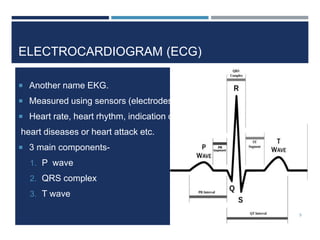
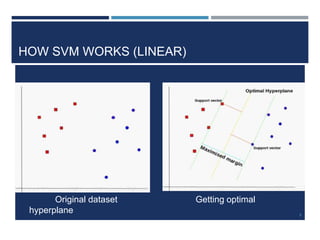
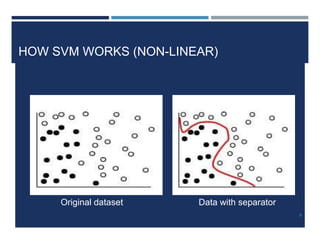
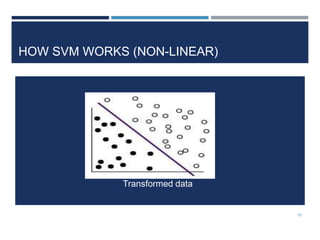
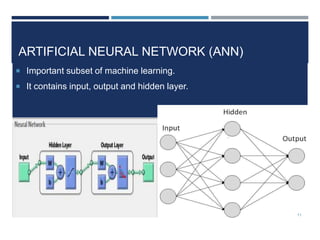
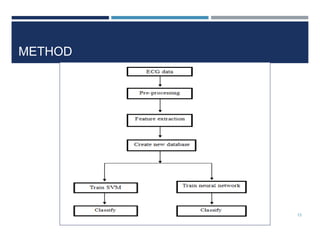
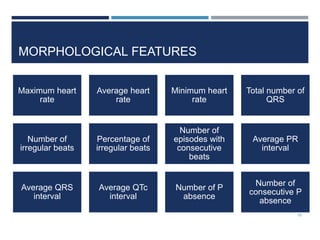
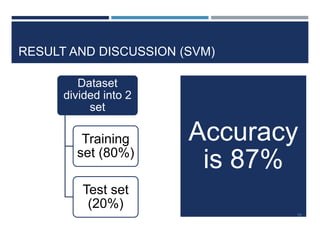
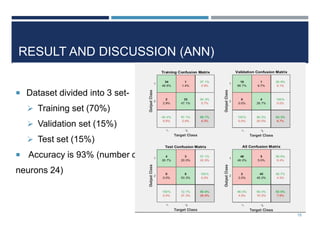
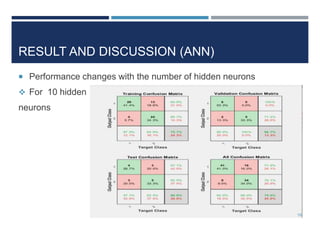
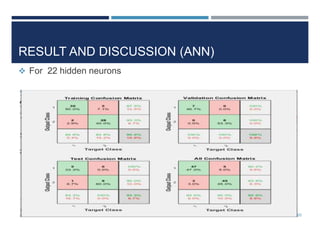
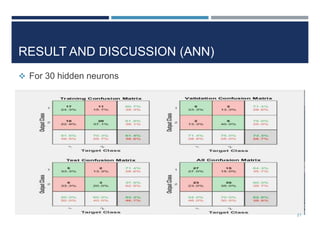
This document outlines a study that used support vector machines (SVM) and artificial neural networks (ANN) to classify electrocardiogram (ECG) data. ECG data from 100 subjects across 4 databases was preprocessed and 12 morphological features were extracted. SVM was trained on 80% of the data and achieved 87% accuracy on the test set. ANN was trained with different numbers of hidden neurons and achieved highest accuracy of 93% with 24 neurons. While results were promising, limitations included inability to work with raw data and need for more accuracy. Future work proposed using more advanced neural networks and identifying most important features.