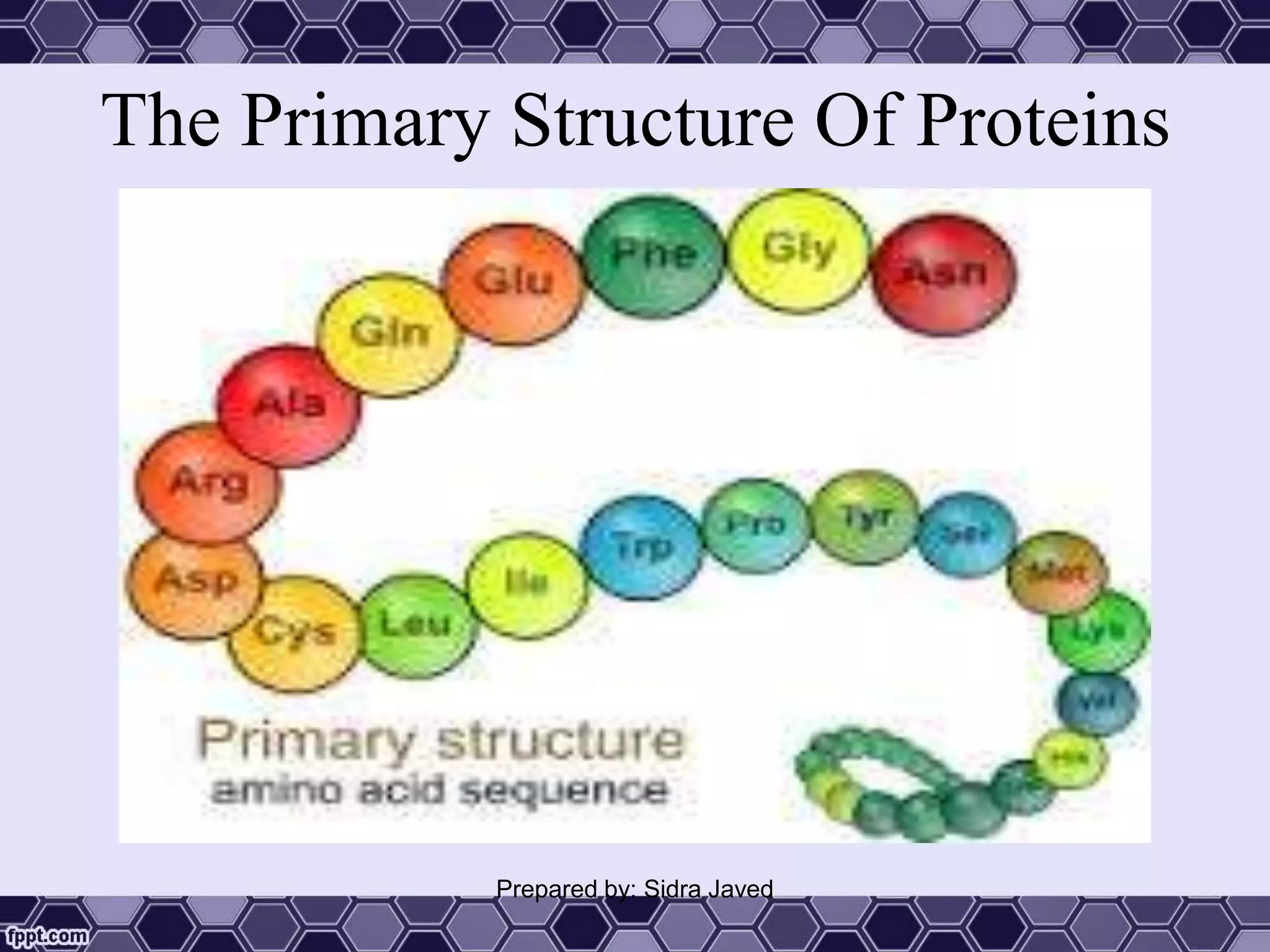
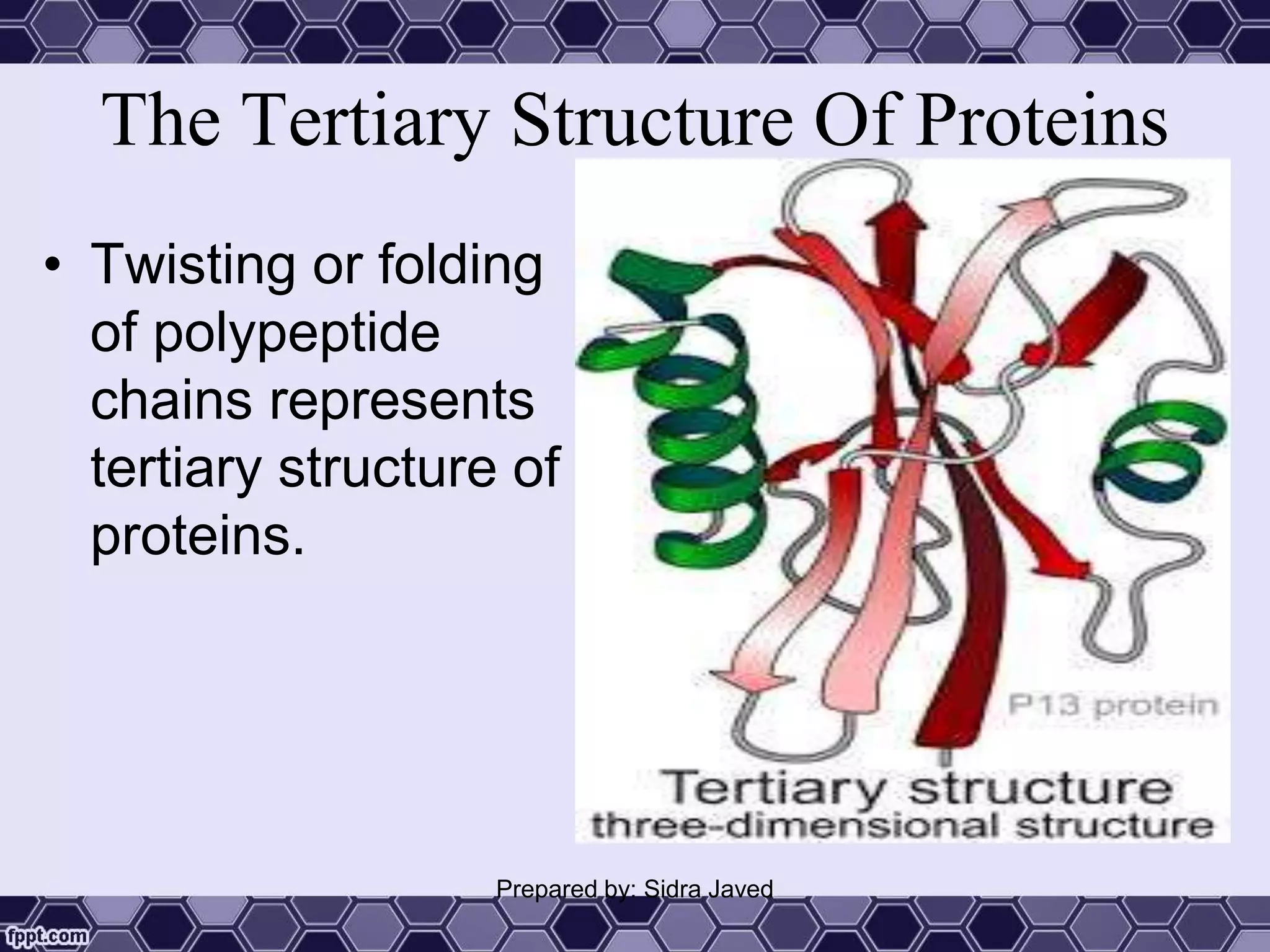
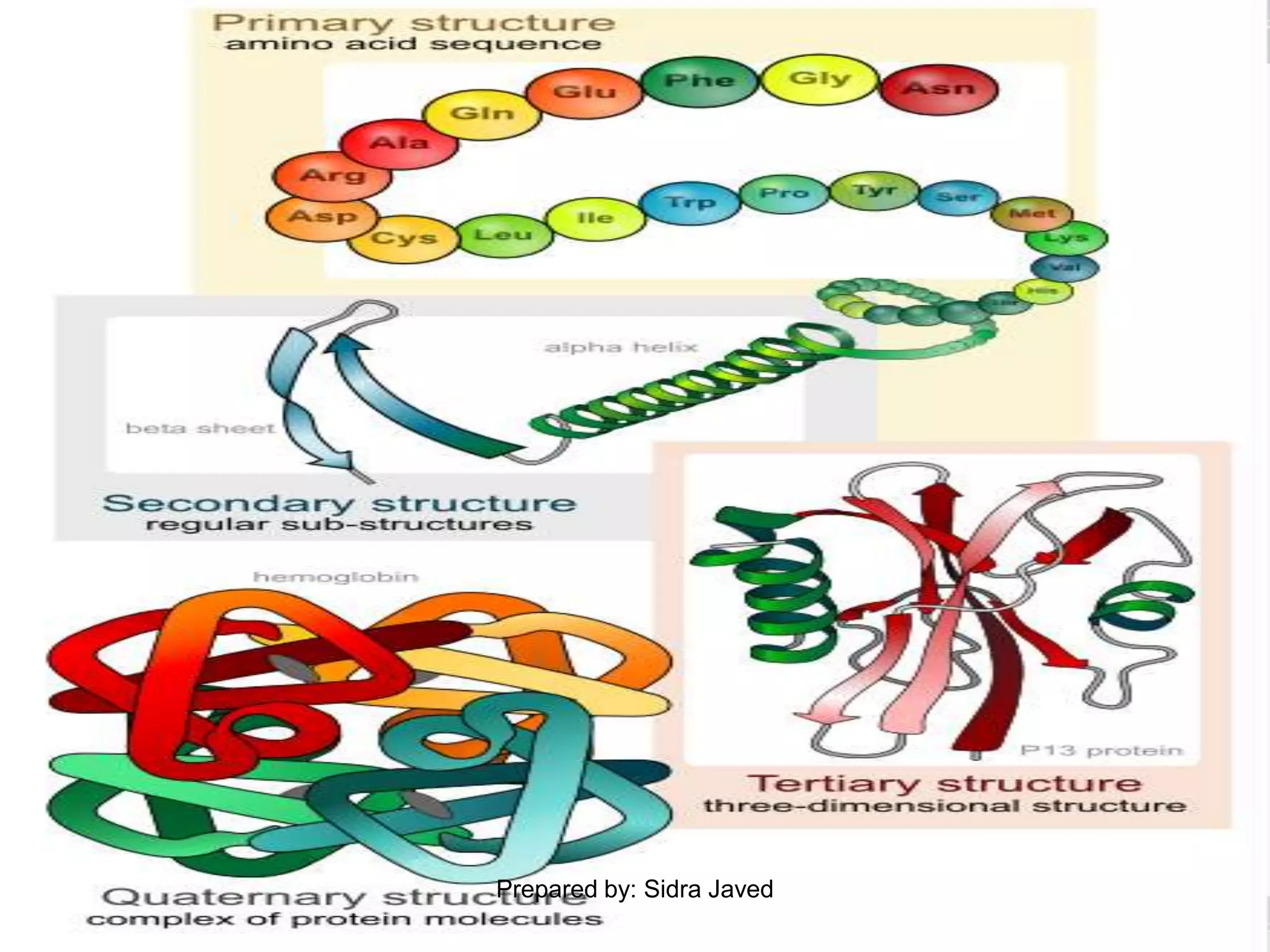
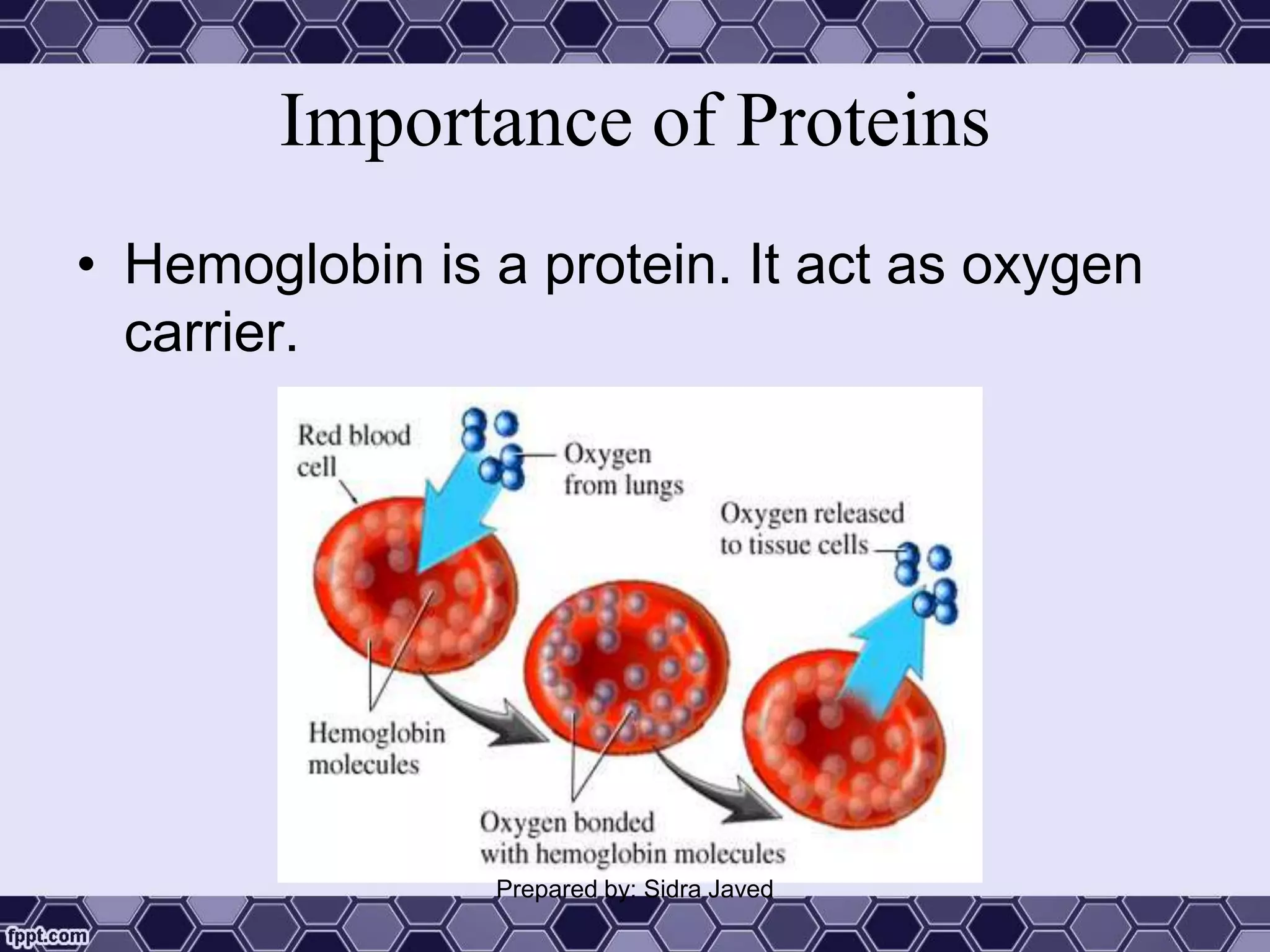
Proteins are polymers of amino acids that play essential roles in the structure and function of living organisms. They can be classified as simple, conjugated, or derived proteins based on their composition. Proteins have complex structures including primary, secondary, tertiary, and sometimes quaternary structures defined by the sequence and folding of polypeptide chains. Important proteins serve as enzymes, antibodies, hormones, and components of tissues and organs. They are crucial for growth, repair, and maintenance of the human body.