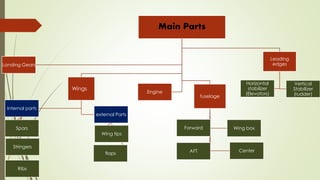
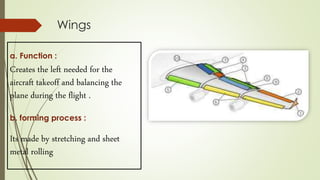
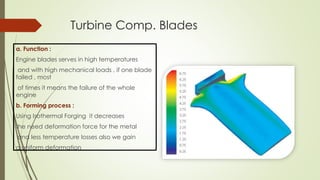
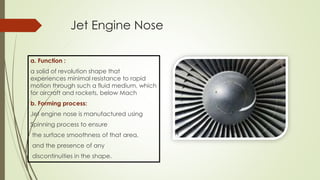
This document discusses forming technology applications in aircraft manufacturing. It describes how forming processes are used to produce critical aircraft parts like wings, ribs, spars, stringers, fuselages, engine components, and more. Rolling, stretching, forging, drawing and other forming methods are used to manufacture parts in a way that meets the strength and durability needs for flight while minimizing costs and production challenges. Forming technology plays a key role in the aircraft industry by enabling the mass production of high-quality, complex shapes for various internal and external aircraft structures and systems.