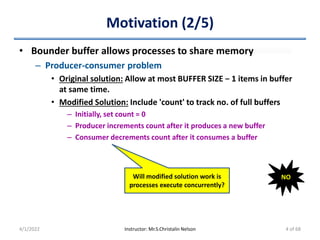
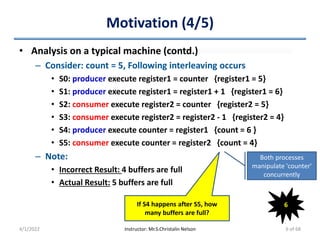
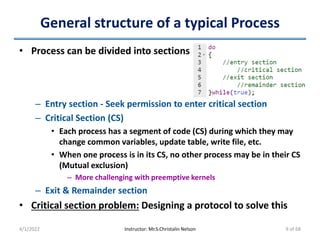
This document discusses process synchronization and solutions to common synchronization problems. It begins by motivating the need for process synchronization when multiple processes concurrently access shared data. It then presents the bounded buffer problem and shows how a race condition can occur when processes increment and decrement a shared counter concurrently. The document goes on to describe general solutions to synchronization including mutual exclusion locks and semaphores. It discusses issues like priority inversion and deadlocks. Finally, it provides overviews of classic synchronization problems like the bounded buffer, readers-writers, and dining philosophers problems.






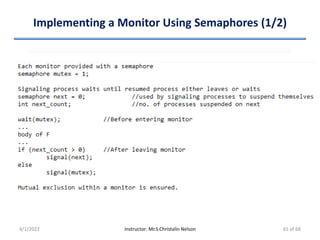
![Algorithm (2/5)
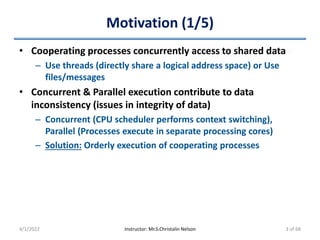
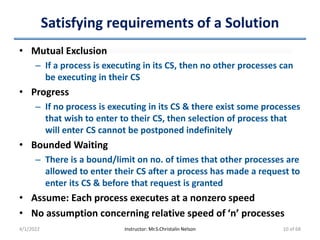
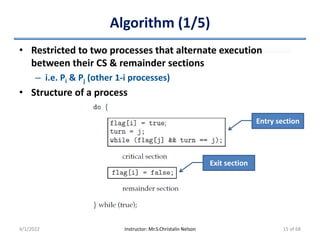
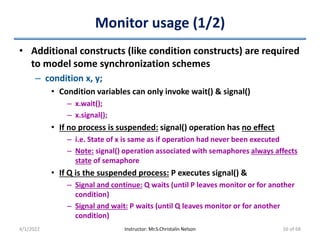
• Processes share two data items
– int turn
• Denotes the process which can enter its CS
• Pi enters CS => Set “turn == i”
– boolean flag[2]
• Denotes the process which is ready to enter its CS
• Pi is ready to enter CS => Set “flag[i] == true”
• Before Pi to enters its CS
– Set flag[i] = true
– Set turn = j
• Asserts Pj to enter CS if required
• Eventual value of 'turn' determines which process is allowed first
to enter its CS
4/1/2022 Instructor: Mr.S.Christalin Nelson 16 of 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processsynchronization-220401090626/85/Process-Synchronization-16-320.jpg)
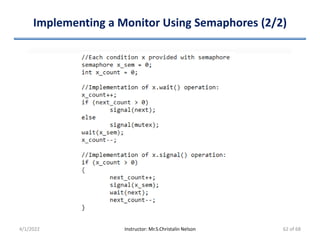
![Algorithm (4/5)
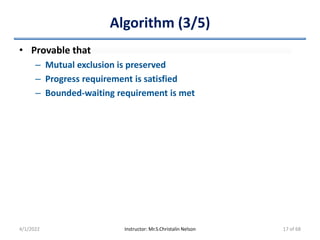
• Proof of Property 1 (Mutual Exclusion)
– Each Pi can enter its CS if flag[j] == false or turn == i
– Both processes can be executing in their CSs at same time, if
flag[0] == flag[1] == true
• P0 & P1 cannot successfully execute their while statements at
about same time since turn == 0 or 1 (cannot be both)
– Hence, one of the processes (say Pj) must have successfully
executed while statement
– Whereas Pi had to execute at least one more statement (“turn == j”)
– Now, flag[j] == true & turn == j. This condition persists as Pj is in CS
– Hence mutual exclusion is preserved
4/1/2022 Instructor: Mr.S.Christalin Nelson 18 of 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processsynchronization-220401090626/85/Process-Synchronization-18-320.jpg)
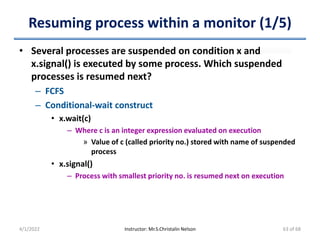
![Algorithm (5/5)
• Proof of Properties 2 & 3 (Progress & Bounded waiting)
– Pj is not ready to enter CS, set flag[j] == false. Then, Pi can
enter its CS
– Pj is ready to enter CS, set flag[j] == true & is also executing in
its while statement
– Pj will enter CS, eventually turn == j
• Else Pi will enter CS (turn == i)
– Pj exits CS, reset flag[j] == false. Then, Pi can enter CS
– Pj wants to enter CS again, resets flag[j] == true, it also sets
turn == i
• Now, Pi does not change value of turn while executing while
statement & hence Pi will enter CS (progress) after at most one
entry by Pj (bounded waiting)
• Pi can be prevented from entering CS only if it is stuck in while
loop with flag[j] == true & turn == j
4/1/2022 Instructor: Mr.S.Christalin Nelson 19 of 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processsynchronization-220401090626/85/Process-Synchronization-19-320.jpg)

















