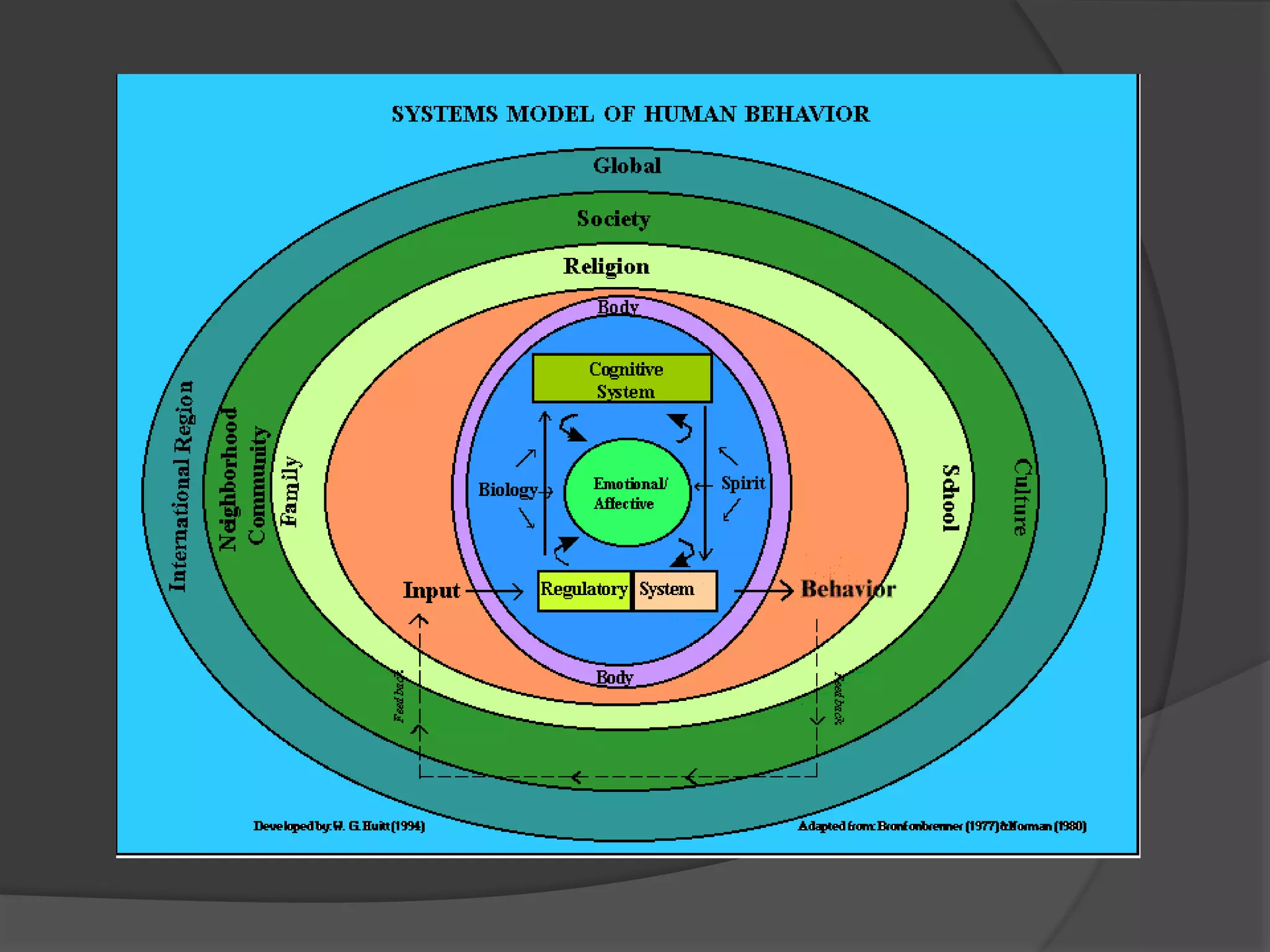
This document outlines a course on educational psychology that covers human development and personality. It discusses key topics like the definition and processes of human development, the five major traits of personality, and Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory of the contexts that influence development. The course aims to help students describe, identify, explain, and discuss concepts of human development and personality and apply that understanding to teaching careers.