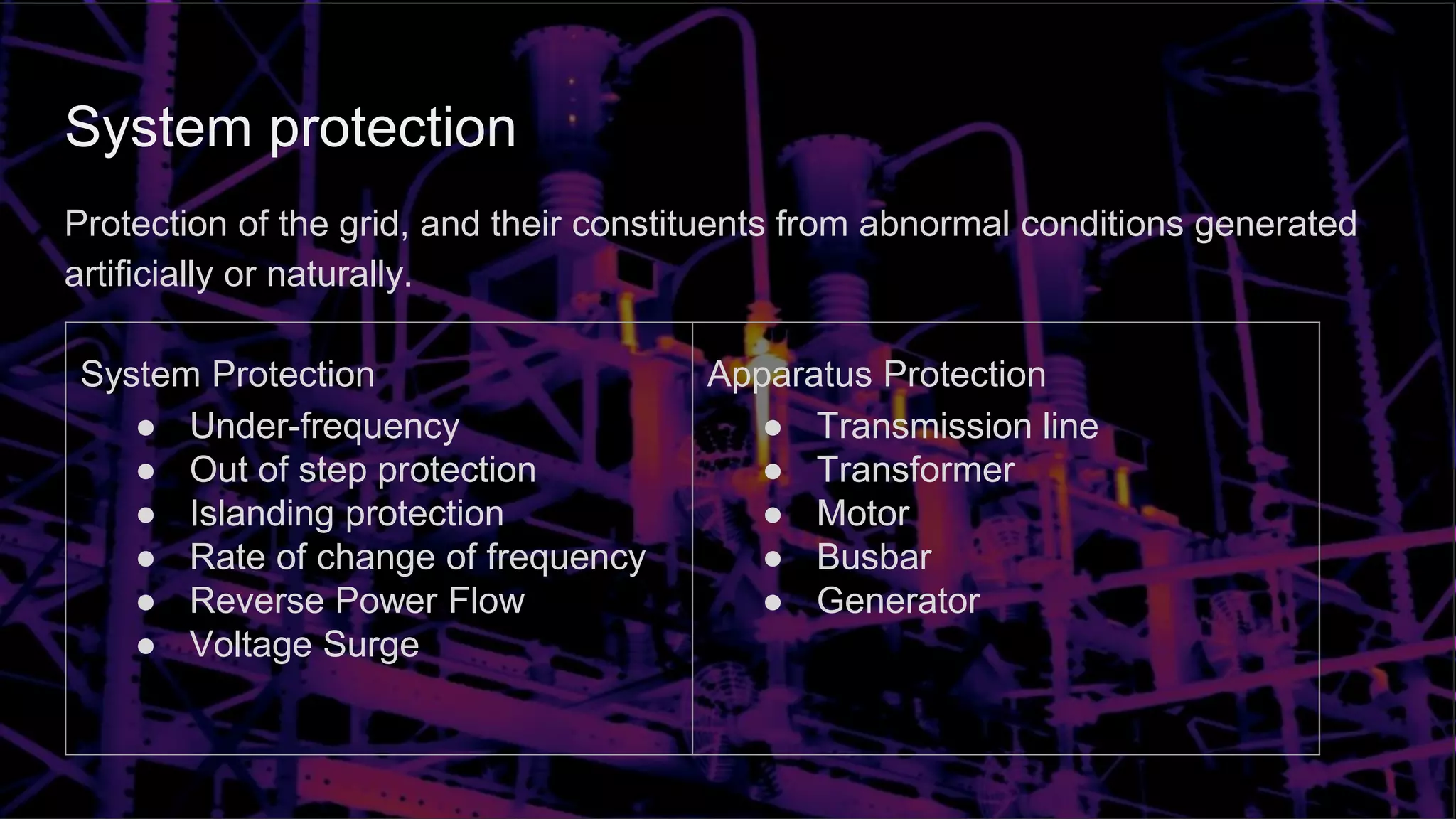
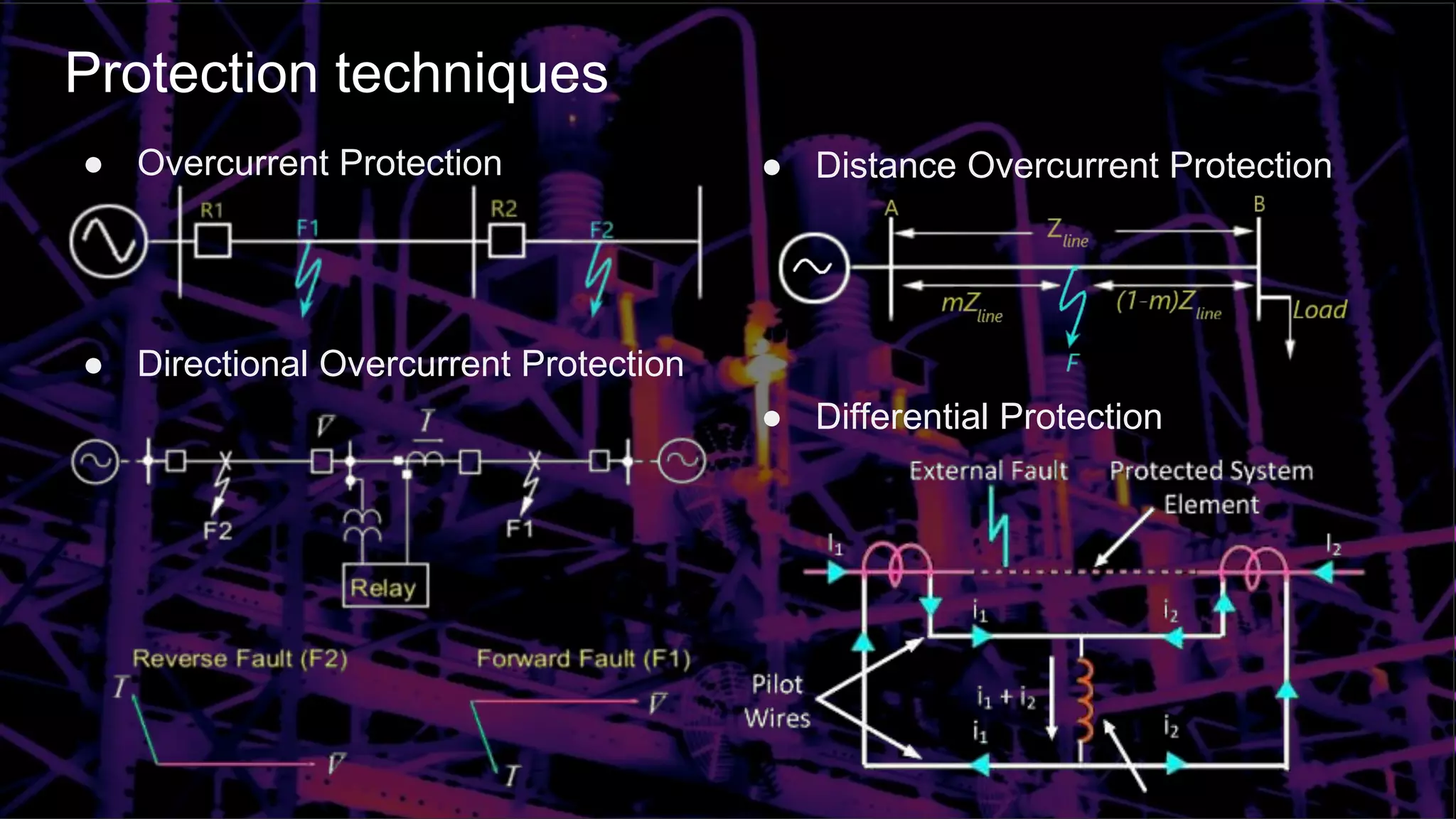
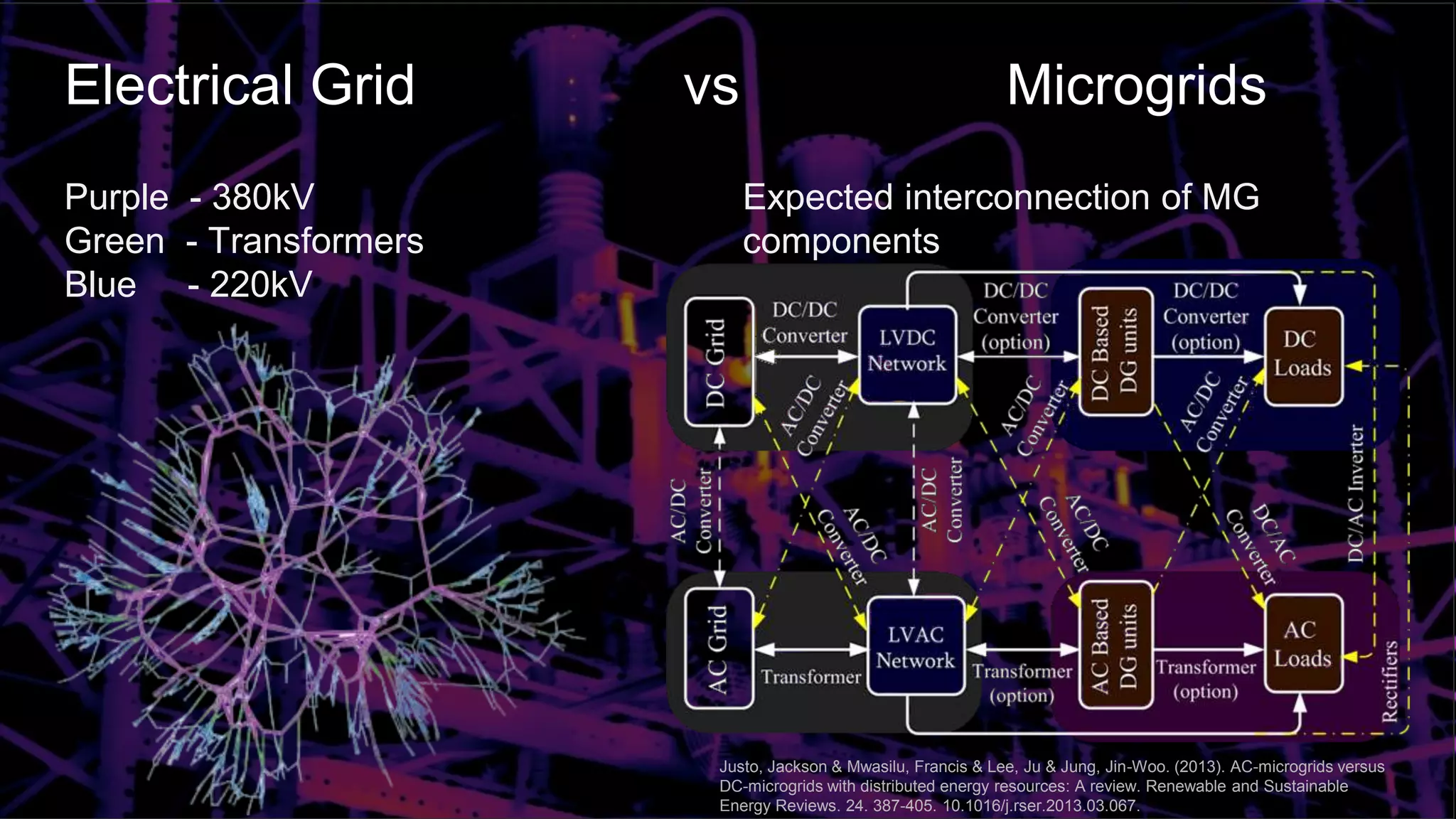
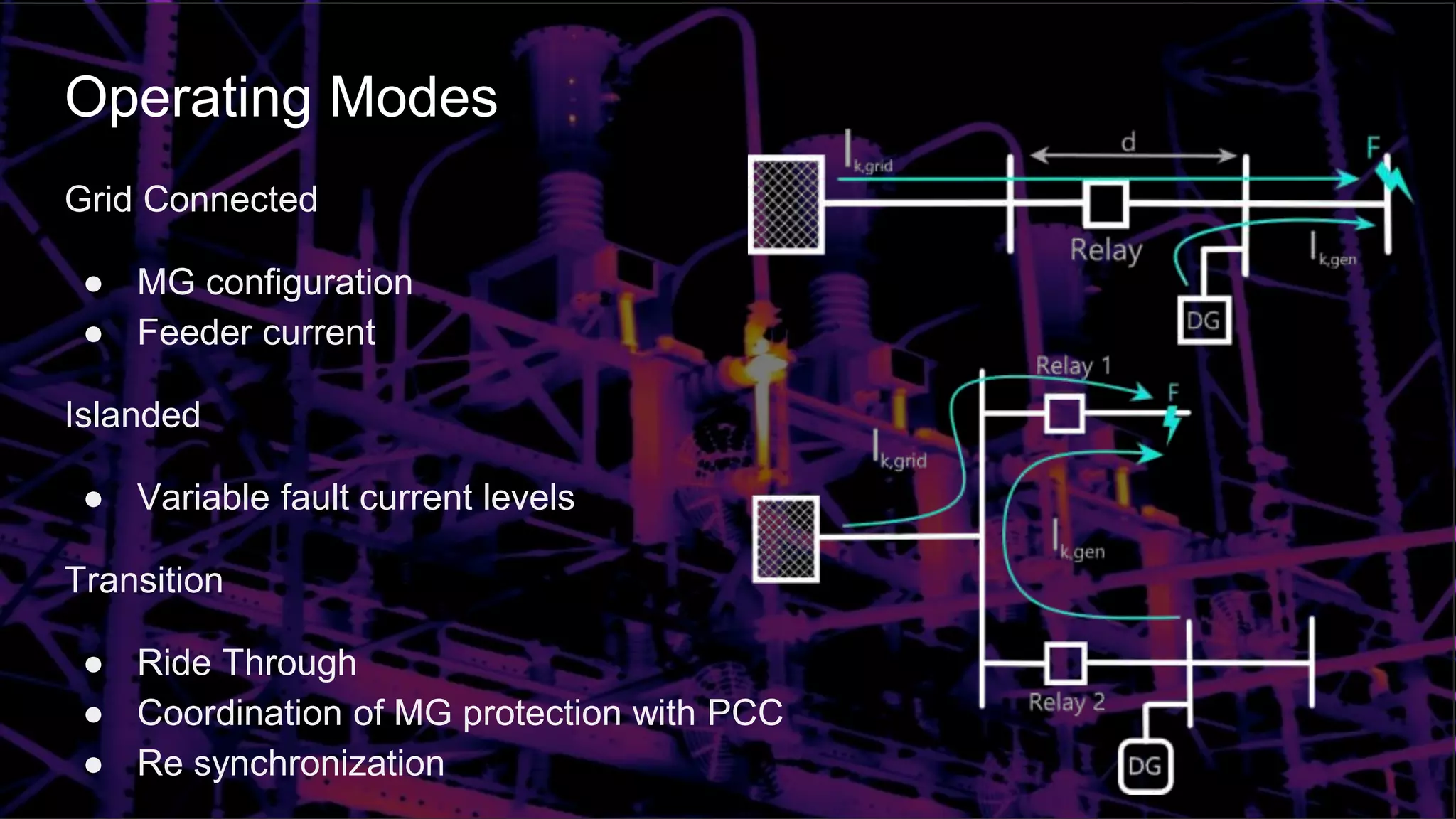
This document discusses protection schemes for inverter-based microgrids. It begins by defining system protection and apparatus protection in conventional grids. It then defines microgrids and their operating modes of grid-connected and islanded. Challenges in microgrid protection include bidirectional power flow, different operating modes and fault current levels. Various proposed protection schemes are described for the islanded and grid-connected modes, including adaptive directional overcurrent, travelling wave, multi-agent, and pattern recognition schemes. Future microgrid protection is expected to involve communication between relays, machine learning techniques, complex signal processing and fast response times.






