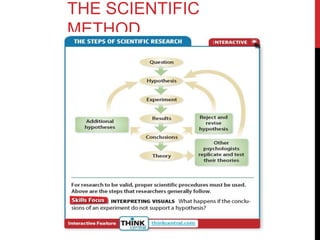
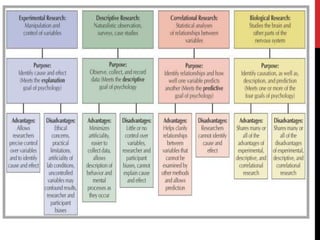
This chapter discusses psychological research methods. It explains that psychologists follow the scientific method, which involves identifying questions, developing hypotheses, conducting research studies, analyzing data, and building theories. There are two main types of research: basic research examines theoretical concepts without trying to solve problems, while applied research utilizes psychology principles to address real-world issues. Common research methods described include observational studies, surveys, correlational research which examines relationships between variables, and experimental research which manipulates variables to test cause-and-effect. The chapter also discusses ethics in psychological research involving human and animal subjects.