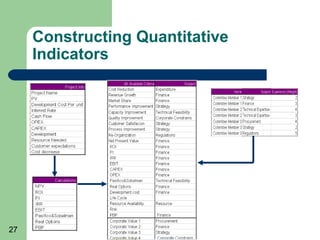
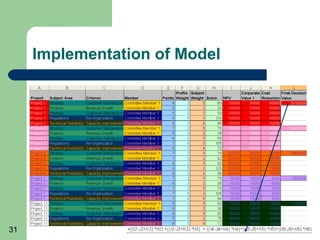
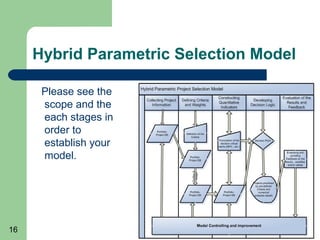
This document outlines steps to establish a hybrid parametric model for project selection and decision making in an organization. The model combines known methods with a weighted scoring approach. Key steps include: collecting project information; defining selection criteria and weights; constructing quantitative indicators; developing decision logic; implementing the model; evaluating results and providing feedback; and ongoing model controlling and improvement. The goal is to reduce biases while capturing important factors for value-maximizing project choices.


![How a Decision Model Should Work?
“Humans have limited information processing skills,
can be biased, and are often inconsistent when
making choices.“ [3]
People are good at creative tasks like generating
alternatives. They are also good at recognizing
structure and at making the sort of "small", well-
defined judgments that are required in order to
provide inputs to models.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectselectionecdraft-121126004942-phpapp02/85/Project-Selection-Model-4-320.jpg)
![How a Decision Model Should Work?
Because a successful decision model must capture
every critical aspect of the decision, more complex
decisions require more sophisticated models.
“There is not a simple solution to every complex
problem” [H. L. Mencken]. This reality creates a
major challenge to constructing a one ideal model
which should solve all project selection problems.
Project decisions are often high-stakes, dynamic
decisions with complex technical issues.
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectselectionecdraft-121126004942-phpapp02/85/Project-Selection-Model-5-320.jpg)




![Decision Models
Decision analysis is a
theory and collection
of associated [1]
methods for making
decisions under
uncertainty.
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectselectionecdraft-121126004942-phpapp02/85/Project-Selection-Model-10-320.jpg)
![Decision Models
The approach involves
constructing and analyzing a
model of the decision
problem to identify the
choice, or sequence of
choices, leading to
outcomes most consistent
[4] with the preferences of the
decision maker.
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectselectionecdraft-121126004942-phpapp02/85/Project-Selection-Model-11-320.jpg)


![Constructing a Project Selection Model
There is where
our model
should fit
[3]
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectselectionecdraft-121126004942-phpapp02/85/Project-Selection-Model-14-320.jpg)






![Defining Criteria and Weights
Differently from most of the
known models I would
suggest weighting profiles as
well.
You can weight members of
decision committee for each [1]
subject in order to reflect and
balance subject matter
expertise to selection
decisions.
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectselectionecdraft-121126004942-phpapp02/85/Project-Selection-Model-23-320.jpg)