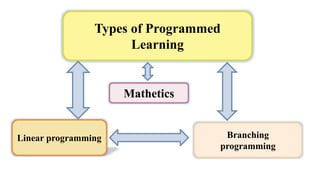
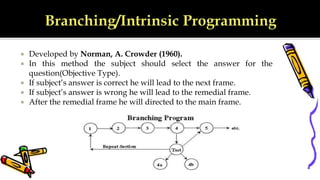
Programmed instruction was first developed in 1943 by B.F. Skinner. It involves breaking material down into small sequential steps and providing immediate feedback. There are three main types: linear programming which presents material in a straight path; branching programming which allows remedial paths for incorrect answers; and mathetics which uses a reverse chaining approach focusing on mastery of content. The techniques aim to actively engage students and allow self-paced learning without a teacher present. While effective for some, they also have limitations such as lack of motivation and difficulty developing materials.