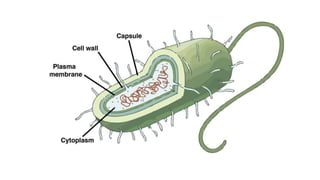
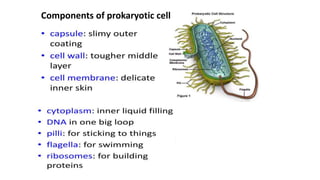
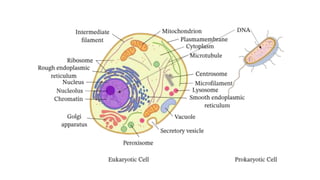
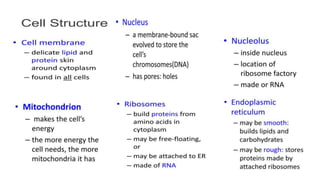
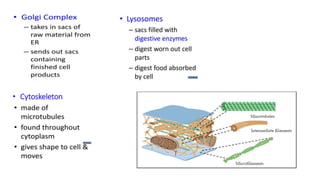
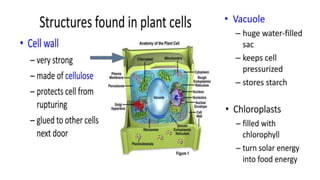
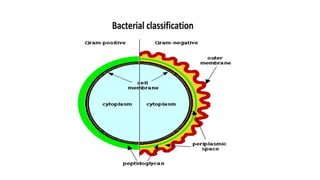
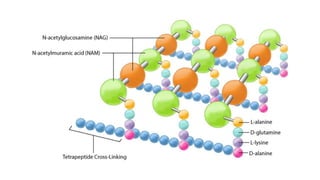
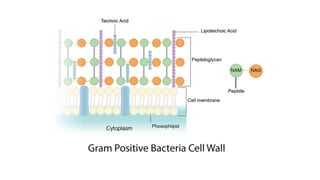
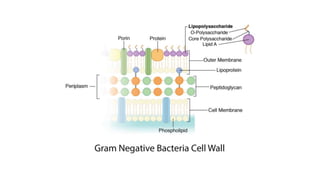
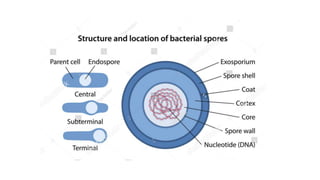
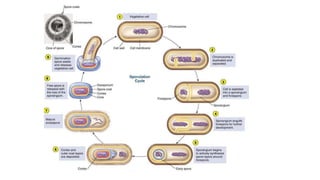
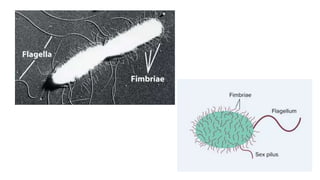
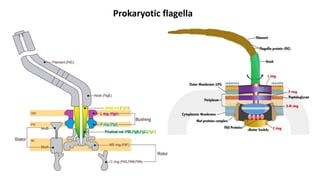
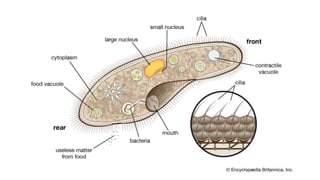
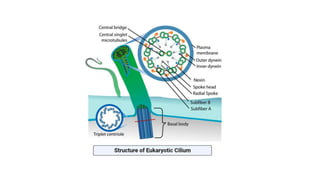
Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665 using a microscope. He defined cells as the fundamental units of life. Later, Schleiden and Schwann defined cells as the basic units of plant and animal structure, respectively. Prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells, lack membrane-bound organelles, and have their DNA found in the cytoplasm rather than a nucleus. The endosymbiotic theory explains how eukaryotic cells evolved from large cells engulfing smaller cells that became organelles in a symbiotic relationship around 2 billion years ago.