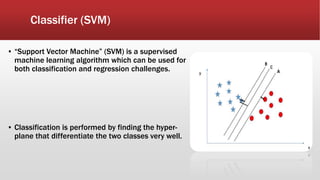
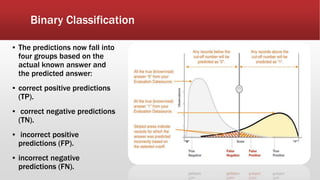
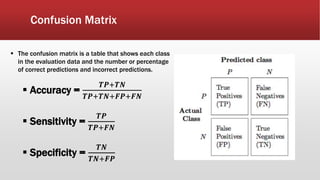
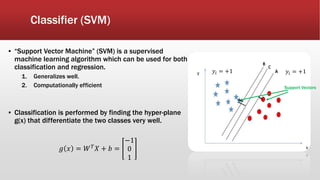
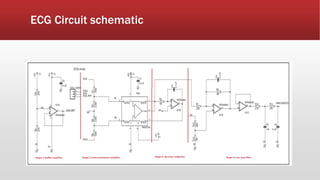
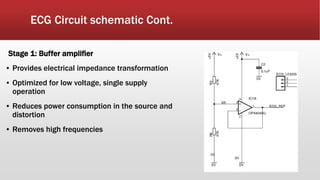
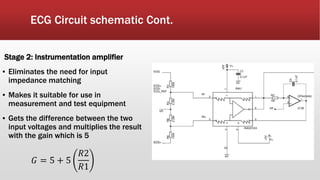
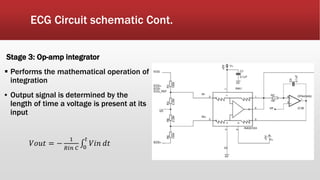
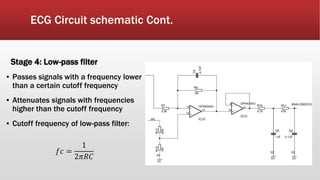
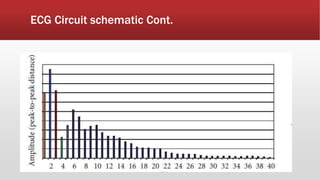
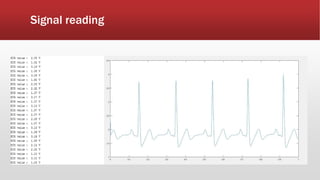
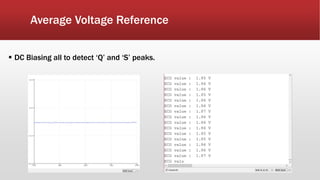
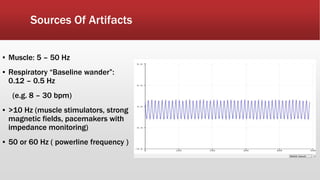
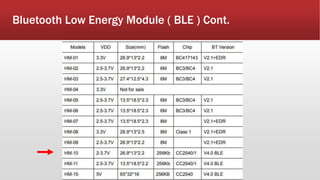
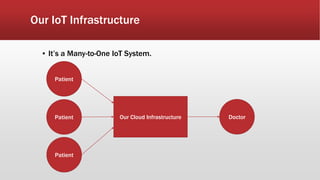
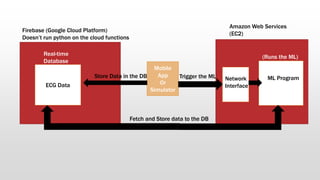
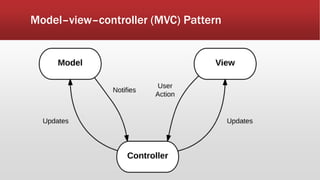
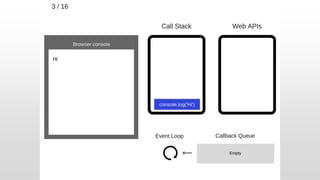
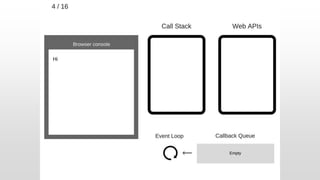
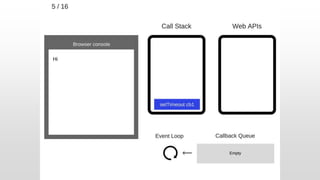
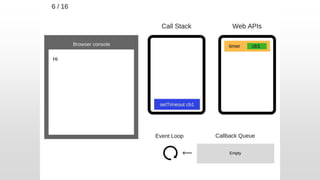
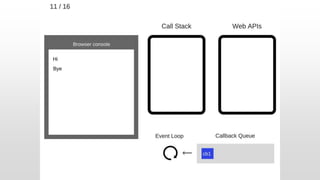
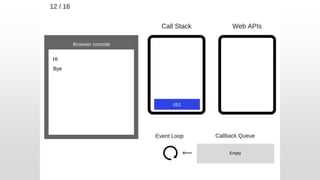
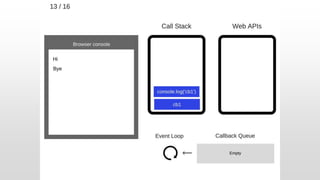
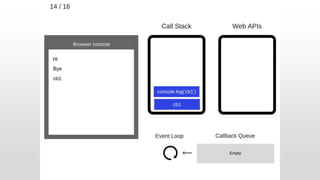
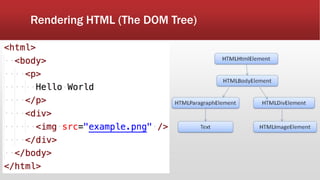
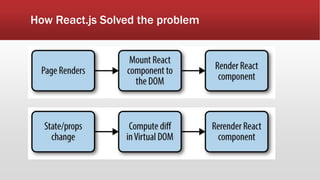
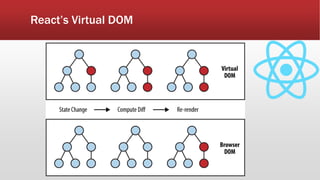