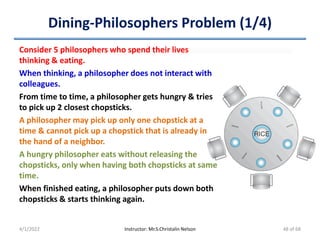
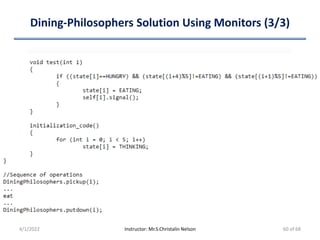
![Dining-Philosophers Problem (2/4)
• Allocation of several resources among several processes in a
deadlock-free & starvation-free manner
• Solution: Represent each chopstick with a shared semaphore
– semaphore chopstick[5] = {1};
– A philosopher
• Executes wait() to get a chopstick
• Executes signal() on appropriate semaphore to release chopsticks
4/1/2022 Instructor: Mr.S.Christalin Nelson 49 of 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processsynchronization-220401090626/85/Process-Synchronization-49-320.jpg)



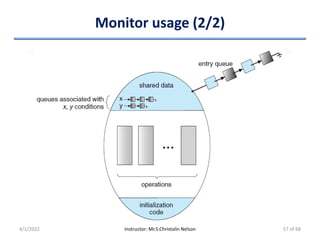
![Dining-Philosophers Solution Using Monitors (1/3)
• Philosopher picks chopsticks only if both are available (in CS)
• States of a Philosopher
– enum {THINKING, HUNGRY, EATING} state[5];
• Default state of all philosophers: THINKING
• Philosopher ‘i' can eat, if its present state is HUNGRY & its two
neighbors are not EATING
– i.e. state[i] = EATING only if
» state[i] = HUNGRY
» state[(i+4) % 5] != EATING
» state[(i+1)% 5] != EATING
4/1/2022 Instructor: Mr.S.Christalin Nelson 58 of 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processsynchronization-220401090626/85/Process-Synchronization-58-320.jpg)