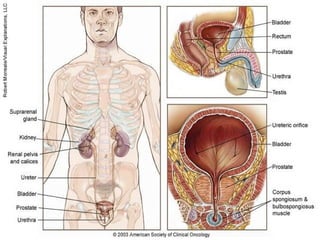
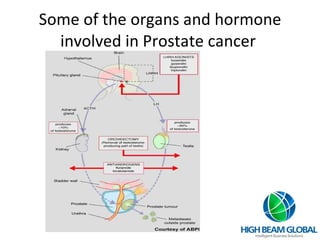
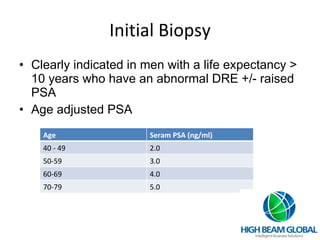
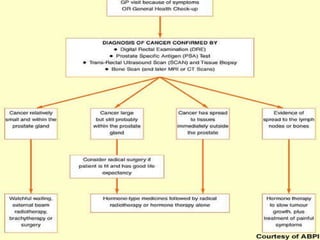
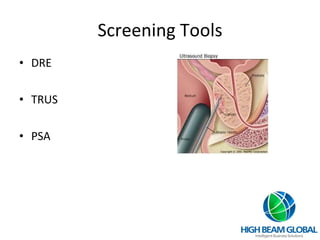
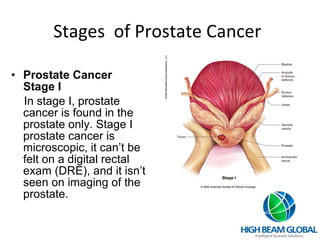
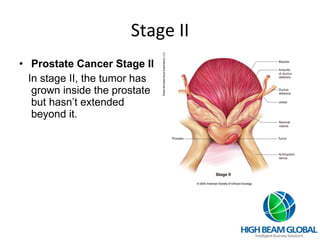
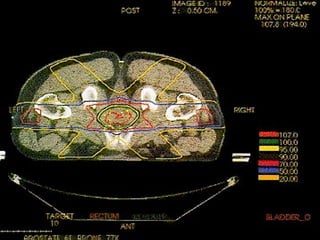
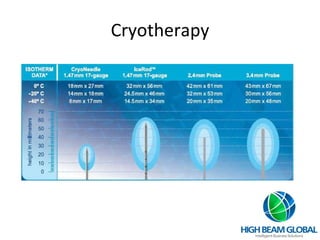
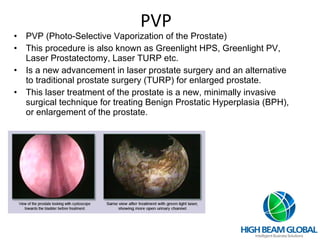
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men and the second leading cause of cancer death. It occurs when cells in the prostate gland grow abnormally. There are often no early symptoms but some men experience urinary issues or discomfort. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, cryotherapy, hormonal therapy, and watchful waiting. Screening tools include digital rectal exams, transrectal ultrasound, and PSA tests.











![High Beam Global 209, Udyog Vihar, Phase – 1, Gurgaon. Phone: +91-124-4824560 Fax: +91-124-4824550 E-mail: info@medicalfacilitiesinindia.com [email_address] Web address: www.highbeamglobal.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highbeamglobal-prostatecancer-101208034945-phpapp01/85/Prostate-Cancer-31-320.jpg)