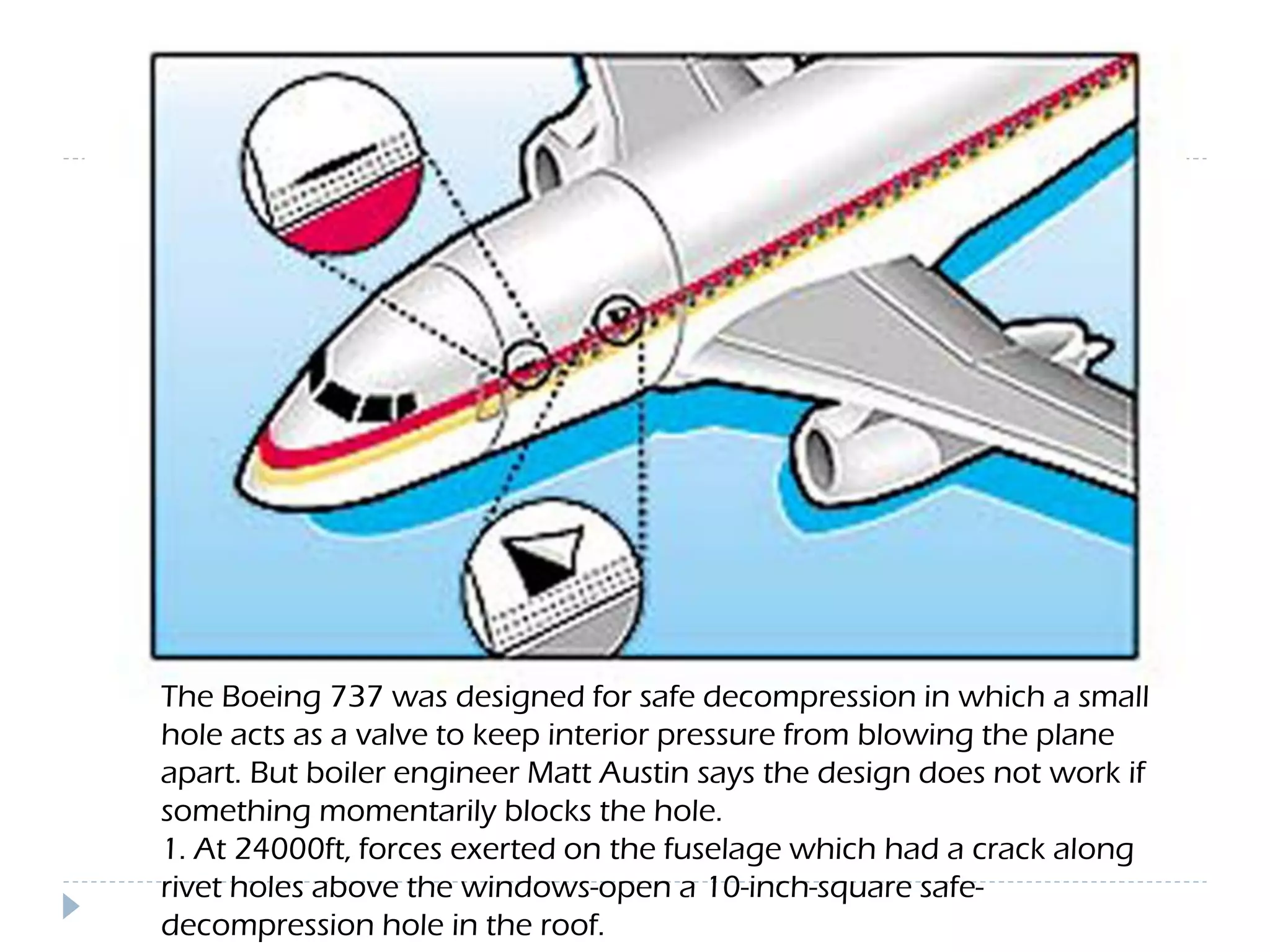
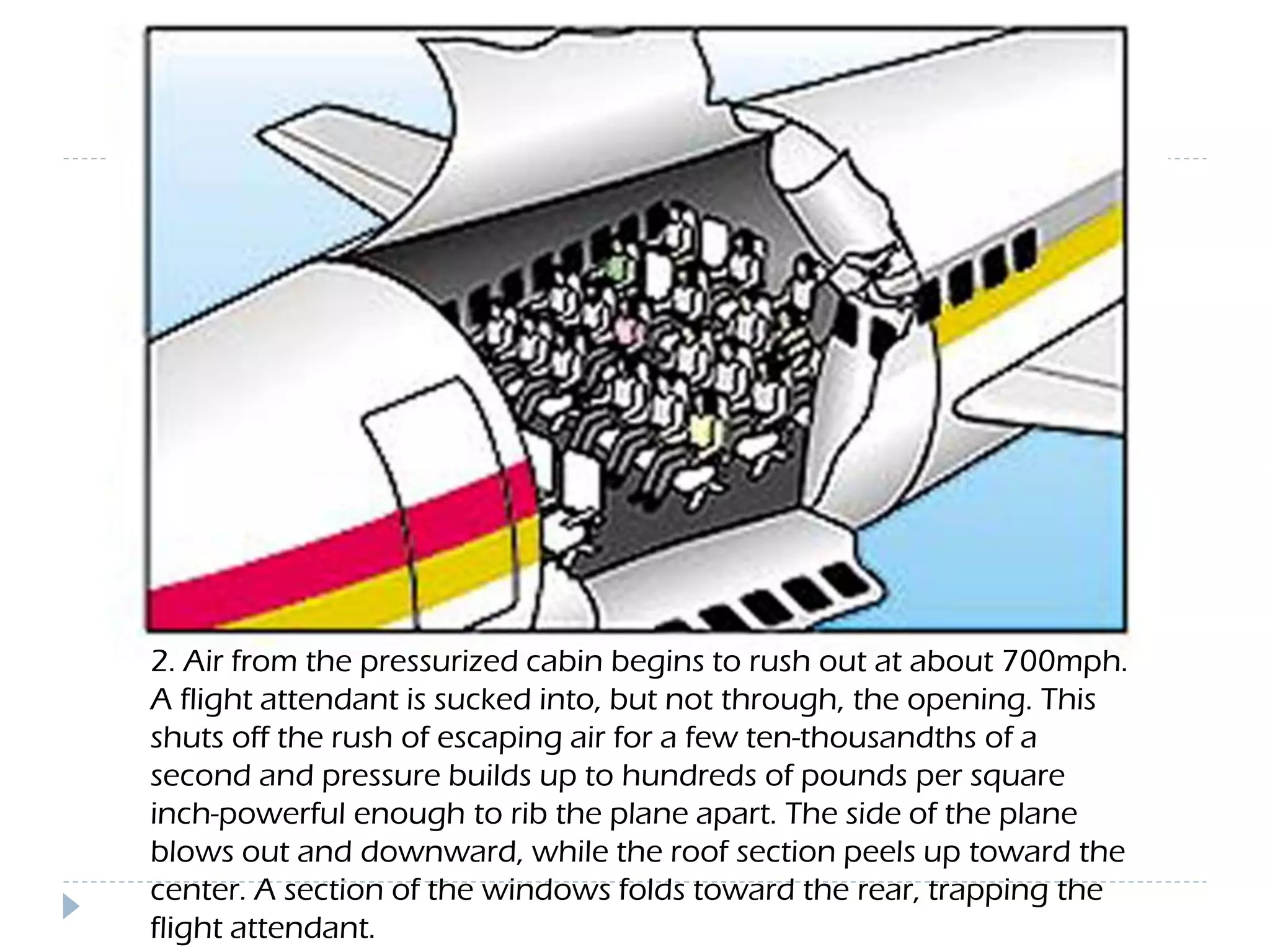
