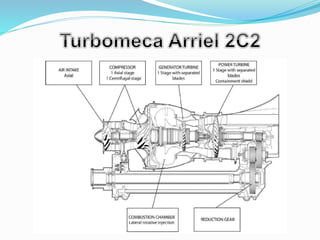
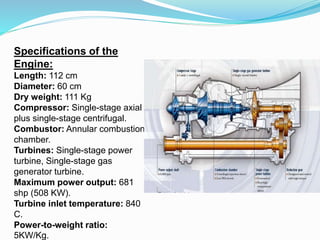
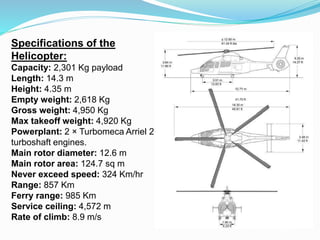
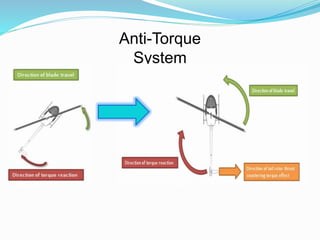
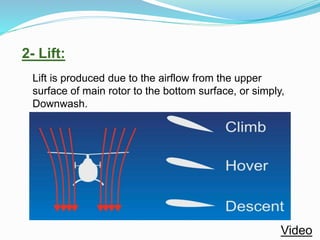
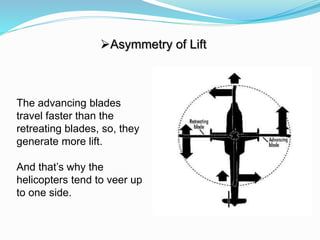
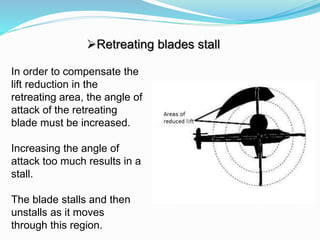
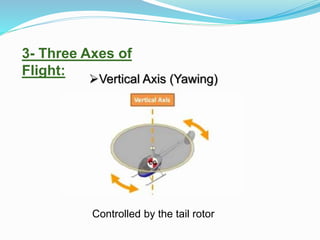
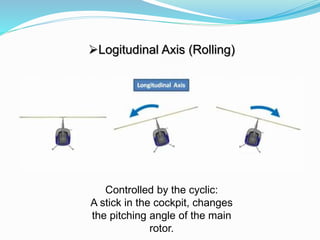
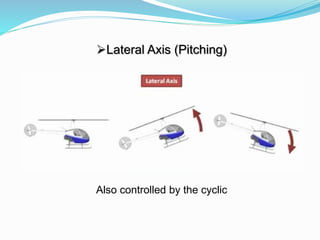
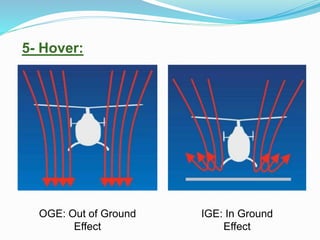
The document provides detailed information about the Eurocopter EC155-B, highlighting its specifications, performance, and operational capabilities. The helicopter is powered by two Turbomeca Arriel 2C2 turboshaft engines, offering a maximum speed of 324 km/h and a range of 857 km. It features a spacious cabin for 5-12 passengers, advanced avionics, and a high-efficiency rotor system, making it suitable for various missions including passenger transport and emergency services.