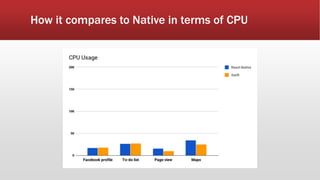
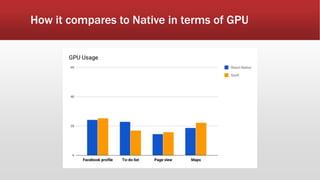
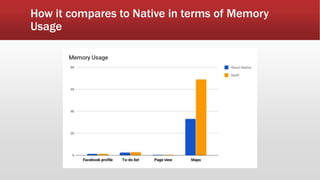
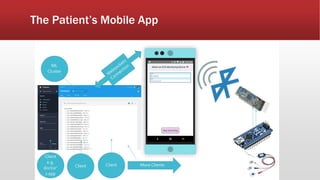
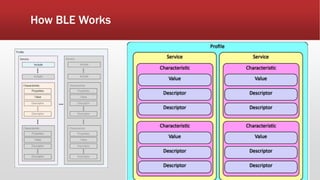
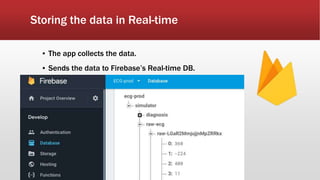
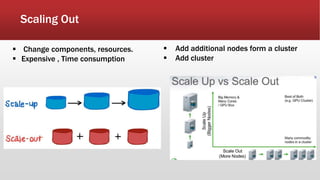
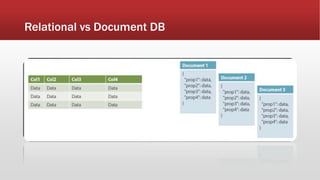
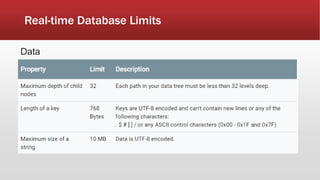
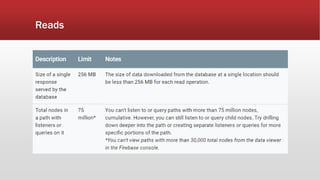
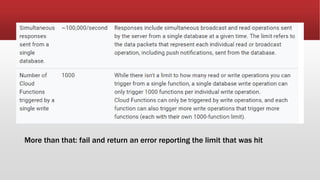
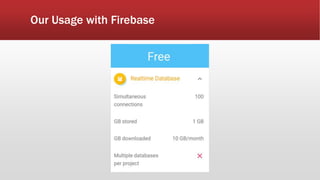
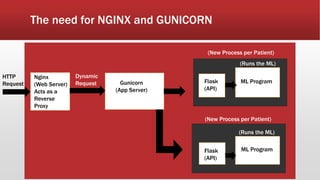
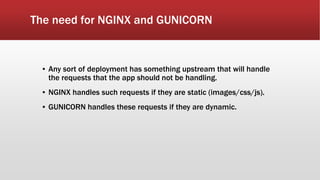
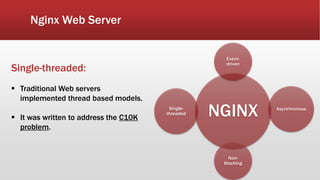
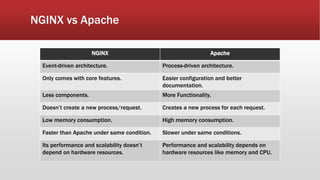
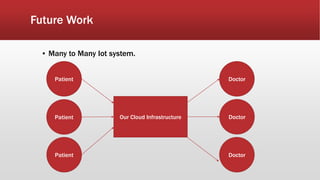
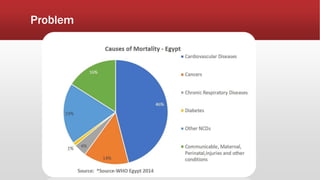
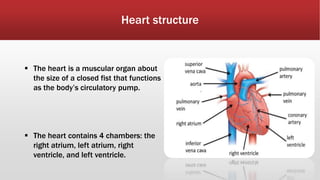
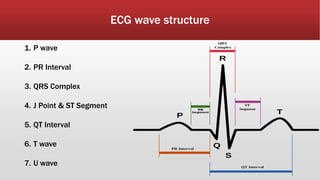
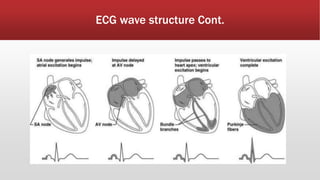
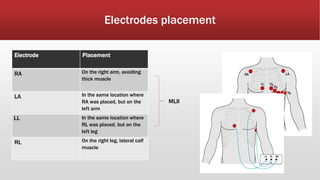
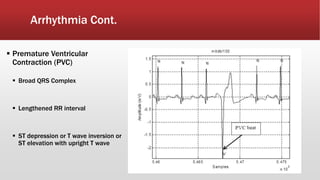
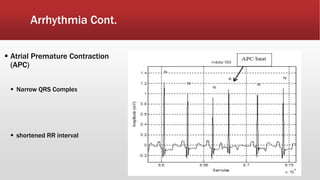
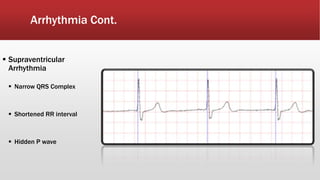
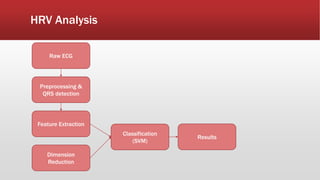
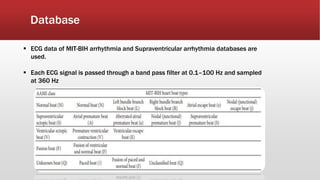
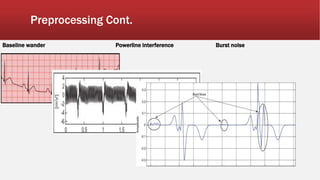