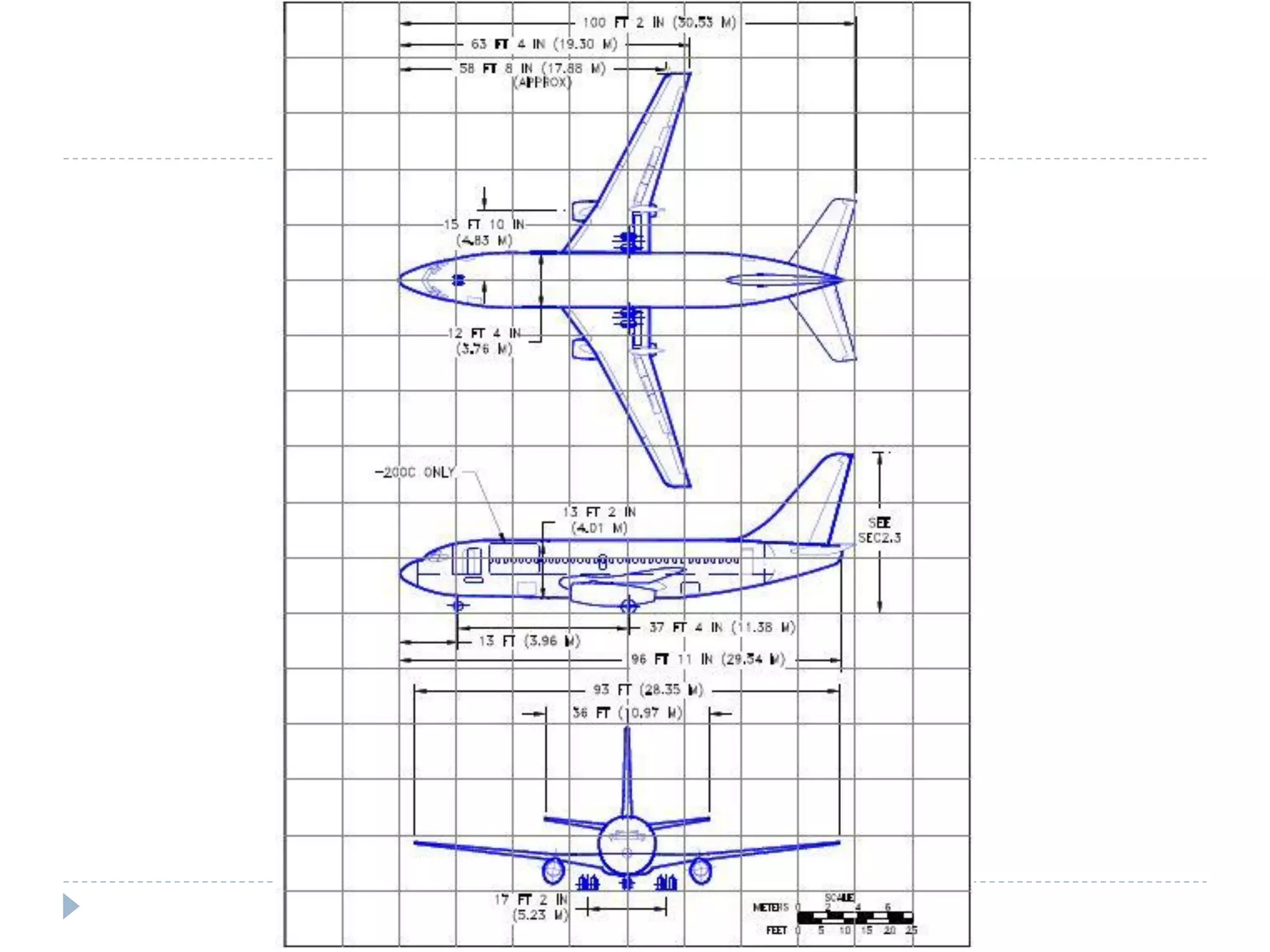
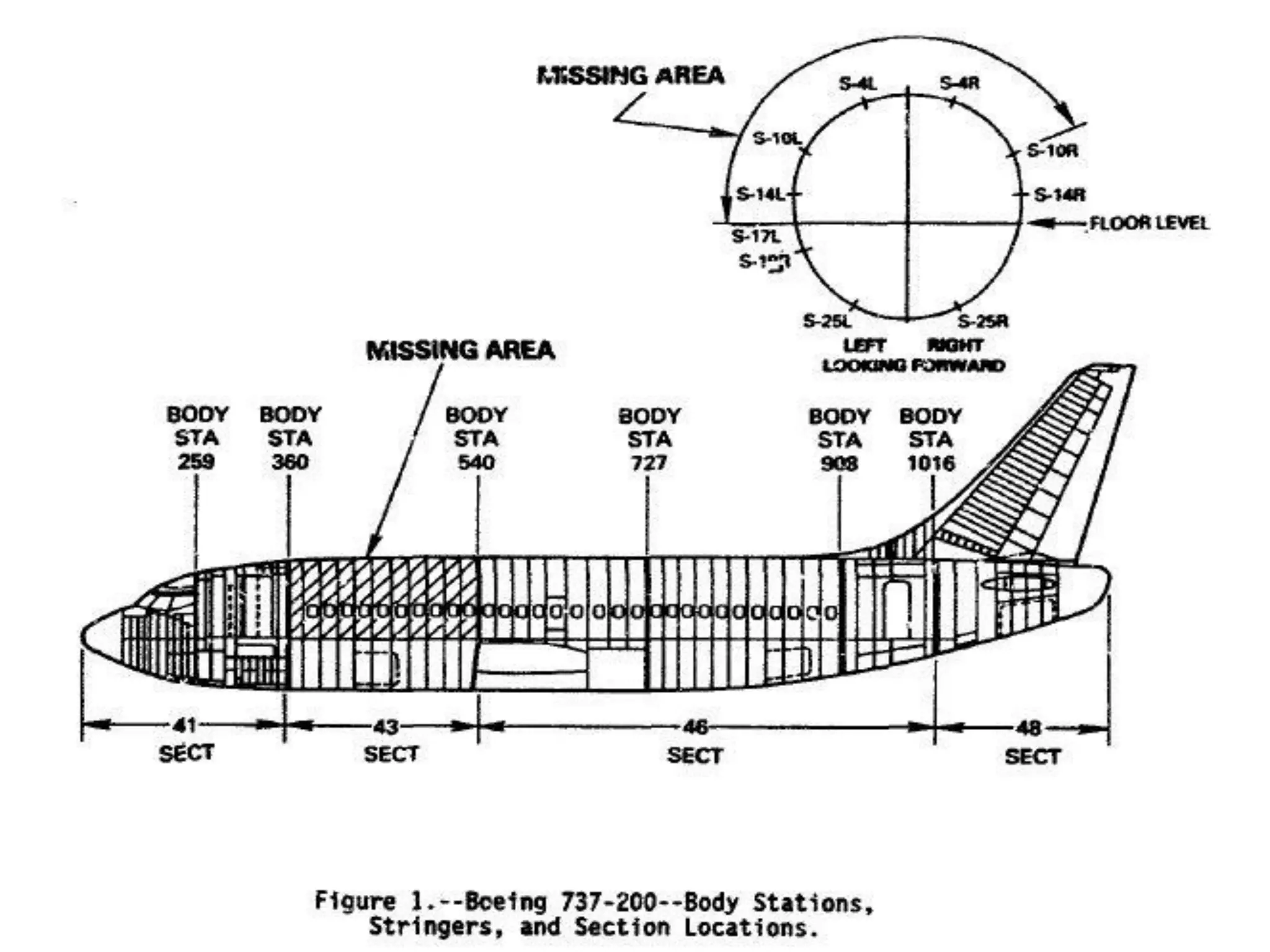
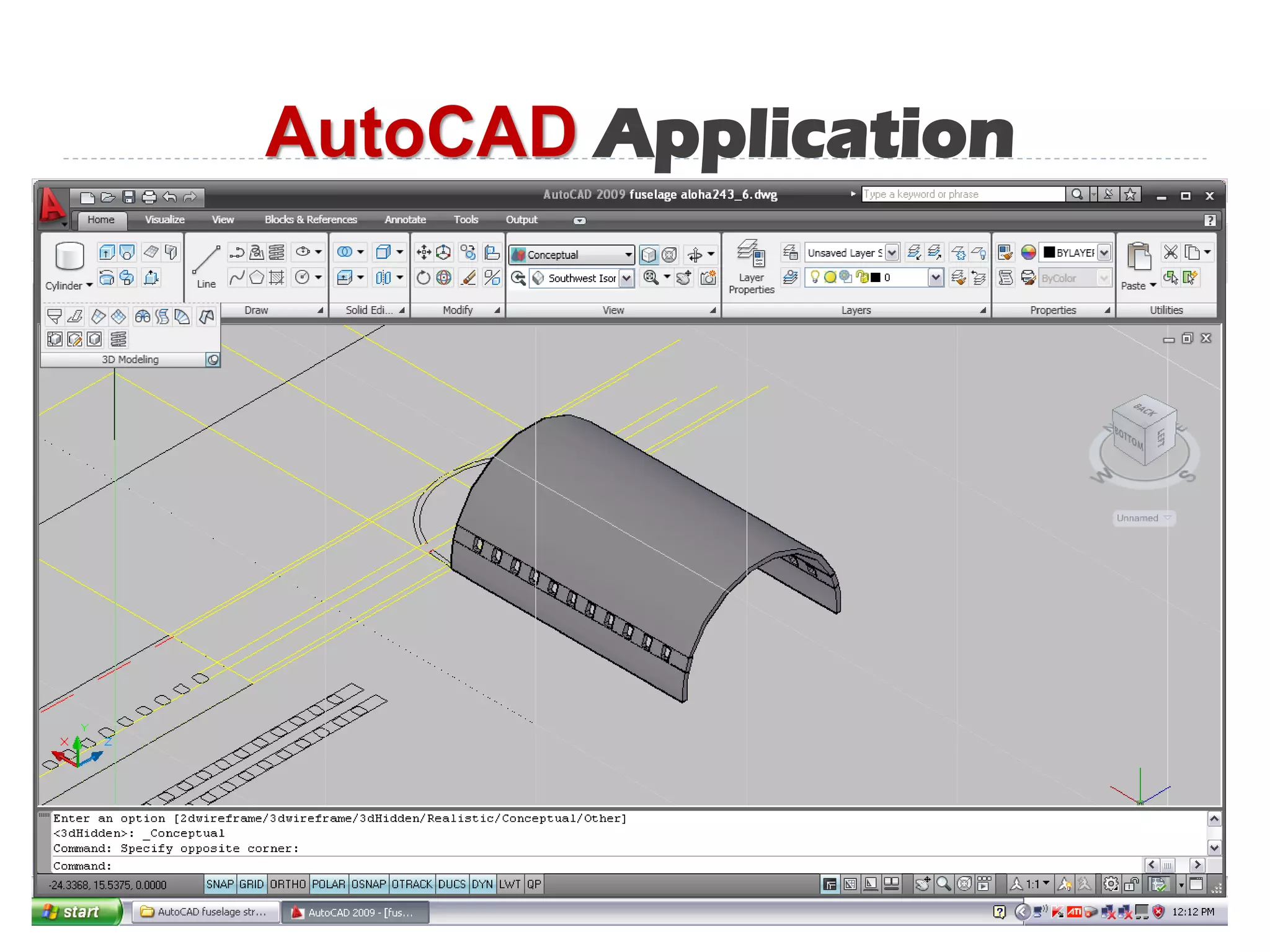
