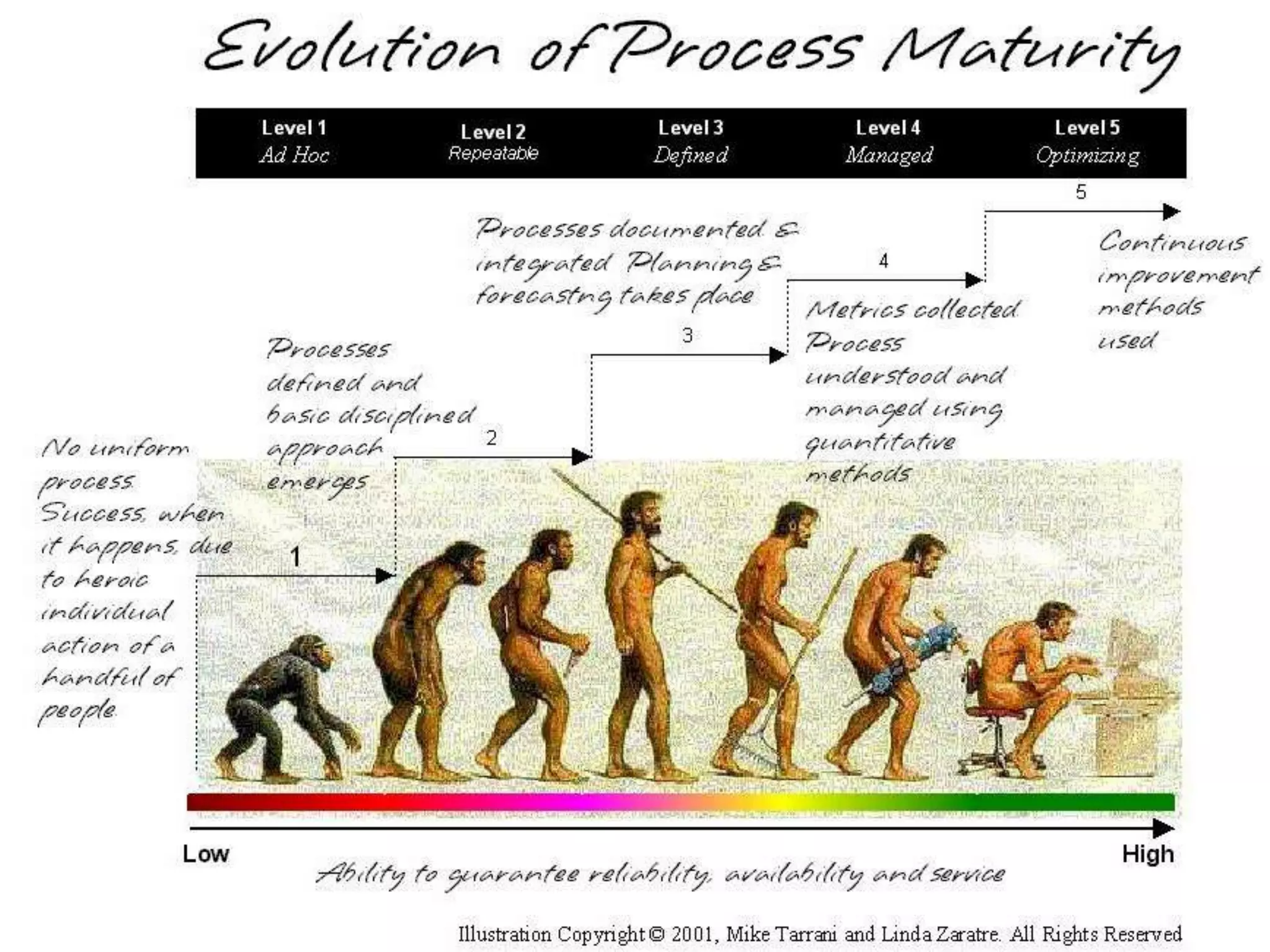
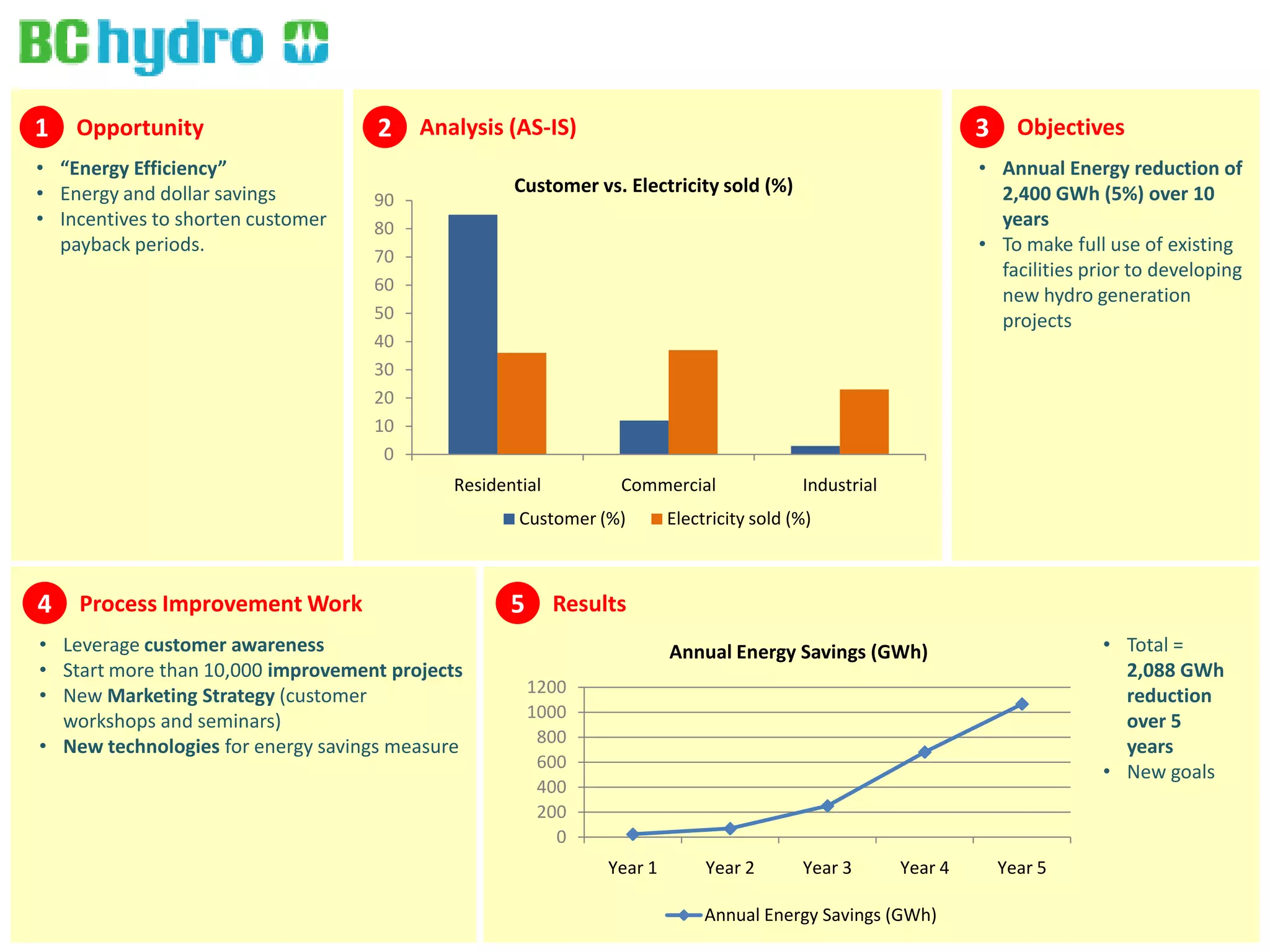
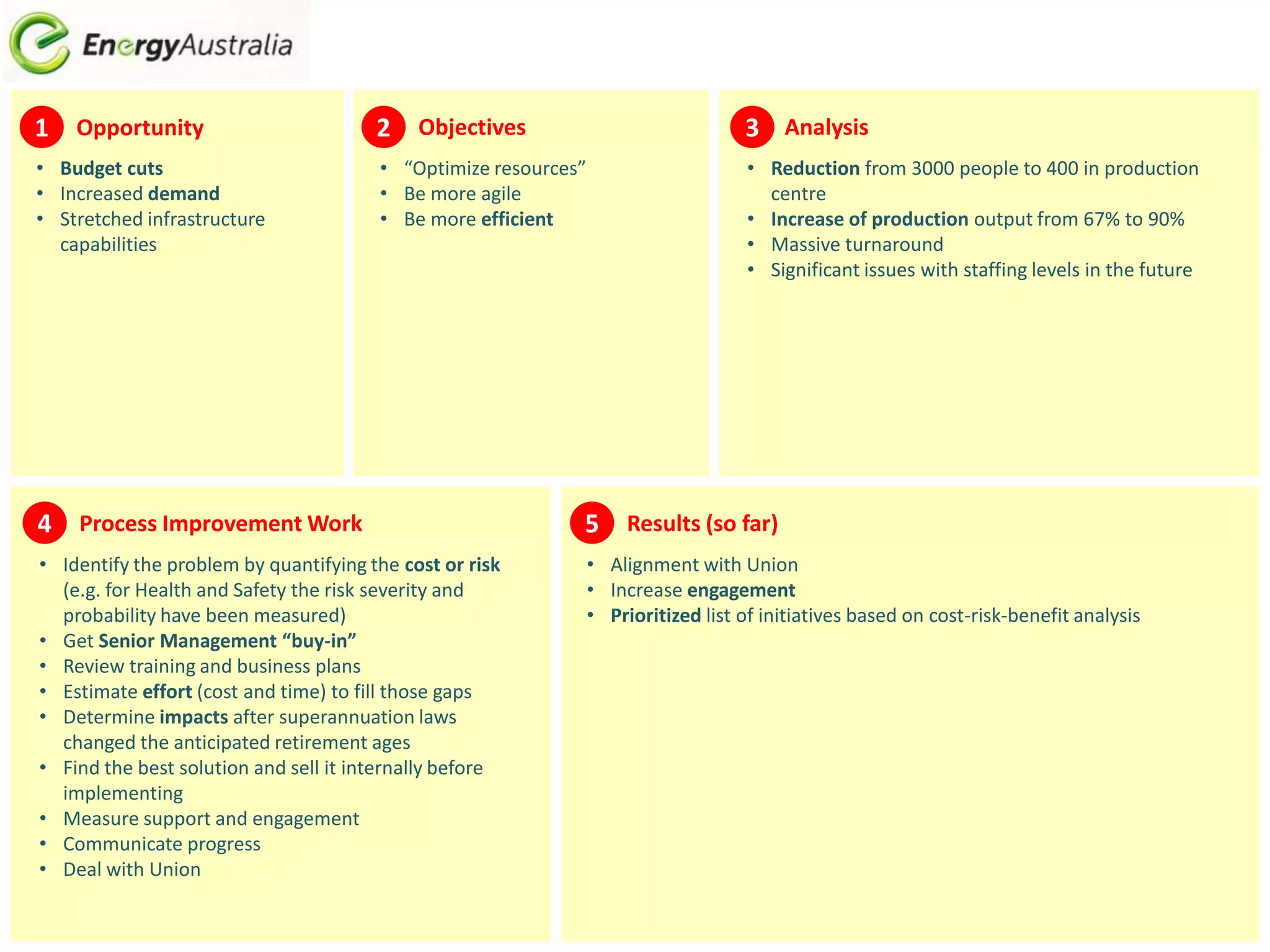
1. The document discusses business process improvement in various industries including utilities. It provides examples of how organizations in the public sector, utilities, and energy industries have improved processes to increase efficiency, reduce costs and waste, and better meet customer and stakeholder needs.
