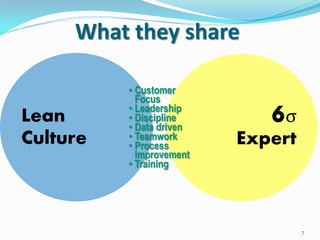
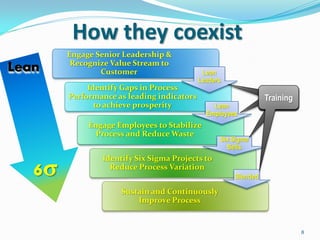
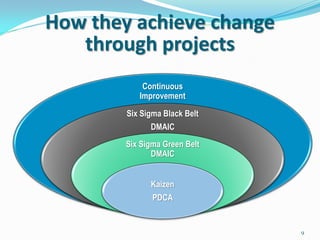
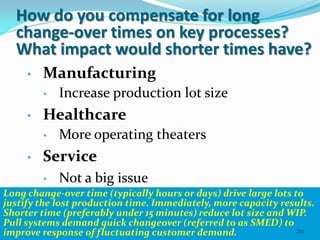
The document discusses the interplay between Lean and Six Sigma methodologies, emphasizing their unique focuses—Lean on waste reduction and employee engagement, and Six Sigma on statistical analysis and defect reduction. It outlines how these approaches can coexist by promoting leadership, team engagement, and sustained improvement through various training and project management techniques. Additionally, it poses critical questions for assessing organizational readiness for Lean and Six Sigma practices while underlining the importance of process reliability and quality performance.