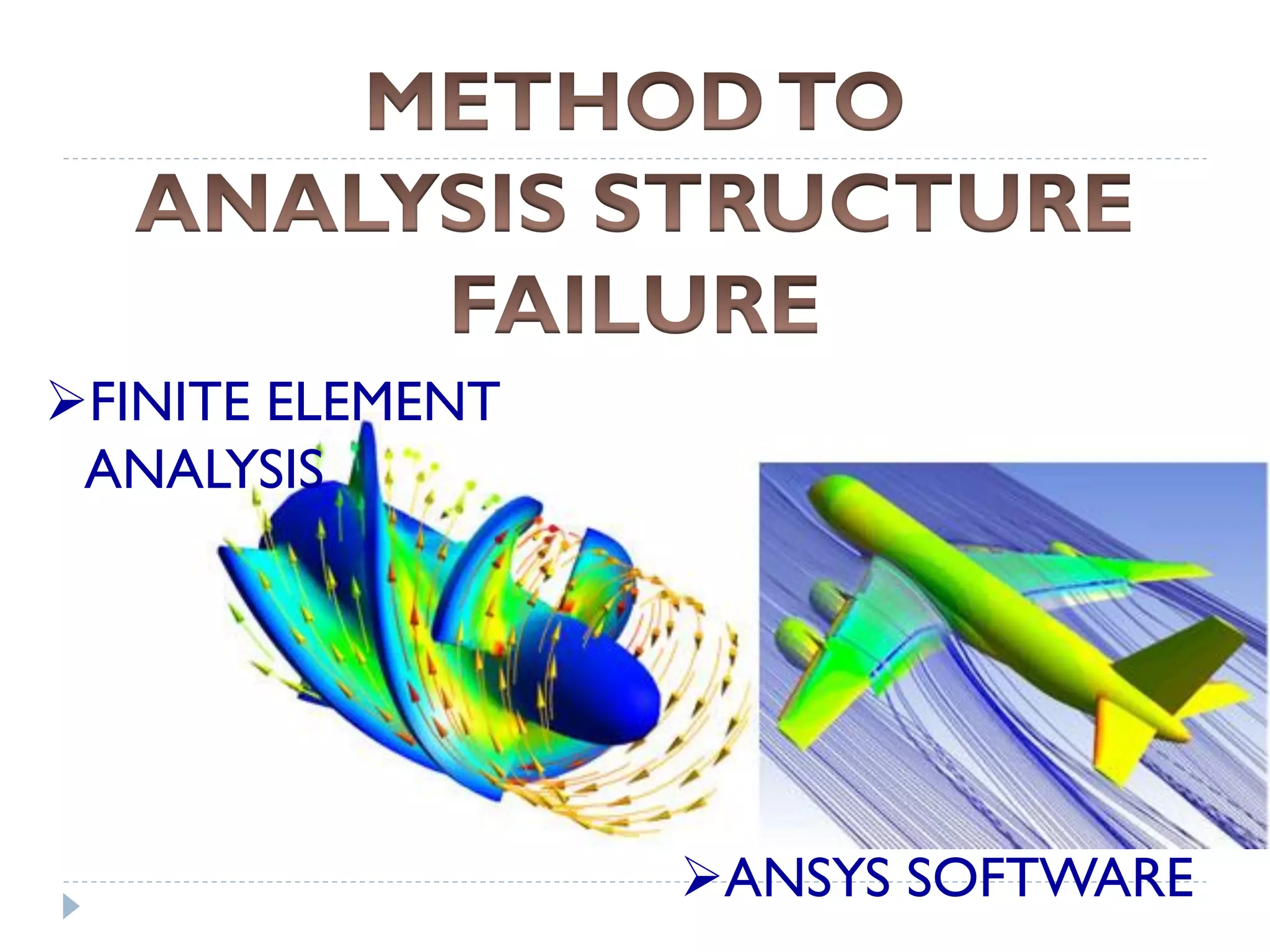
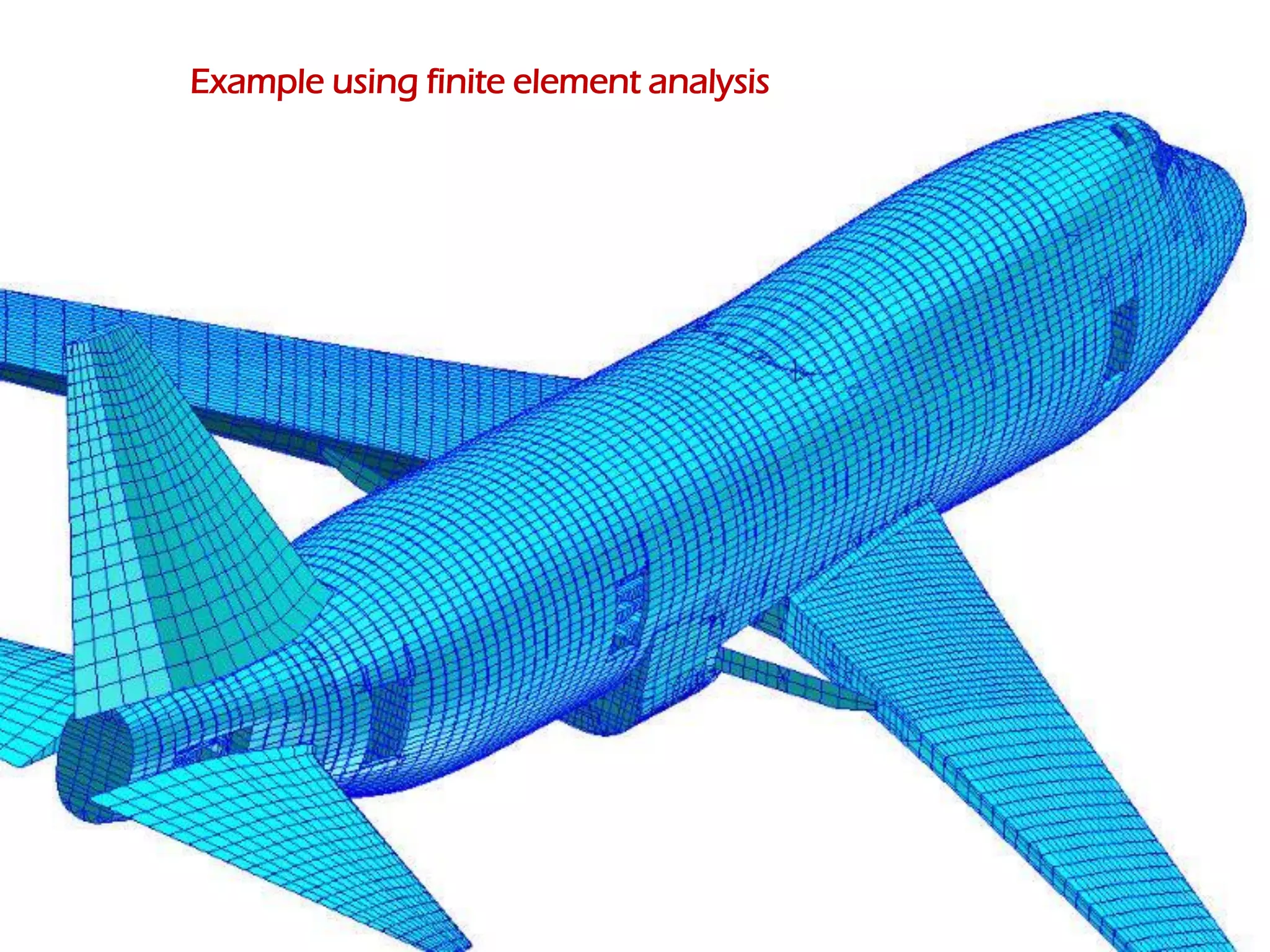
