long-term outcome of EBV-specific
T-cell infusions to prevent or treat EBV-related lymphoproliferative disease
in transplant recipients. Blood 115:925, 2010.
Hishizawa M, Kanda J, Utsunomiya A, et al: Transplantation of allogeneic
hematopoietic stem cells for adult T-cell leukemia: A nationwide retrospec-
tive study. Blood 116:1369, 2010.
Ito M, Kusunoki H, Mochida K, et al: HCV infection and B-cell lymphoma-
genesis. Adv Hematol 2011:835314, 2011.
Jaffe ES, Campo E, Swerdlow SH, et al: The 2008 WHO classification of
lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applica-
tions. Blood 117:5019, 2011.
Keegan TH, Glaser SL, Clarke CA, et al: Epstein-Barr virus as a marker of
survival after Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A population-based study. J Clin Oncol
23:7604, 2005.
Kelly GL, Rickinson AB: Burkitt lymphoma: Revisiting the pathogenesis of
a virus-associated malignancy. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program
2007:277, 2007.
Kitahata MM, Achenbach CJ, Saag MS: Age at cancer diagnosis
among persons with AIDS. Ann Int Med 154:642; author reply 643,
2011.
Levine AM: HIV-associated lymphoma. Blood 115:2986, 2010.
Libra M, Polesel J, Russo AE, et al: Extrahepatic disorders of HCV infection:
A distinct entity of B-cell neoplasia? Int J Oncol 36:1331, 2010.
Matsuoka M, Jeang KT: Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1)
infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat Rev Cancer 7:270, 2007.
Matsuoka M, Jeang KT: Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and
leukemic transformation: Viral infectivity, Tax, HBZ and therapy. Onco-
gene 30:1379, 2011.
Moore PS, Chang Y: KSHV: Forgotten but not gone. Blood 117:6973, 2011.
Ratner L, Harrington W, Feng X, et al: Human T cell leukemia virus reactiva-
tion with progression of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma. PLoS One
4:e4420, 2009.
Rudek MA, Flexner C, Ambinder RF: Use of antineoplastic agents in patients
with cancer who have HIV/AIDS. Lancet Oncol 12:905, 2011.
Savoldo B, Goss JA, Hammer MM, et al: Treatment of solid organ transplant
recipients with autologous Epstein Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T lympho-
cytes (CTLs). Blood 108:2942, 2006.
Sparano JA, Lee JY, Kaplan LD, et al: Rituximab plus concurrent infusional
EPOCH chemotherapy is highly effective in HIV-associated B-cell non-
Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 115:3008, 2010.
Uldrick TS, Polizzotto MN, Aleman K, et al: High-dose zidovudine plus
valganciclovir for Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus-associated multicentric Cas-
tleman disease: A pilot study of virus-activated cytotoxic therapy. Blood
117:6977, 2011.
Vereide DT, Sugden B: Lymphomas differ in their dependence on Epstein-
Barr virus. Blood 117:1977, 2011.
For complete list of references log on to www.expertconsult.com.
protease inhibitors) and other factors. The field is rapidly evolving,
and colleagues with specific expertise in appropriate antiviral
approaches should be consulted.76
Rituximab has posed an interesting dilemma for the treatment of
patients with HCV and lymphoma. It has been reported that HCV
plasma RNA increases following rituximab treatment, and there is
certainly the possibility that elimination of B cells for 3 to 18 months
following treatment may compromise humoral responses to the evo-
lution of HCV quasispecies. However, in studies to date overall
survival is not inferior.91
Similarly, combination chemotherapy is safe
in patients with HCV infection.92
Rituximab is specifically recom-
mended for the treatment of HCV-associated cryoglobulinemia
(although as in the treatment of Waldenström macroglobulinemia, it
must be appreciated that the initial response to rituximab may be an
increase in the IgM paraprotein level, necessitating plasmapheresis).