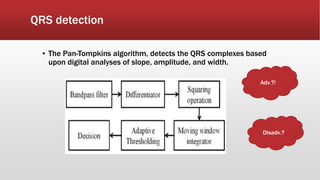
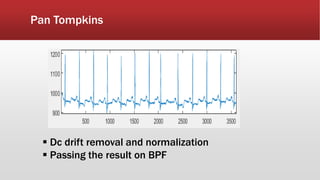
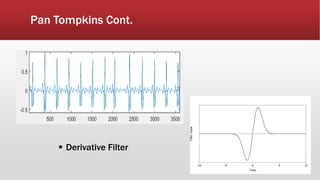
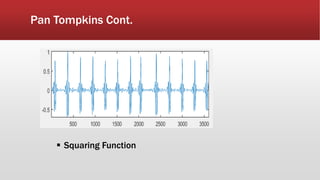
The document outlines the development of an IoT-cloud based ECG monitoring system for elderly patient healthcare, focusing on biomedical and machine learning techniques for arrhythmia detection. It details hardware components, including an ECG sensor and Bluetooth module, and describes the cloud infrastructure utilizing services like Firebase and AWS for real-time data processing and storage. The system aims to provide efficient remote monitoring and analysis, improving healthcare access for patients unable to navigate modern technology.













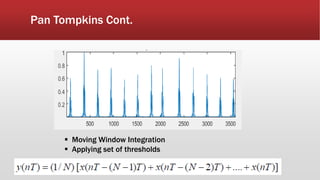
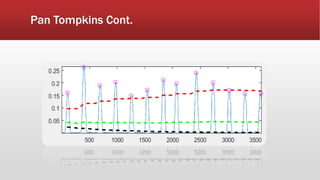


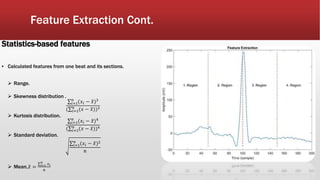
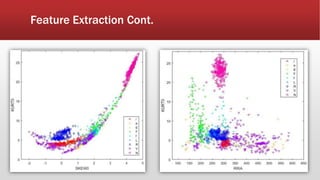
![Feature Extraction Cont.
▪ Features Normalization
▪ neutralize the effect of different
scales across features .
▪ Standardization (Z-score
normalization).
▪ Scaling to [0,1].
𝒛 =
𝒙−μ
σ
, μ=0 and σ=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-191104222929/85/Project-41-320.jpg)