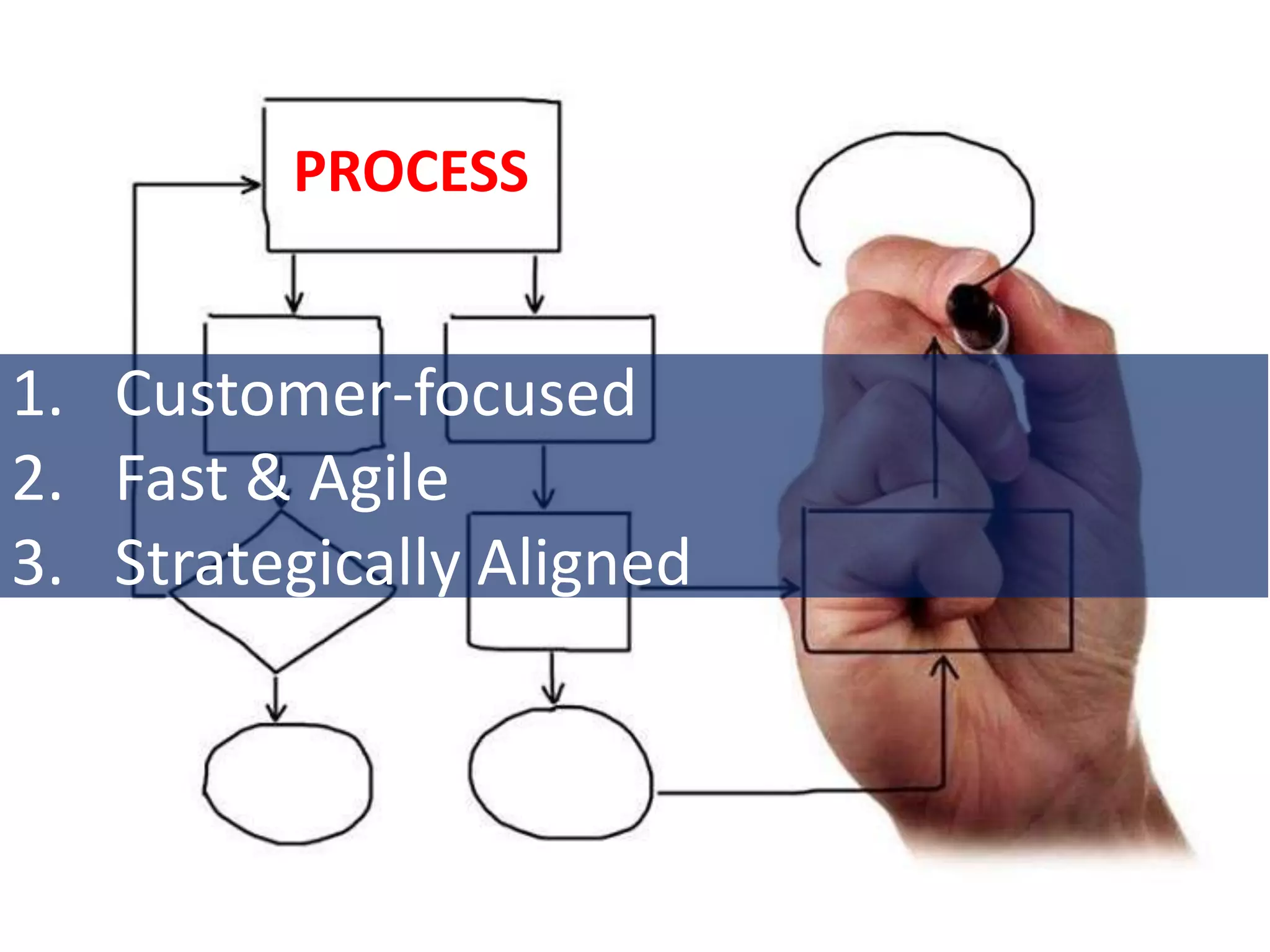
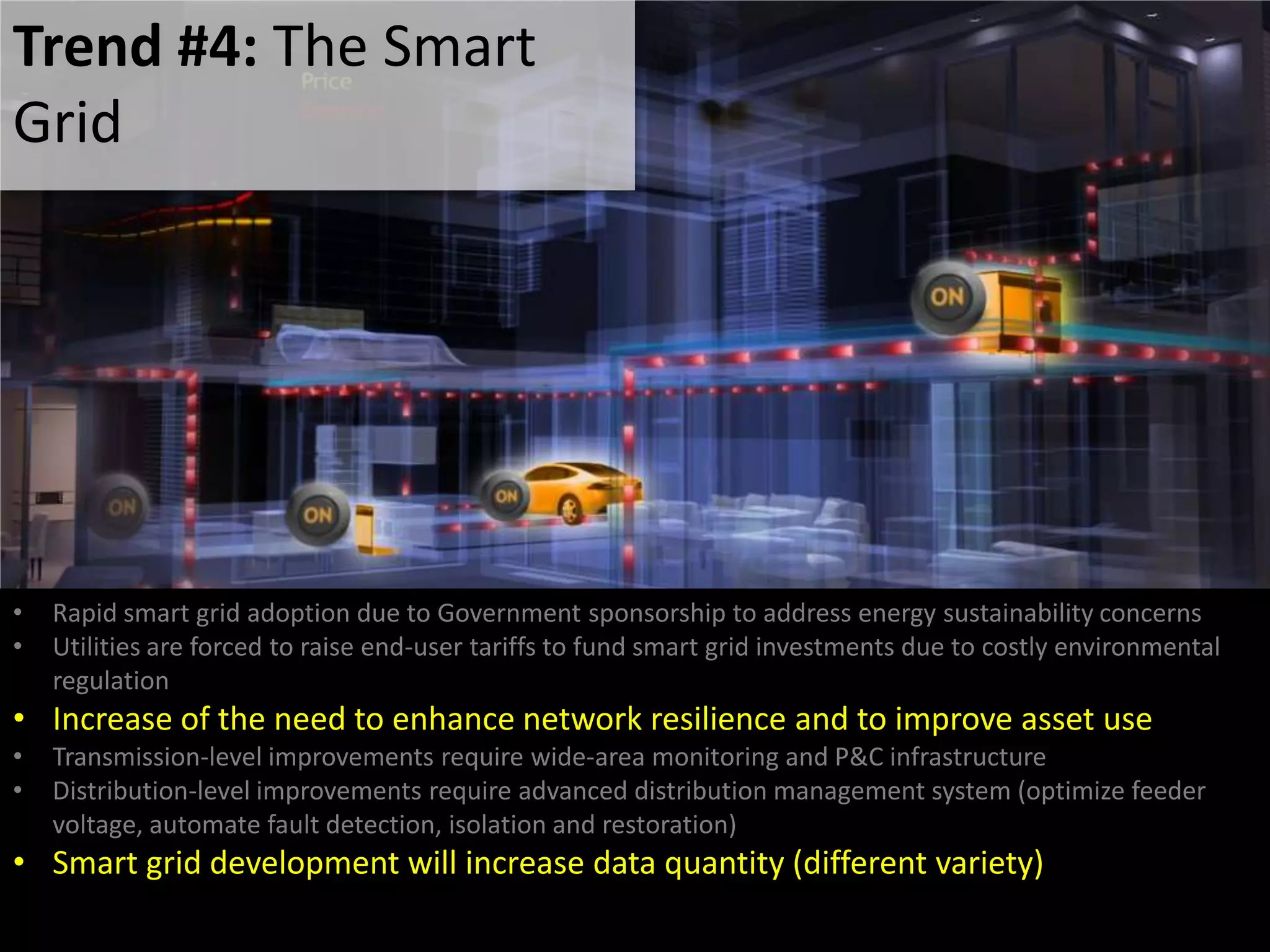
2. The future of process improvement in the utility industry is expected to focus on becoming more customer-focused, fast and agile, and strategically aligned with business objectives. Key trends include an aging workforce, environmental concerns, reliability challenges, and the development of smart grids.