Aspects of Therapy
With regards to the use of rituximab to treat B-cell lymphomas in
patients with HCV, overall survival is not inferior, although there do
appear to be increased rates of hepatotoxicity and rises in HCV viral
load during therapy. Similarly, combination chemotherapy is safe in
patients with HCV infection, although HCV RNA levels can rise
during treatment. Interestingly, patients with HCV and splenic MZL
have had regression of their tumors with treatment for HCV infection
with interferon-α and ribavirin, an effect not seen in HCV-negative
patients with splenic MZL treated with the same regimen.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
In this chapter a variety of virus-associated lymphomas and lympho-
proliferative diseases have been reviewed. For most of these lympho-
mas, standard antiviral drugs do not have a role in treatment. There
are, however, several exceptions, and these are worth highlighting.
Antiviral therapy for HCV-associated splenic lymphoma with villous
lymphocytes is accepted as a standard approach and likely has a role
in the treatment of other HCV-associated indolent lymphomas. Simi-
larly, ganciclovir or valganciclovir appears to have a role in the man-
agement of MCD associated with KSHV in HIV patients. And of
course there is an established role for antiretroviral therapy in the
treatment of HIV patients with malignancy. There are virus-targeted
therapies that are broadly accepted as standard, including adoptive
immunotherapy with EBV-specific T cells for PTLD. The use of
targeted T cells also has promise in other settings, including EBV-
associated HL. Other virus-targeted therapies are being developed.
Some involve vaccination; others involve induction of viral genes in
tumor cells, rendering them more susceptible to pharmacologic treat-
ment. Finally, it may ultimately be possible to prevent some kinds of
lymphoma by preventing viral infection or altering the host response
to viral infection.
SUGGESTED READINGS
Balsalobre P, Diez-Martin JL, Re A, et al: Autologous stem-cell transplanta-
tion in patients with HIV-related lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 27:2192,
2009.
Barta SK, Lee JY, Kaplan LD, et al: Pooled analysis of AIDS malignancy
consortium trials evaluating rituximab plus CHOP or infusional EPOCH
chemotherapy in HIV-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer doi:
10.1002/cncr.26723. [Epub ahead of print], 2011.
Bazarbachi A, Suarez F, Fields P, et al: How I treat adult T-cell leukemia/
lymphoma. Blood 118:1736, 2011.
Bower M, Newsom-Davis T, Naresh K, et al: Clinical features and outcome
in HIV-associated multicentric Castleman’s disease. J Clin Oncol 29:2481,
2011.
Carbone A, Cesarman E, Spina M, et al: HIV-associated lymphomas and
gamma-herpesviruses. Blood 113:1213, 2009.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l3-140613130911-phpapp01/85/Linfomas-y-VIH-III-10-320.jpg)


![Chapter 82 Virus-Associated Lymphoma 1254.e3
48. Epeldegui M, Vendrame E, Martinez-Maza O: HIV-associated immune
dysfunction and viral infection: Role in the pathogenesis of AIDS-related
lymphoma. Immunol Res 48:72, 2010.
49. Kitahata MM, Achenbach CJ, Saag MS: Age at cancer diagnosis among
persons with AIDS. Ann Intern Med 154:642; author reply 643, 2011.
50. Shen L, Siliciano RF: Viral reservoirs, residual viremia, and the potential
of highly active antiretroviral therapy to eradicate HIV infection. J Allergy
Clin Immunol 122:22, 2008.
51. Gaidano G, Pasqualucci L, Capello D, et al: Aberrant somatic hypermu-
tation in multiple subtypes of AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Blood 102:1833, 2003.
52. Epeldegui M, Thapa DR, De la Cruz J, et al: CD40 ligand (CD154)
incorporated into HIV virions induces activation-induced cytidine
deaminase (AID) expression in human B lymphocytes. PloS one 5:e11448,
2010.
53. Dean M, Jacobson LP, McFarlane G, et al: Reduced risk of AIDS lym-
phoma in individuals heterozygous for the CCR5-Δ32 mutation. Cancer
Res 59:3561, 1999.
54. Goedert JJ: The epidemiology of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
malignancies. Semin Oncol 27:390, 2000.
