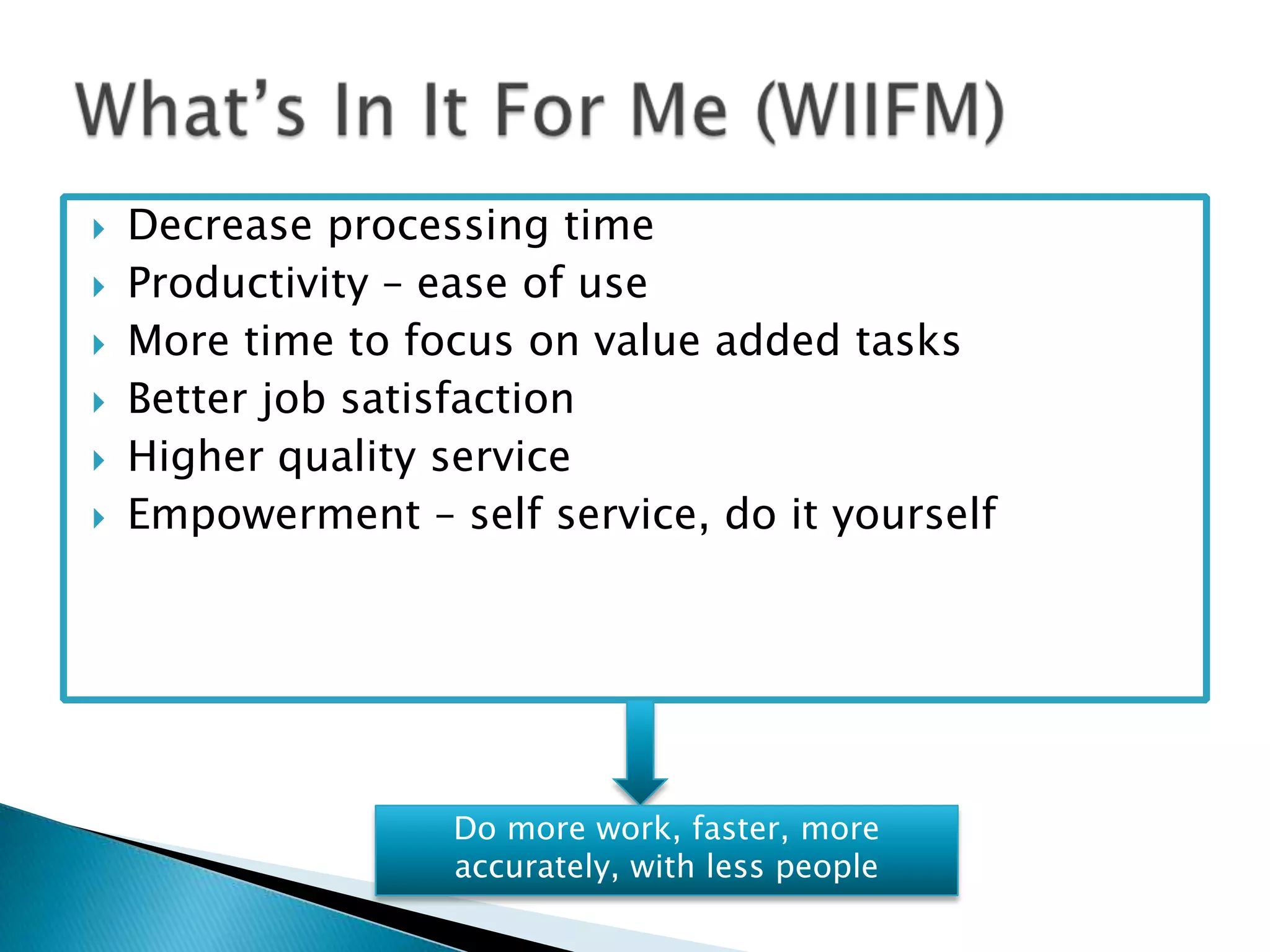
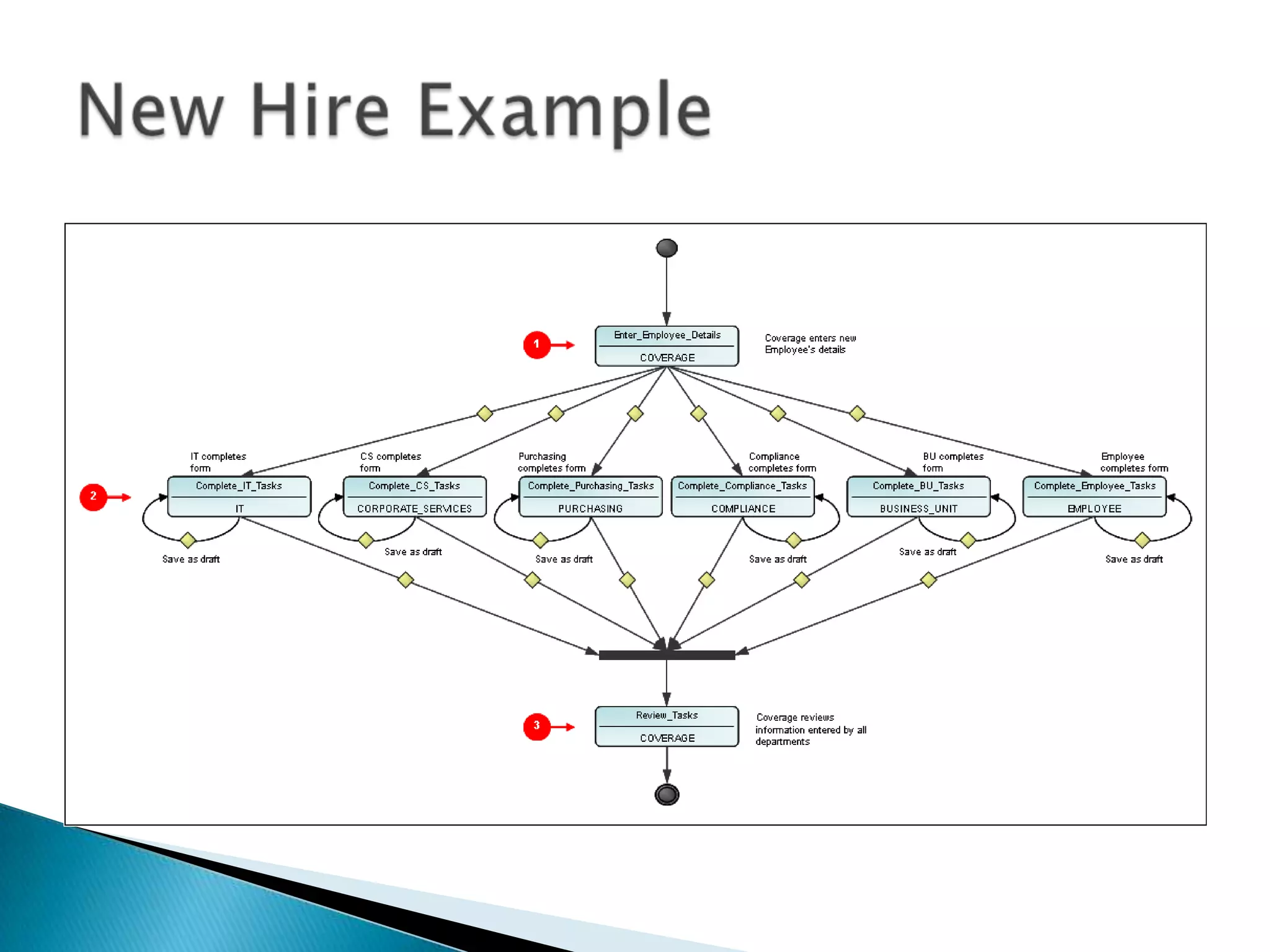
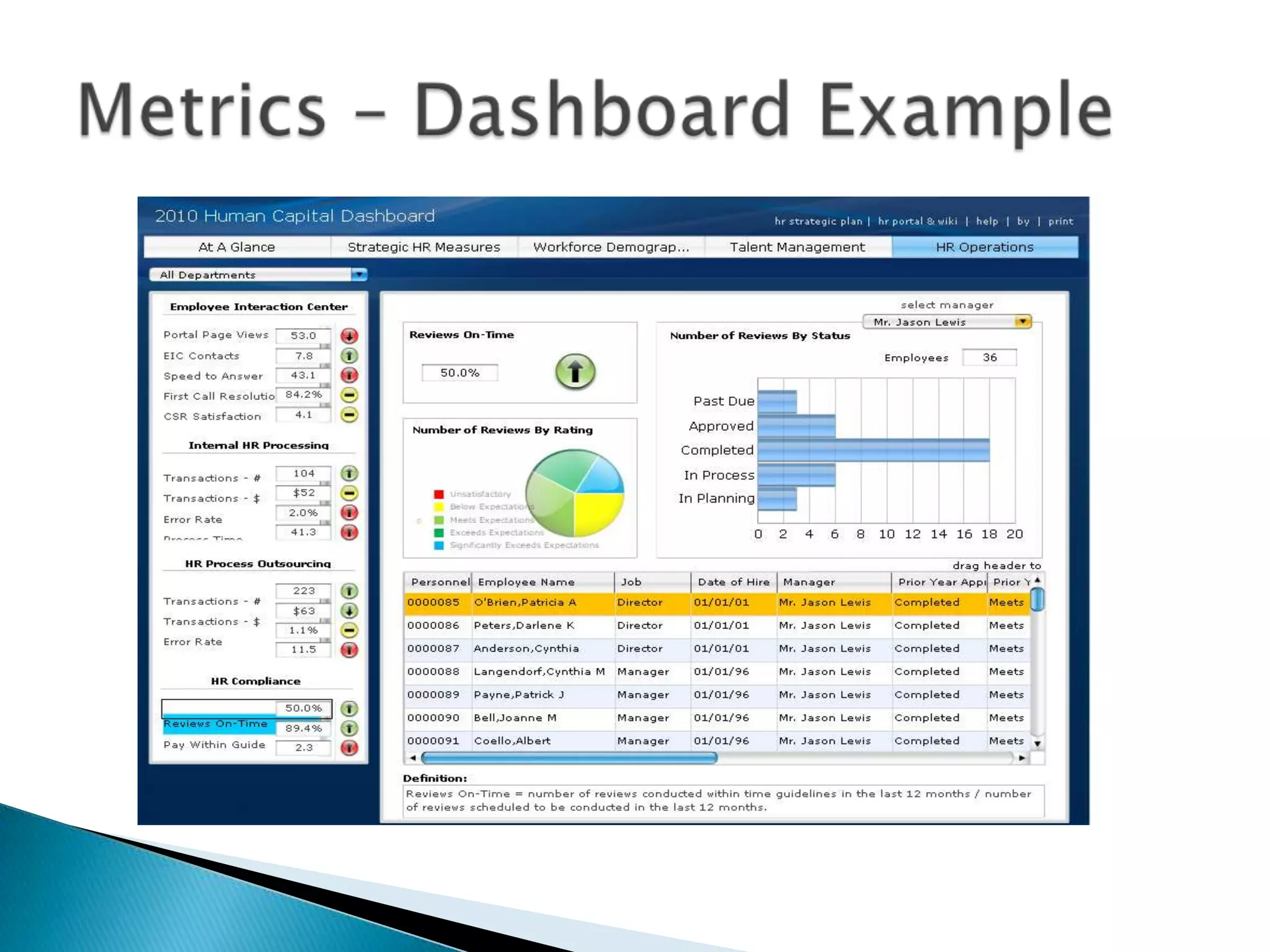
