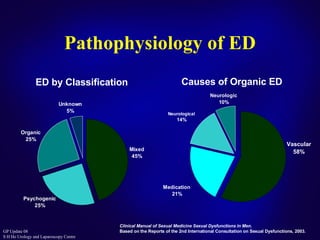
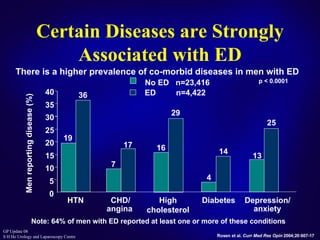
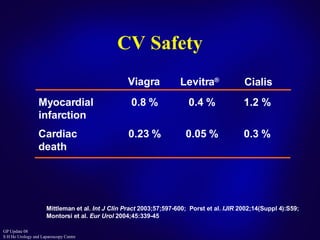
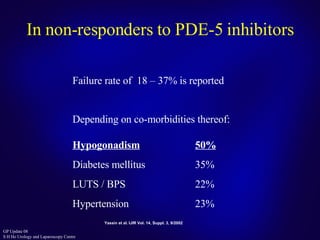
This document discusses the approach to treating erectile dysfunction. It defines erectile dysfunction and outlines its diagnosis and investigations. It describes how erectile dysfunction is often associated with other medical conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and depression. The document then discusses current treatment options for erectile dysfunction like PDE5 inhibitors, testosterone replacement therapy, and surgery. It provides details on the effectiveness, safety profiles, and proper use of PDE5 inhibitors.