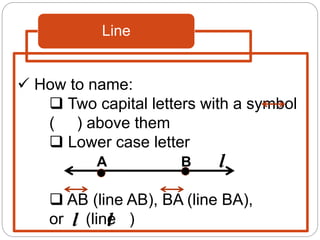
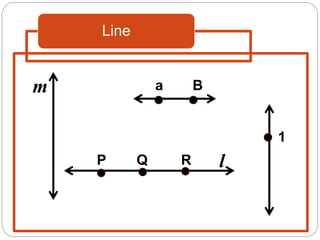
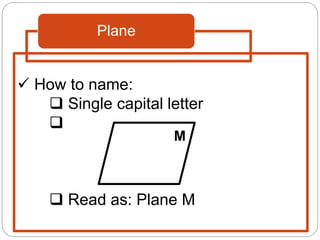
This document defines key geometric terms and concepts including:
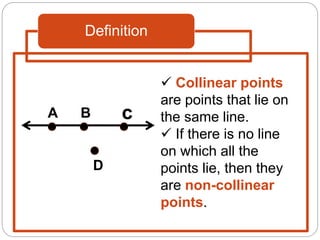
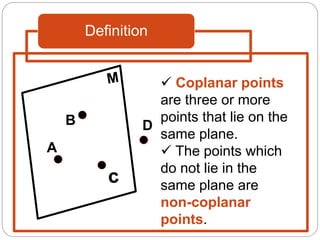
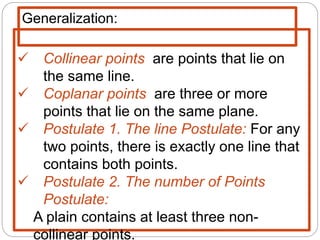
- Collinear points which lie on the same line. Coplanar points which lie on the same plane.
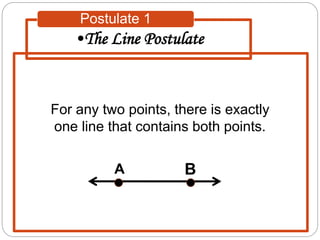
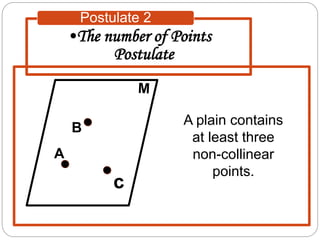
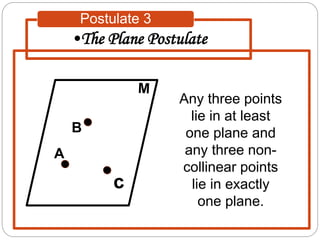
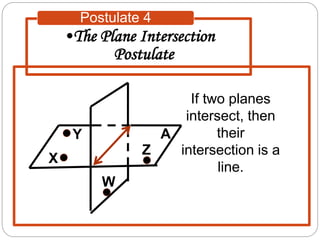
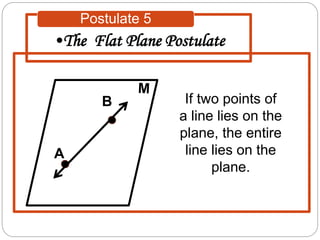
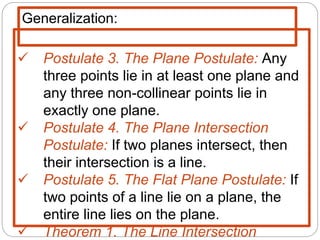
- Five postulates outline the fundamental properties of points, lines, and planes: any two points define a single unique line; a plane contains at least three non-collinear points; any three points lie in a single plane; intersecting lines or planes meet at a point or line.
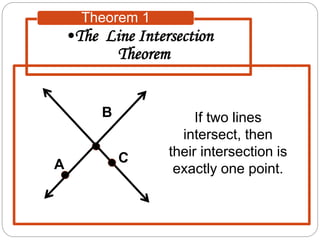
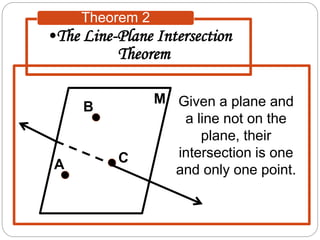
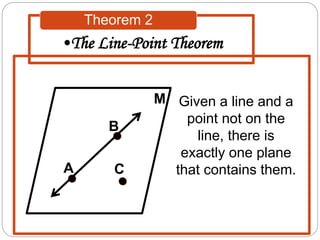
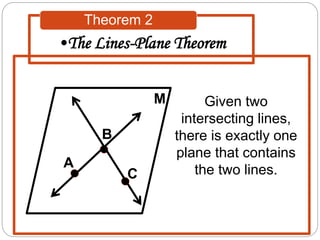
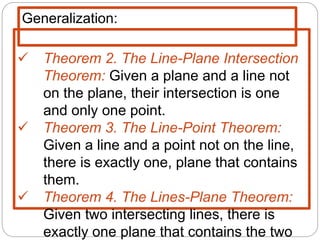
- Theorems describe relationships between lines and planes, such as two intersecting lines lying in a single plane, or a line and point not on the line defining a unique plane.