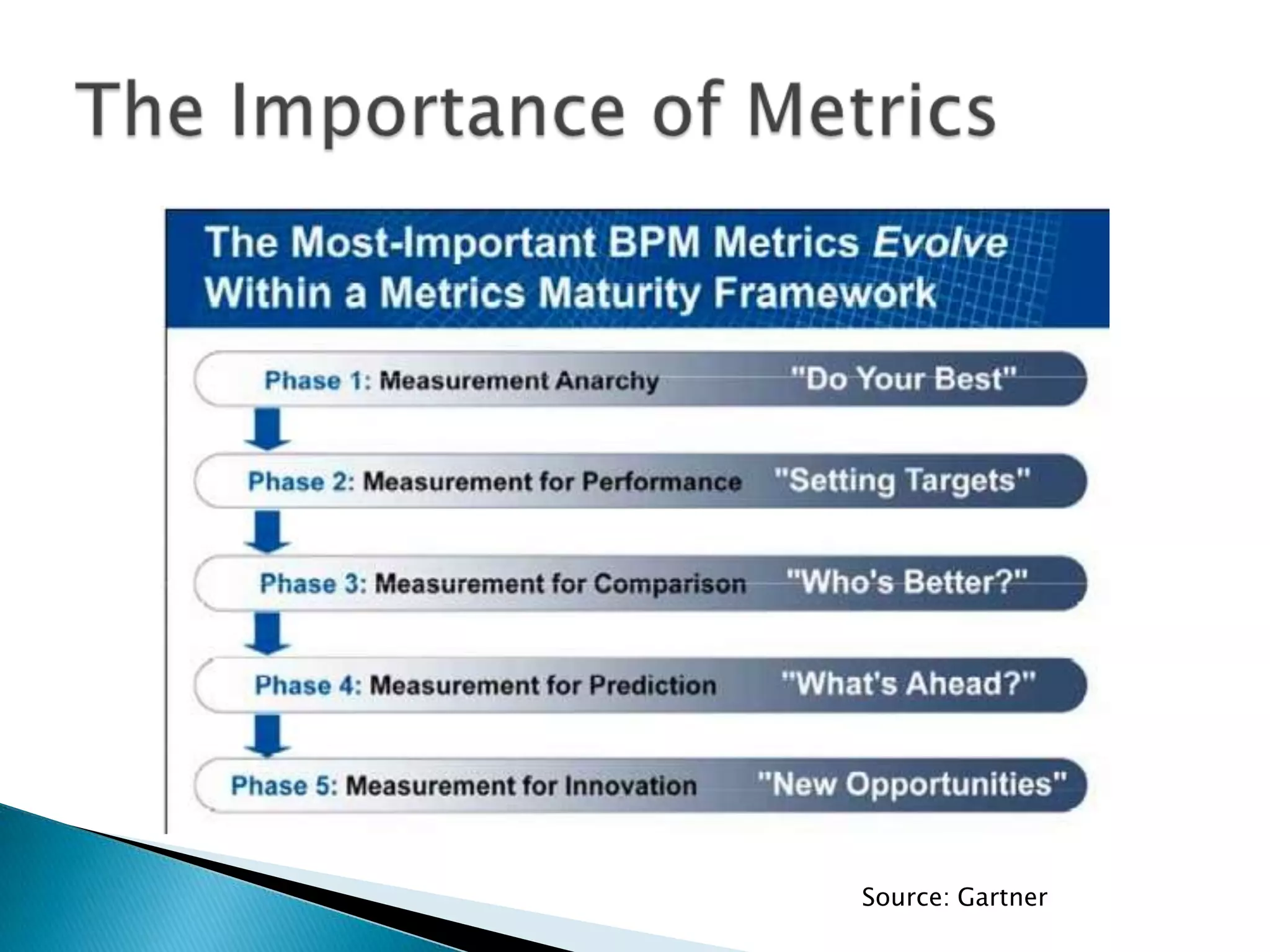
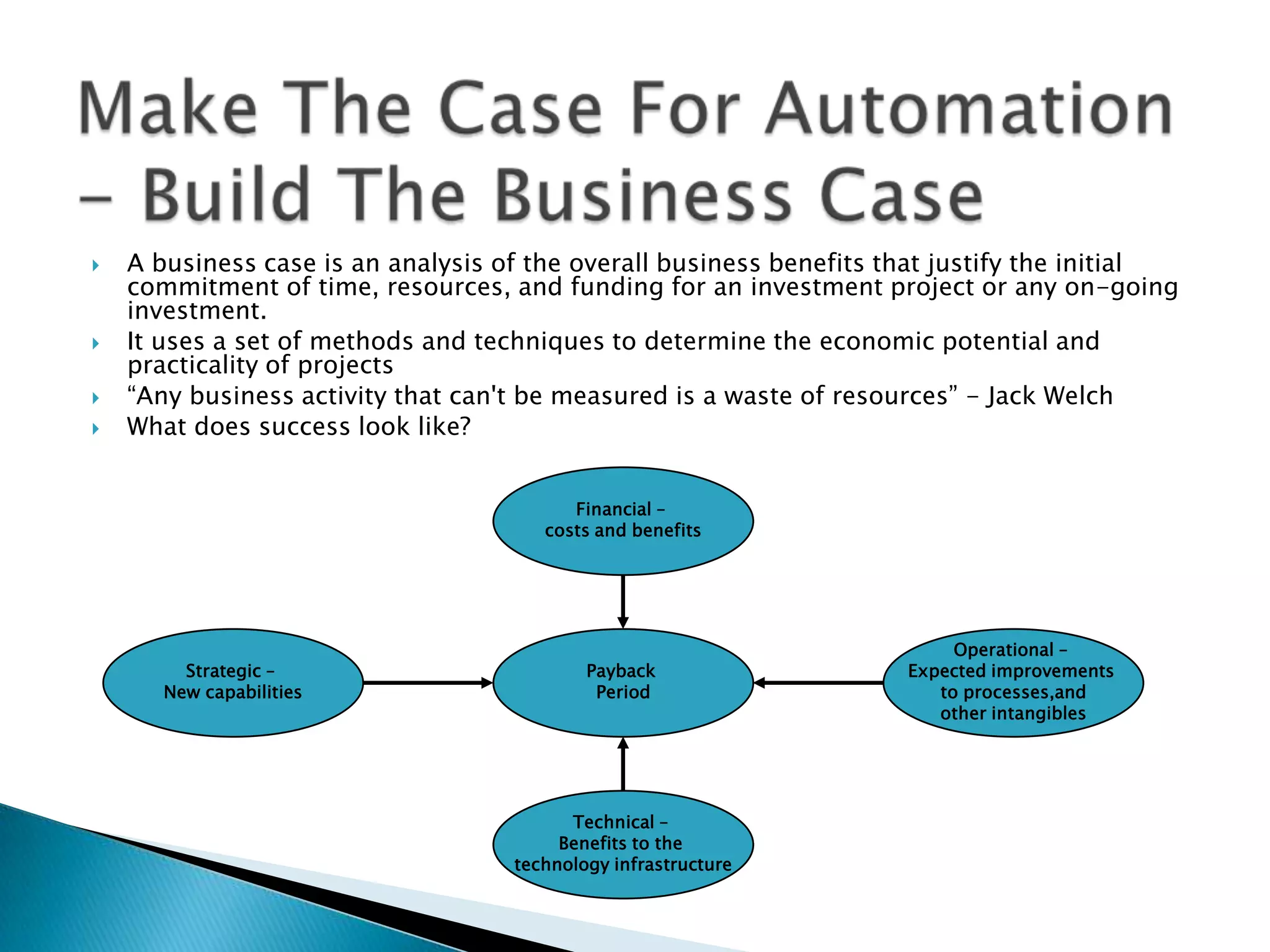
The document outlines best practices for optimizing business processes, focusing on efficiency, scalability, and risk management. It emphasizes the importance of a structured workflow management system for tracking process steps, enhancing job satisfaction, and accountability through KPIs. Additionally, the document discusses the need for collaboration between HR and IT and the significance of continuous improvement and proper technology integration.