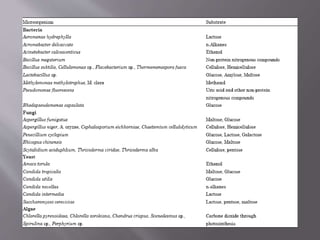
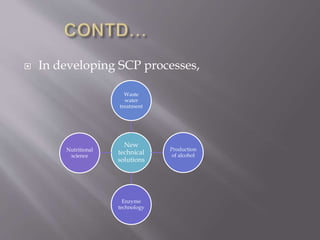
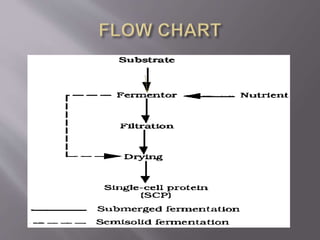
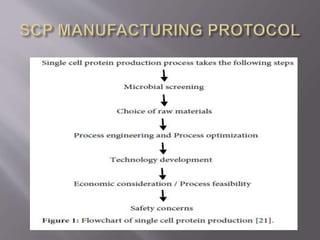
Single cell protein (SCP) refers to edible microorganisms or their extracts used as a protein supplement. SCP can be produced using bacteria, yeast, fungi or algae through fermentation. It has high nutritional value but also has some limitations. Research is focused on improving production methods and addressing issues like high nucleic acid content and digestibility. SCP shows potential as a sustainable protein source but more work is needed before it will be widely accepted as human food.