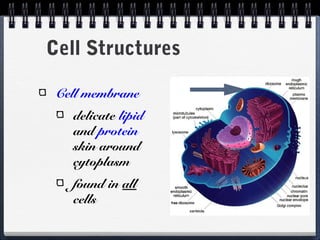
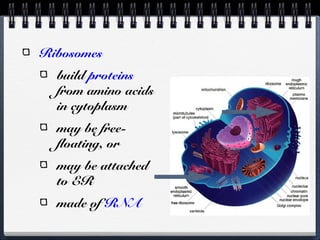
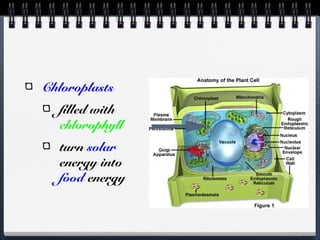
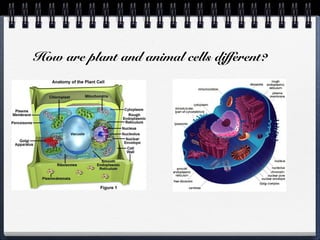
This document compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler, lacking organelles and existing as single-celled organisms. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, containing membrane-bound organelles and existing as both single and multicellular organisms. A key difference is that eukaryotic cells evolved from endosymbiotic relationships between prokaryotes, where cellular structures like mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from incorporated prokaryotes.