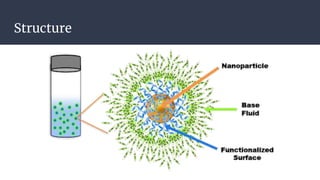
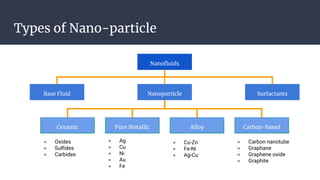
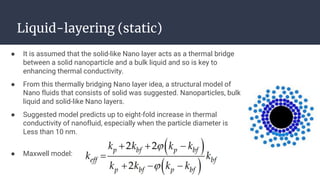
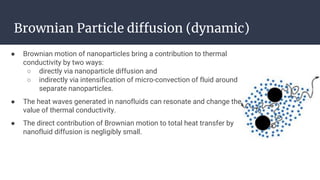
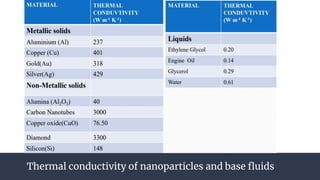
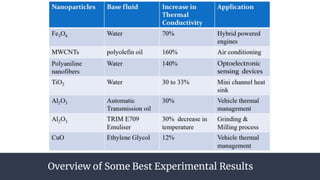
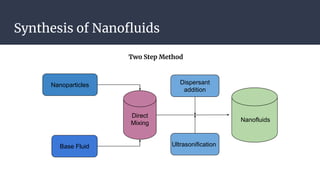
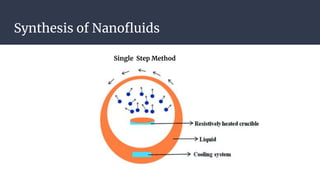
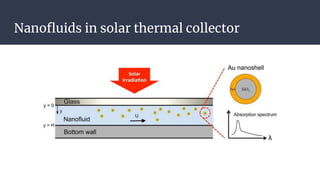
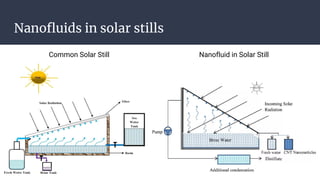
This document summarizes research on nano-particles in heat transfer. It discusses how nanofluids are engineered by dispersing nanoparticles smaller than 100nm in conventional heat transfer fluids to enhance thermal performance. It outlines different types of nanoparticles and base fluids that can be used. The key mechanisms for how nanofluids improve heat transfer are liquid layering around nanoparticles, Brownian motion, and microconvection induced by nanoparticle movement. Experimental results show increases in thermal conductivity compared to base fluids alone. Parameters like particle size and material affect conductivity. Nanofluids have applications in solar energy collection and storage. Synthesis methods include two-step mixing of nanoparticles and base fluids or single-step production.









![REFERENCES
[1]ENGINEERING NANOFLUIDS FOR HEAT TRANSFER APPLICATIONS (ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (KTH)):
HTTPS://WWW.DIVA-PORTAL.ORG/SMASH/GET/DIVA2:712511/FULLTEXT01.PDF
[2]ASTUDY OF HEAT TRANSFER WITH NANOFLUIDS (SANJYOT VARADE*,CHINMAY PATIL AND S.P.WADKAR):
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING,SAVITRIBAI PHULE PUNE UNIVERSITY,PUNE,INDIA
HTTP://INPRESSCO.COM/WP-CONTENT/UPLOADS/2017/06/PAPER74314-318.PDF
[3]MECHANISMS OF ENHANCED HEAT TRANSFER IN NANOFLUIDS (J.A.EASTMAN):
HTTP://FNOES.INLN.CNRS.FR/FNOES-TALKS/EASTMAN.PDF
[4]NANOFLUIDS FOR HEAT TRANSFER:AN ENGINEERING APPROACH (ELENA VTIMOFEEVA*,WENHUA YU,DAVID MFRANCE,DILEEP SINGH,JULES LOUTBORT):
HTTP://IMAGES.BIOMEDSEARCH.COM/21711700/1556-276X-6-182.PDF?AWSACCESSKEYID=AKIAIBOKHYOLP4MBMRGQ&EXPIRES=1540771200&SIGNATURE=EF5W9U81WC6ZW
EBO0V6KM3JFFSQ%3D
[5]INVESTIGATION OF NANOPARTICLE AGGREGATION EFFECT ON THERMAL PROPERTIES OF NANOFLUID BY A COMBINED EQUILIBRIUM AND NON-EQUILIBRIUM MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION
(MINA SEDIGHI,ALI MOHEBBI):
HTTPS://AC.ELS-CDN.COM/S0167732214001858/1-S2.0-S0167732214001858-MAIN.PDF?_TID=4047AFF8-561E-4110-8A35-CA537F349122&ACDNAT=1540674451_3BF65B2
DC468CBD15C0FA1D72B0EE3B9
[6]ASIMPLEYETEFFECTIVEMODELFORTHERMALCONDUCTIVITYOFNANOFLUIDS (M.M.MACDEVETTE,H.RIBERA,ANDT.G.MYERS):
HTTP://WWW.CRM.CAT/EN/PUBLICATIONS/PUBLICATIONS/2013/PR1149.PDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tfdseminar-181028093019/85/Nanoparticles-in-heat-transfer-applications-21-320.jpg)