![References
[1] IEEE recommended practice for grounding of industrial and commercial power systems. IEEE Std 142-2007 (Revision of IEEE Std
142-1991), pages 1–225, Nov 2007.
[2] H Al-Nasseri and MA Redfern. A new voltage based relay scheme to protect microgrids dominated by embedded generation using
solid state converters. In 19th International Conference Electricity Distribution, pages 1–4, 2007.
[3] Belwin J Brearley and R Raja Prabu. A review on issues and approaches for microgrid protection. Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Reviews, 67:988–997, 2017.
[4] G Buigues, A Dysko, V Valverde, I Zamora, and E Fern´andez. Microgrid protection: Technical challenges and existing techniques.
In International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality, volume 1, pages 222–227, 2013.
[5] E. Casagrande, W. L. Woon, H. H. Zeineldin, and D. Svetinovic. A differential sequence component protection scheme for
microgrids with inverter-based distributed generators. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 5(1):29–37, Jan 2014.
[6] E. A. A. Coelho, P. C. Cortizo, and P. F. D. Garcia. Small-signal stability for parallel-connected inverters in stand-alone ac supply
systems. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 38(2):533–542, March 2002.
[7] Y. Han, X. Hu, and D. Zhang. Study of adaptive fault current algorithm for microgrid dominated by inverter based distributed
generators. In The 2nd International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems, pages 852– 854, June
2010.
[8] Seyed Amir Hosseini, Hossein Askarian Abyaneh, Seyed Hossein Hesamedin Sadeghi, Farzad Razavi, and Adel Nasiri. An
overview of microgrid protection methods and the factors involved. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 64:174–186, 2016.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protectionofinverterbasedmicrogrids-191209074747/75/Protection-of-inverter-based-microgrids-12-2048.jpg)
![References (cotd.)
[9] Patrick Tendayi Manditereza and Ramesh Bansal. Renewable distributed generation: The hidden challenges–a review from the
protection perspective. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 58:1457–1465, 2016.
[10] Aushiq Ali Memon and Kimmo Kauhaniemi. A critical review of ac microgrid protection issues and available solutions. Electric
Power Systems Research, 129:23–31, 2015. 22
[11] D. P. Mishra, S. R. Samantaray, and G. Joos. A combined wavelet and data-mining based intelligent protection scheme for
microgrid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 7(5):2295–2304, Sep. 2016.