55. Levine AM: HIV-associated lymphoma. Blood 115:2986, 2010.
56. Bohlius J, Schmidlin K, Costagliola D, et al: Incidence and risk factors
of HIV-related non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in the era of combination
antiretroviral therapy: A European multicohort study. Antivir Ther
14:1065, 2009.
57. Bonnet F, Lewden C, May T, et al: Malignancy-related causes of death
in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in the era of highly
active antiretroviral therapy. Cancer 101:317, 2004.
58. Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM, Landgren O, et al: Immunologic and virologic
predictors of AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the highly active
antiretroviral therapy era. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 54:78, 2010.
59. Biggar RJ, Jaffe ES, Goedert JJ, et al: Hodgkin lymphoma and immu-
nodeficiency in persons with HIV/AIDS. Blood 108:3786, 2006.
60. Guech-Ongey M, Simard EP, Anderson WF, et al: AIDS-related Burkitt
lymphoma in the United States: What do age and CD4 lymphocyte
patterns tell us about etiology and/or biology? Blood 116:5600, 2010.
61. Ambinder RF, Bhatia K, Martinez-Maza O, et al: Cancer biomarkers in
HIV patients. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 5:531, 2010.
62. Rudek MA, Flexner C, Ambinder RF: Use of antineoplastic agents in
patients with cancer who have HIV/AIDS. Lancet Oncol 12:905, 2011.
63. Kaplan LD, Straus DJ, Testa MA, et al: Low-dose compared with
standard-dose m-BACOD chemotherapy for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. National Insti-
tute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases AIDS Clinical Trials Group.
N Engl J Med 336:1641, 1997.
64. Little RF, Pittaluga S, Grant N, et al: Highly effective treatment of
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related lymphoma with dose-
adjusted EPOCH: Impact of antiretroviral therapy suspension and
tumor biology. Blood 101:4653, 2003.
65. Ratner L, Lee J, Tang S, et al: Chemotherapy for human immunodefi-
ciency virus-associated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in combination with
highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Clin Oncol 19:2171, 2001.
66. Mounier N, Spina M, Gabarre J, et al: AIDS-related non-Hodgkin
lymphoma: Final analysis of 485 patients treated with risk-adapted inten-
sive chemotherapy. Blood 107:3832, 2006.
67. Kaplan LD, Lee JY, Ambinder RF, et al: Rituximab does not improve
clinical outcome in a randomized phase 3 trial of CHOP with or without
rituximab in patients with HIV-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma:
AIDS-Malignancies Consortium Trial 010. Blood 106:1538, 2005.
68. Sparano JA, Lee JY, Kaplan LD, et al: Rituximab plus concurrent infu-
sional EPOCH chemotherapy is highly effective in HIV-associated B-cell
non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 115:3008, 2010.
69. Barta SK, Lee JY, Kaplan LD, et al: Pooled analysis of AIDS malignancy
consortium trials evaluating rituximab plus CHOP or infusional
EPOCH chemotherapy in HIV-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Cancer doi: 10.1002/cncr.26723. [Epub ahead of print], 2011.
70. Levine AM: Management of AIDS-related lymphoma. Curr Opin Oncol
20:522, 2008.
71. Oriol A, Ribera JM, Bergua J, et al: High-dose chemotherapy and immu-
notherapy in adult Burkitt lymphoma: Comparison of results in human
immunodeficiency virus-infected and noninfected patients. Cancer
113:117, 2008.
72. Gopal S, Martin K, Richards K, et al: Clinical presentation, treatment,
and outcomes among 65 patients with HIV-associated lymphoma treated
at the University of North Carolina, 2000-2010. AIDS Res Hum Retro-
viruses [Epub ahead of print] 2011.
73. Balsalobre P, Diez-Martin JL, Re A, et al: Autologous stem-cell trans-
plantation in patients with HIV-related lymphoma. J Clin Oncol
27:2192, 2009.
74. Gabarre J, Marcelin AG, Azar N, et al: High-dose therapy plus autolo-
gous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for human immunodefi-
ciency virus (HIV)-related lymphoma: Results and impact on HIV
disease. Haematologica 89:1100, 2004.
