This document discusses prosocial behavior and helping others from an evolutionary and psychological perspective. It covers several key points:
1) Prosocial behavior involves actions that help others with no immediate benefit to the helper. Evolutionary factors like kin selection and reciprocal altruism provide partial explanations for why individuals help.
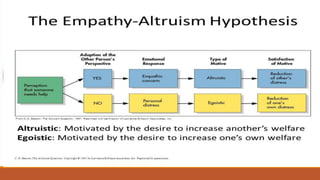
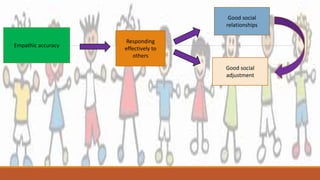
2) Empathy, which involves understanding and sharing another's emotional experience, plays an important role in helping behaviors. Empathy has cognitive and emotional components and likely evolved to strengthen parent-child bonds and relationships.
3) Helping often provides psychological rewards to the helper like feeling good and pride. These rewards, along with social and moral norms, can motivate helping even without immediate tangible benefits. However, helping also