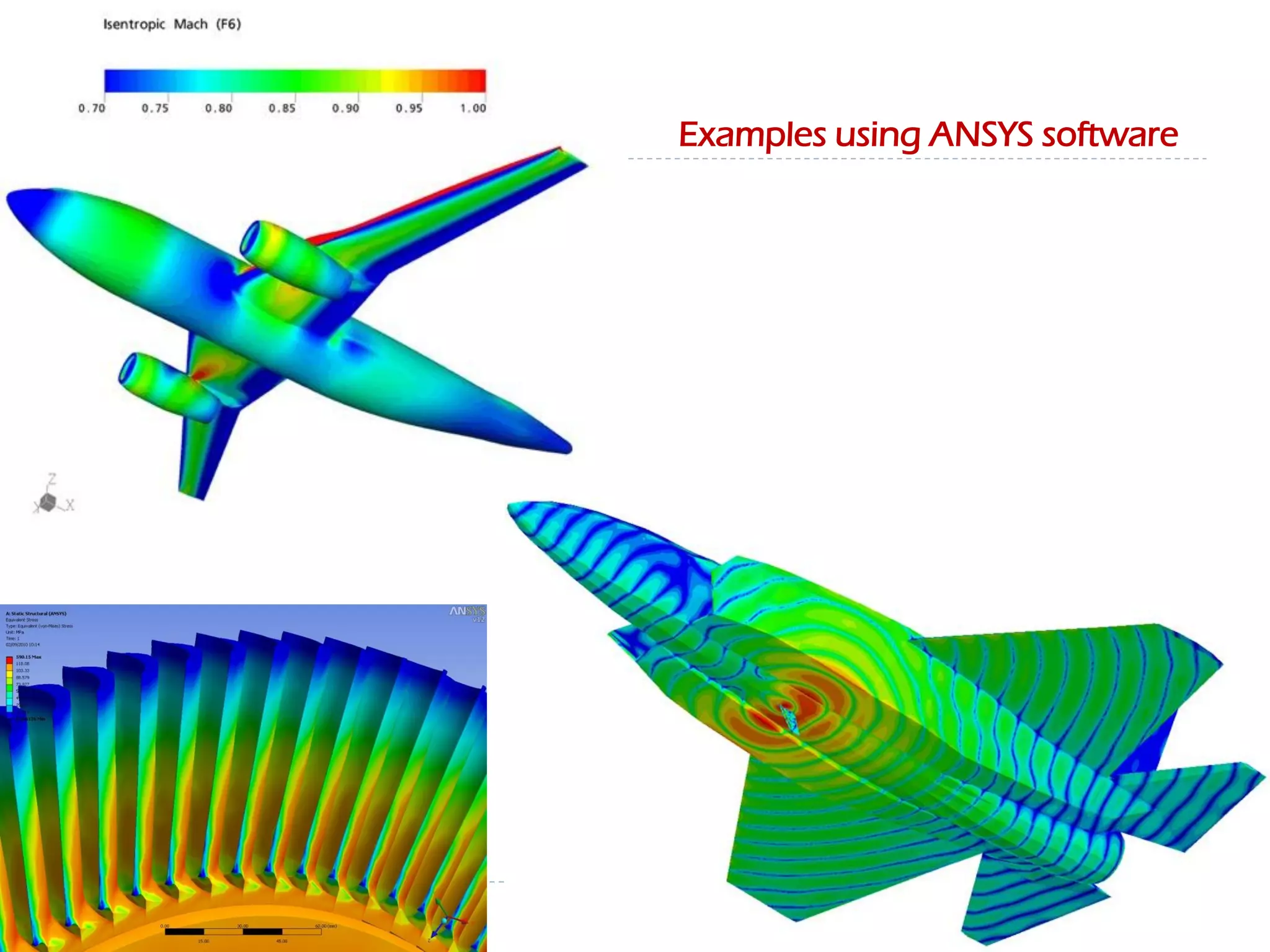
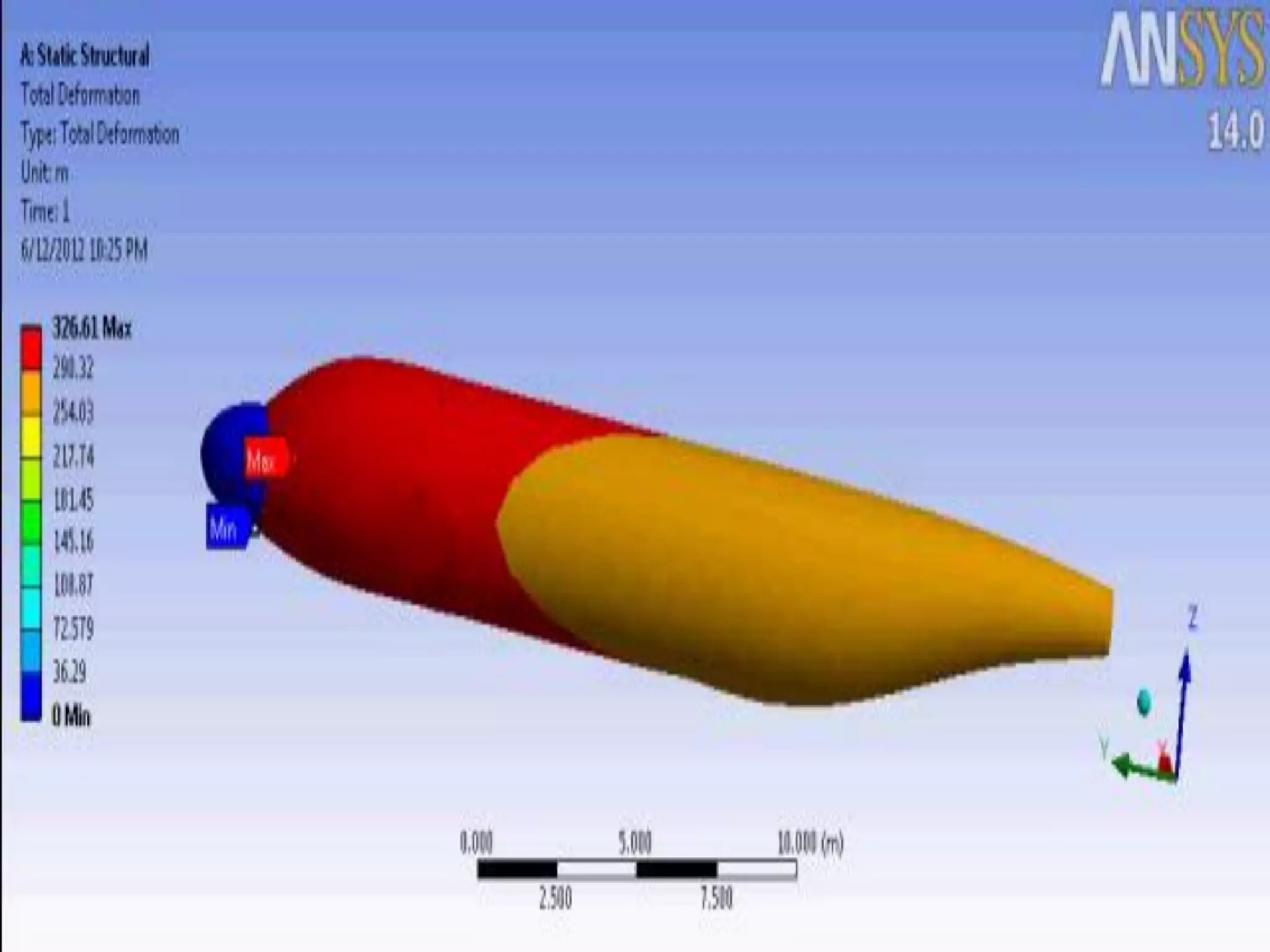
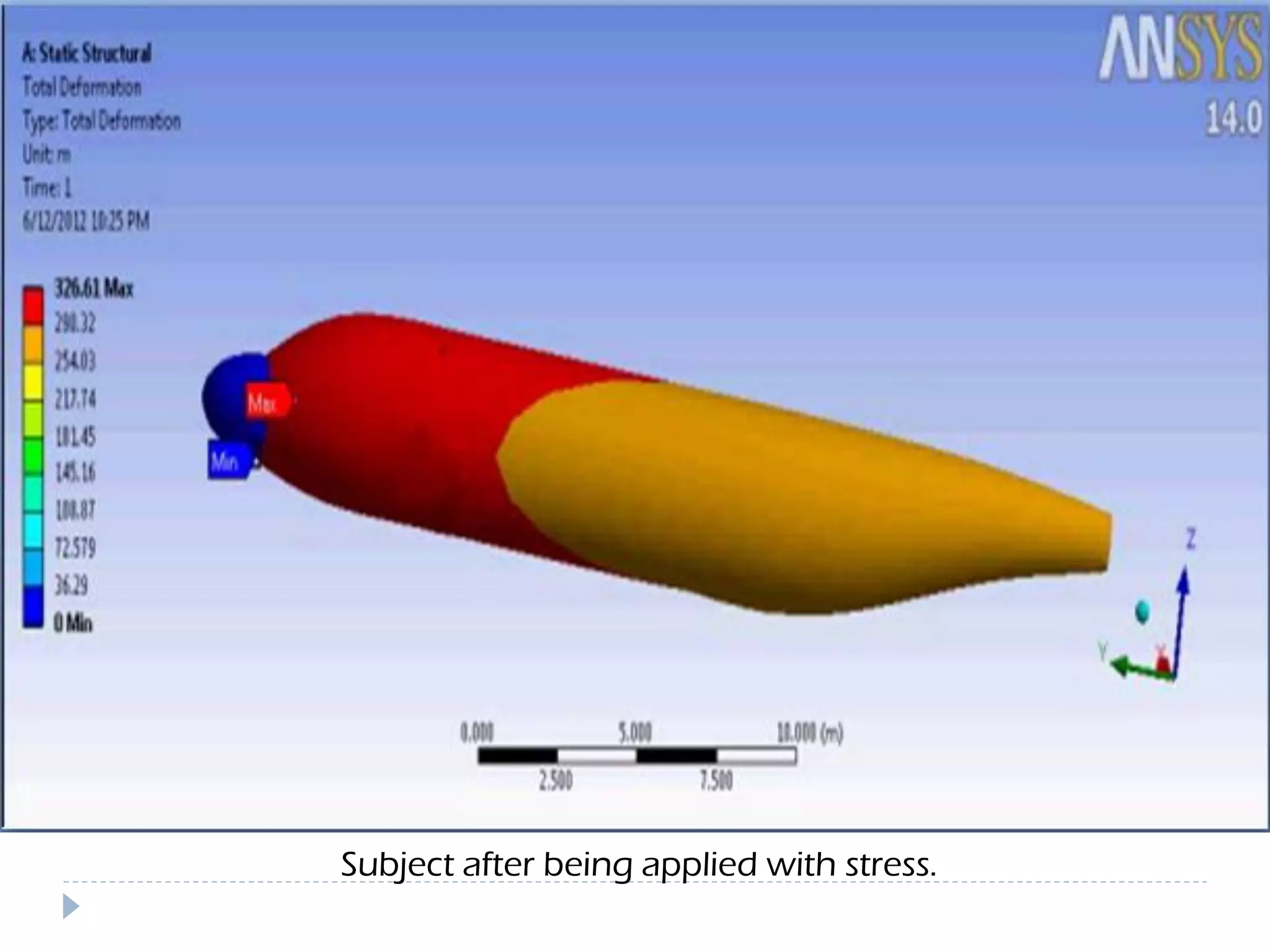
This document discusses an aircraft structures failure project analyzing the 1988 Aloha Airlines Flight 243 accident. It provides an overview of the accident, describing how part of the Boeing 737's fuselage tore apart in flight. It then summarizes the finite element analysis conducted using ANSYS software to simulate stresses on the aircraft structure. Images and references are included at the end.