75. Bryant A, Milliken S: Successful reduced-intensity conditioning alloge-
neic HSCT for HIV-related primary effusion lymphoma. Biol Blood
Marrow Transplant 14:601, 2008.
76. Rosen HR: Clinical practice. Chronic hepatitis C infection. N Engl
J Med 364:2429, 2011.
77. Ito M, Kusunoki H, Mochida K, et al: HCV infection and B-cell lym-
phomagenesis. Adv Hematol 2011:835314, 2011.
78. Della Rossa A, Baldini C, Tavoni A, et al: How HCV has changed the
approach to mixed cryoglobulinemia. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27:S115,
2009.
79. Monti G, Pioltelli P, Saccardo F, et al: Incidence and characteristics of
non-Hodgkin lymphomas in a multicenter case file of patients with
hepatitis C virus-related symptomatic mixed cryoglobulinemias. Arch
Intern Med 165:101, 2005.
80. Anderson LA, Engels EA: Hepatitis C virus infection and non-Hodgkin
lymphoma: Interesting association or causal relationship? Int J Cancer
122:x, 2008.
81. Giordano TP, Henderson L, Landgren O, et al: Risk of non-Hodgkin
lymphoma and lymphoproliferative precursor diseases in US veterans
with hepatitis C virus. JAMA 297:2010, 2007.
82. Libra M, Polesel J, Russo AE, et al: Extrahepatic disorders of HCV infec-
tion: A distinct entity of B-cell neoplasia? Int J Oncol 36:1331, 2010.
83. Amin J, Dore GJ, O’Connell DL, et al: Cancer incidence in people with
hepatitis B or C infection: A large community-based linkage study. J
Hepatol 45:197, 2006.
84. Chuang SS, Liao YL, Chang ST, et al: Hepatitis C virus infection is
significantly associated with malignant lymphoma in Taiwan, particularly
with nodal and splenic marginal zone lymphomas. J Clin Pathol 63:595,
2010.
85. Varma S, Menon MC, Garg A, et al: Hepatitis C virus infection among
patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in northern India. Hepatol Int
5:688, 2011.
86. Omland LH, Jepsen P, Krarup H, et al: Liver cancer and non-Hodgkin
lymphoma in hepatitis C virus-infected patients: Results from the
DANVIR cohort study. Int J Cancer 130:2310, 2012.
87. Isikdogan A, Ayyildiz O, Dursun M, et al: Hepatitis C virus in patients
with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in southeastern Anatolia region of
Turkey: A prospective case-control study of 119 patients. Leuk Lymphoma
44:1745, 2003.
88. Hermine O, Lefrere F, Bronowicki JP, et al: Regression of splenic lym-
phoma with villous lymphocytes after treatment of hepatitis C virus
infection. N Engl J Med 347:89, 2002.
89. Awasthi NP, Kashyap R, Kumari N, et al: Sjogren’s syndrome compli-
cated by non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Spectrum of lymphoid prolifera-
tions and associated hepatitis C virus infection. Indian J Pathol Microbiol
54:430, 2011.
90. Geri G, Terrier B, Semoun O, et al: Surrogate markers of B cell non-
Hodgkin’s lymphoma in patients with hepatitis C virus-related cryo-
globulinaemia vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:2177, 2010.
91. Ennishi D, Maeda Y, Niitsu N, et al: Hepatic toxicity and prognosis in
hepatitis C virus-infected patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
treated with rituximab-containing chemotherapy regimens: A Japanese
multicenter analysis. Blood 116:5119, 2010.
92. Ennishi D, Terui Y, Yokoyama M, et al: Monitoring serum hepatitis C
virus (HCV) RNA in patients with HCV-infected CD20-positive B-cell
lymphoma undergoing rituximab combination chemotherapy. Am J
Hematol 83:59, 2008.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l3-140613130911-phpapp01/85/Linfomas-y-VIH-III-13-320.jpg)