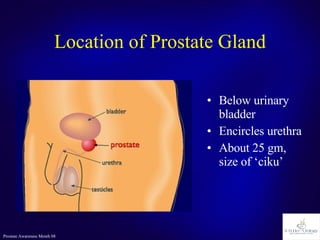
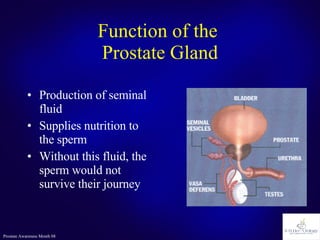
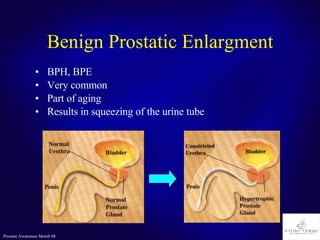
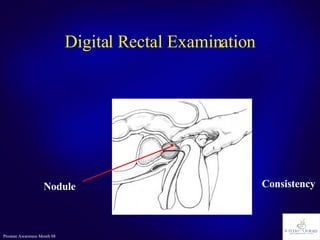
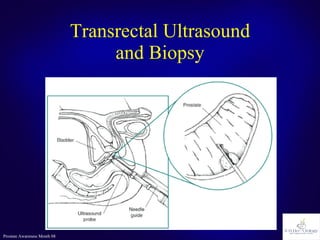
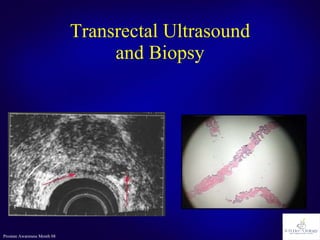
The document discusses the prostate gland's function, common problems associated with aging, and prostate cancer. It highlights the importance of early detection through awareness and medical examinations, as well as the potential for curability if identified early. Factors like family history and age are mentioned as risk indicators for prostate issues.