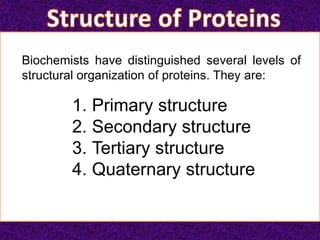
Protein is composed of amino acids linked together in chains. It is essential for life and is contained in every part of the body. There are two main types of protein - fibrous proteins found in animals that serve structural functions, and globular proteins that usually do not have structural roles and can be enzymes or transporters. Protein has critical physiological functions including building, maintaining, and repairing body tissues, and can also be converted to energy when intake is greater than requirements. The structure of proteins involves four levels - primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.