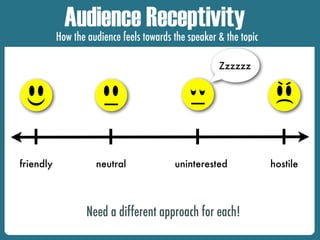
The document outlines the requirements and techniques for preparing an informative presentation, emphasizing the importance of topic selection, audience analysis, and structure. Key points include establishing a clear introduction, body, and conclusion while adhering to citation guidelines and utilizing quality sources. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of understanding audience needs and tailoring the speech accordingly to engage effectively.