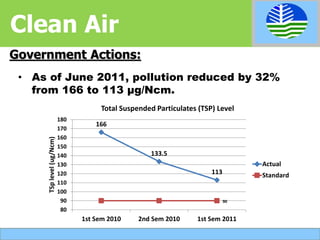
The document discusses the state of the Philippine environment, sustainable development, management of resources, and overconsumption. It outlines the Philippine constitution's protection of people's right to a balanced ecology. It summarizes the government's environmental framework and actions taken in forestry, clean air, clean water, geohazard mapping, mineral reforms, agriculture, and good governance. These actions include reforestation programs, stronger emissions standards, adoption of esteros, hazard mapping, mining reforms, and anti-corruption efforts. It emphasizes that sustainable development meets current needs without limiting future generations by pursuing economic growth while preserving environmental quality.