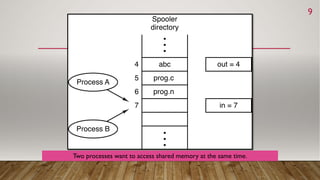
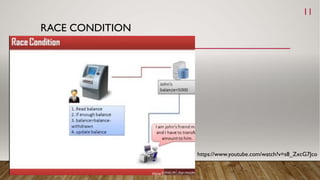
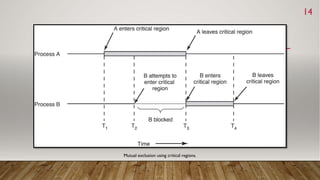
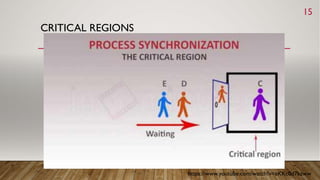
This document discusses process synchronization and mutual exclusion. It begins by explaining race conditions and critical regions. It then covers various solutions for achieving mutual exclusion, including busy waiting, Peterson's algorithm, sleep/wakeup concepts, semaphores, and mutexes. Semaphores use down() and up() operations to control access to shared resources, while mutexes use lock/unlock operations to allow only one thread access to a critical section at a time. Both help processes synchronize access to shared memory and resources.