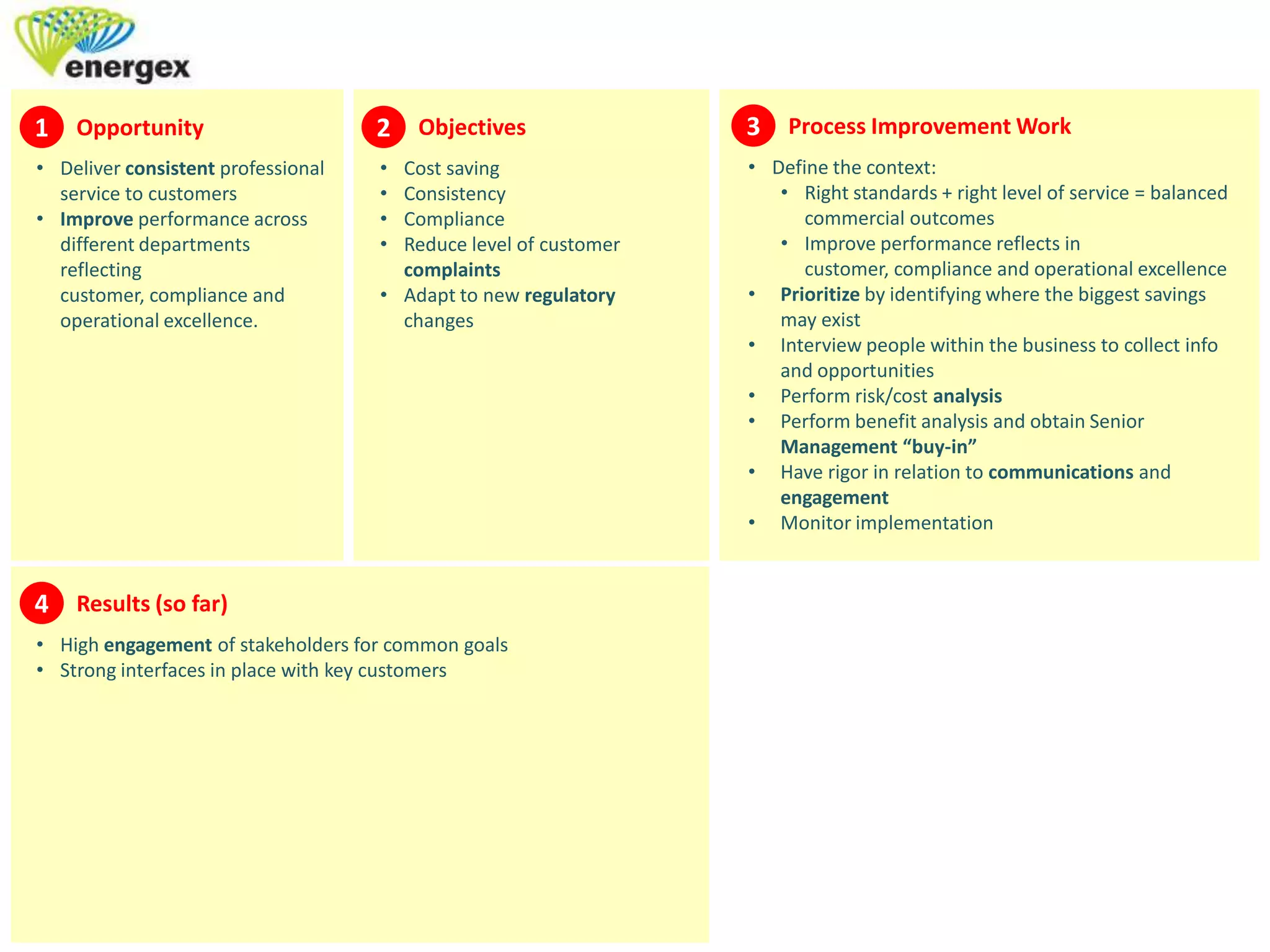
3. Process improvement approaches like defining problems, collecting data, identifying opportunities, and implementing and measuring results can help organizations achieve objectives like cost savings, consistency, and compliance while adapting to changes