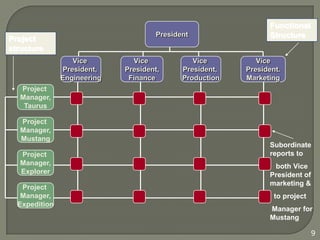
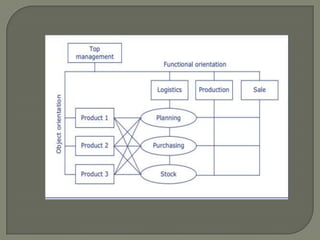
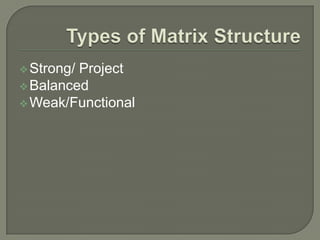
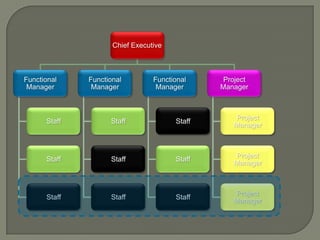
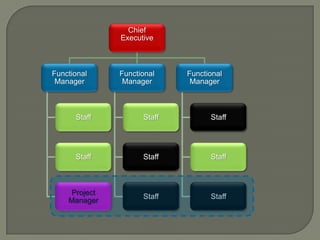
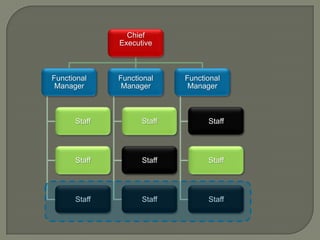
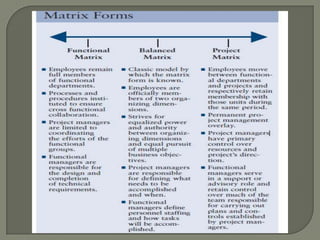
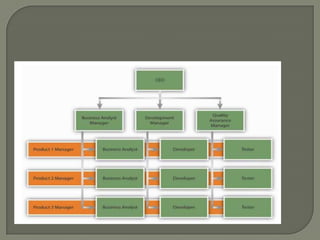
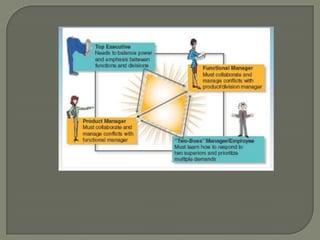
This document discusses matrix organizational structures. It defines a matrix structure as one that takes advantages of both functional and projectized structures, allowing a company to address multiple business dimensions using multiple command structures. The document outlines three main types of matrix structures: strong/project matrix, balanced matrix, and weak/functional matrix. It explains the characteristics of each type and where power typically lies between project managers and functional managers. Advantages and challenges of working in a matrix structure are also presented.