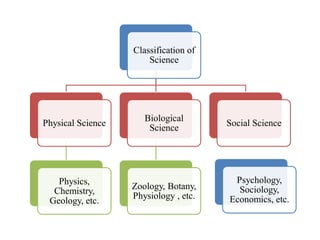
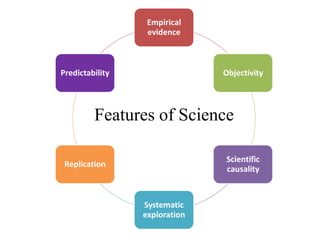
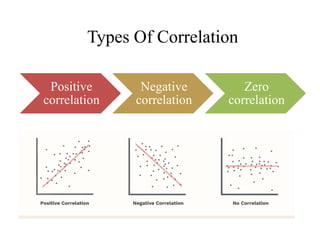
Psychology is considered a science as it fulfills many scientific conditions. It uses various research methods like experimental, survey, observation, case study, and correlation studies. Psychology emerged as a separate discipline in 1879 and has since developed various approaches like structuralism, functionalism, psychoanalysis, behaviorism, humanistic psychology, and cognitivism. Some challenges in establishing psychology as a science include its pre-paradigmatic state and issues related to objectivity, validity, predictability, and replicability when studying humans.