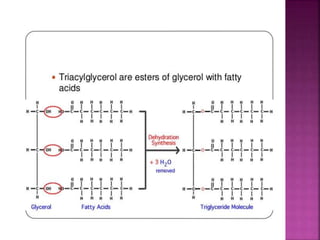
I. Lipids provide stored energy in the form of triacylglycerols and participate in cell membranes as phospholipids. They are hydrophobic and insoluble in water.
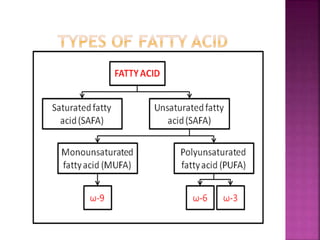
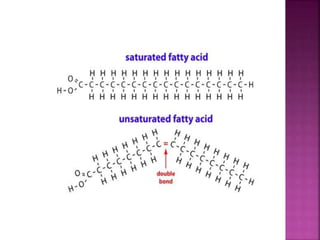
II. The main types of lipids include fatty acids, triacylglycerols, phospholipids, sterols, and derived lipids produced from hydrolysis.
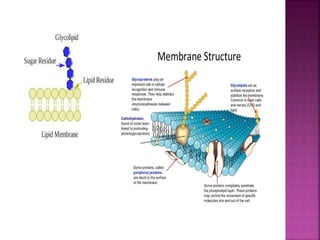
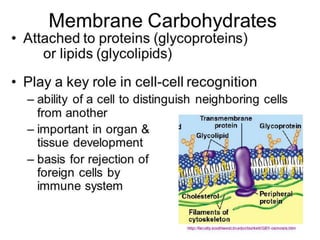
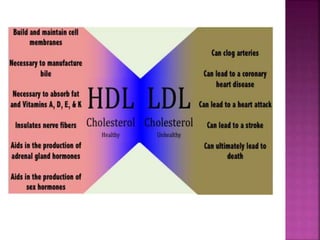
III. Phospholipids are important structural components of cell membranes and contain a phosphate group. Sterols include cholesterol and are amphipathic with a polar hydroxyl group.