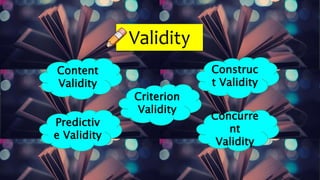
This document discusses key properties that make assessments valid, reliable, fair, practical and ethical. It defines validity as the degree to which a test measures what it is intended to measure. There are several types of validity including content, criterion, predictive and construct validity. Reliability refers to an assessment producing stable and consistent results over time and is measured through inter-rater reliability, test-retest reliability and internal consistency. Fairness means students understand learning targets and the assessment method. Practicality means teachers are familiar with assessments and they are not overly complicated to implement. Ethics in assessment refers to ensuring tests are fair and conform to professional standards of conduct.