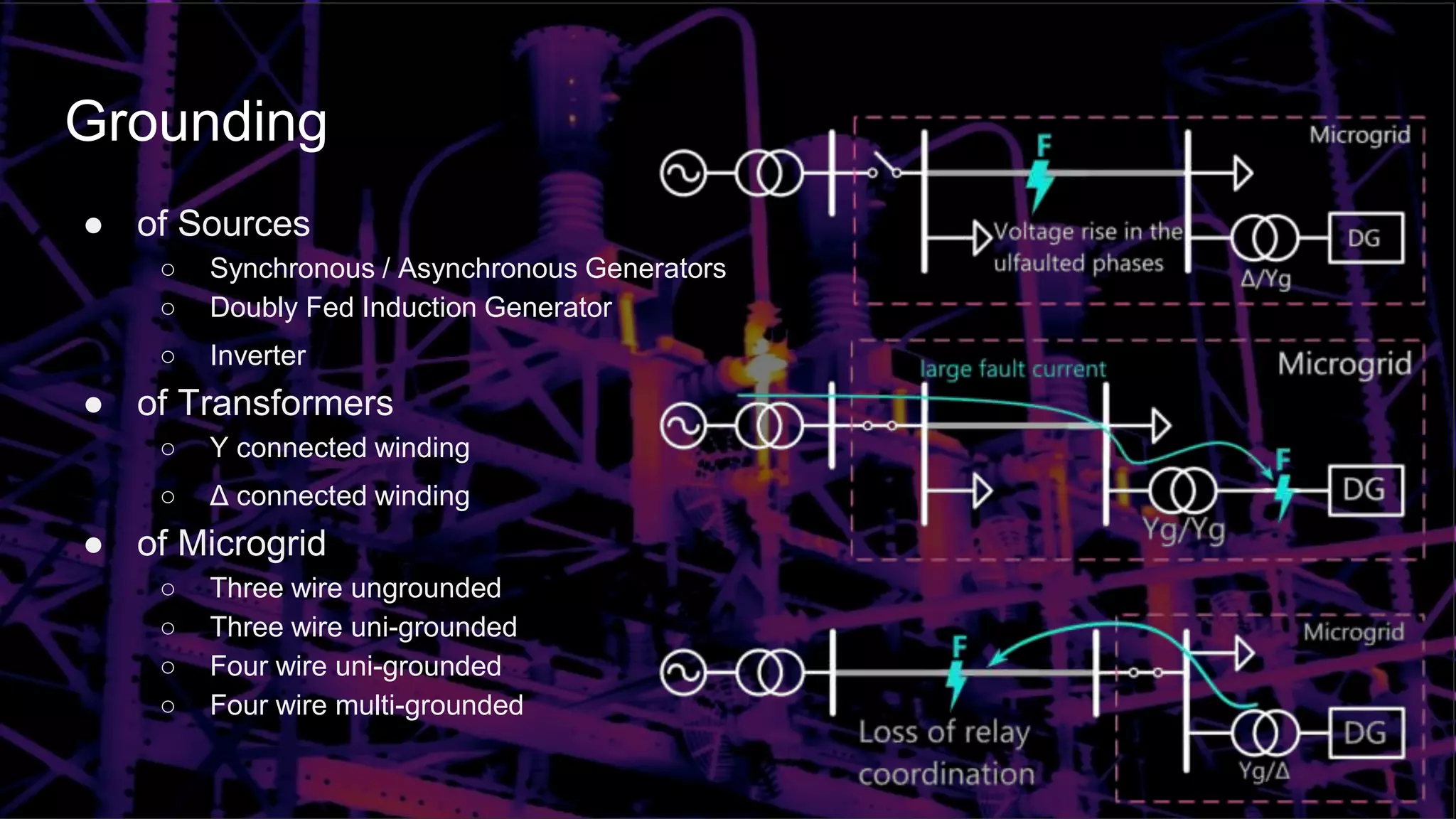
[12] J. Mohammadi, F. Badrkhani Ajaei, and G. Stevens. Grounding the ac microgrid. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,
55(1):98–105, Jan 2019.
[13] H. Nikkhajoei and R. H. Lasseter. Microgrid protection. In 2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, pages 1–6,
June 2007.
[14] Nagaraju Pogaku, Milan Prodanovic, and Timothy C Green. Modeling, analysis and testing of autonomous operation of an inverter-
based microgrid. IEEE Transactions on power electronics, 22(2):613–625, 2007.
[15] Power System Relaying and Control Committee Subcommittee C Working Group C30. Microgrid Protection Systems. IEEE Power
Energy Society, July 2019.
[16] S.A. Soman. Digital protection of power systems. https://nptel.ac.in/courses/ 108101039/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protectionofinverterbasedmicrogrids-191209074747/75/Protection-of-inverter-based-microgrids-13-2048.jpg)