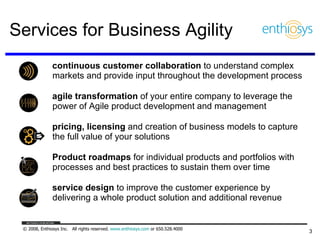
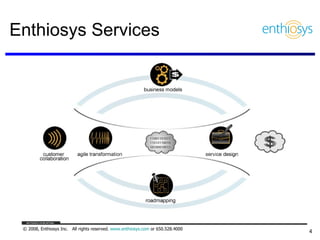
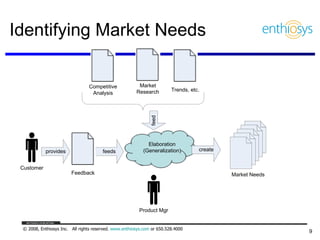
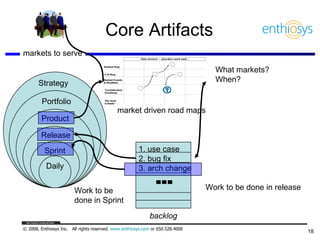
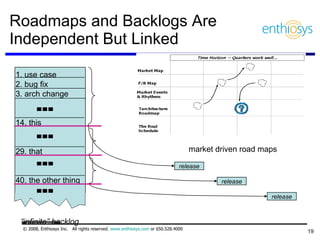
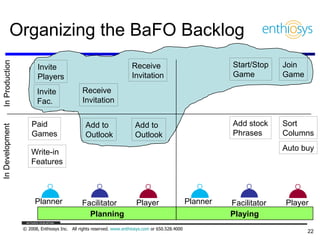
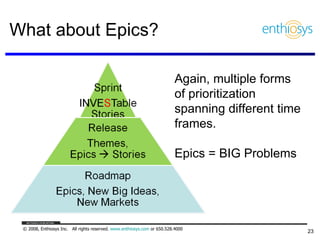
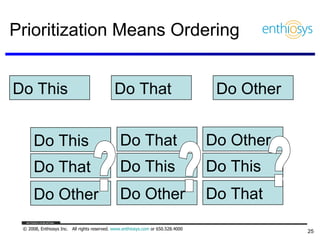
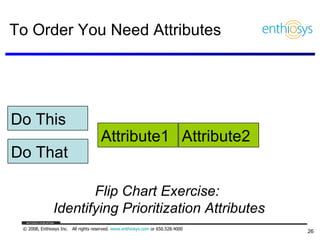
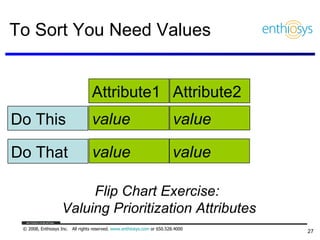
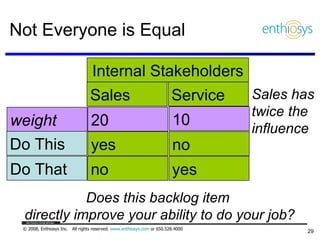
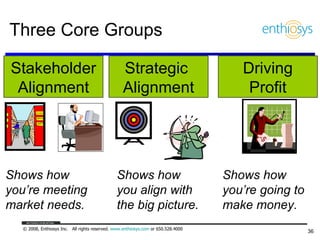
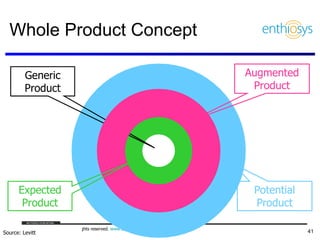
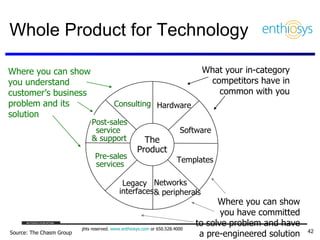
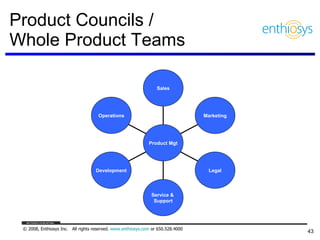
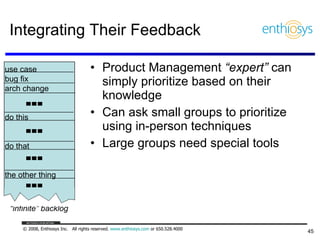
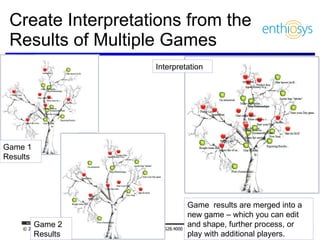
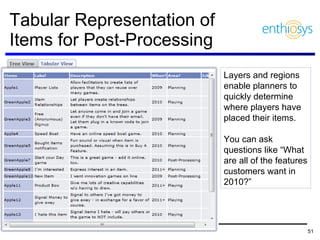
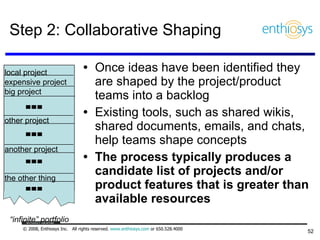
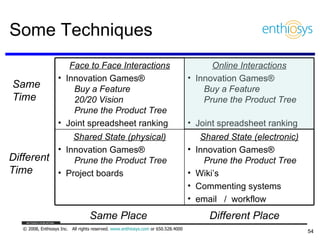
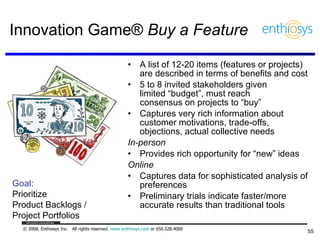
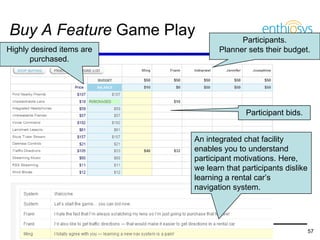
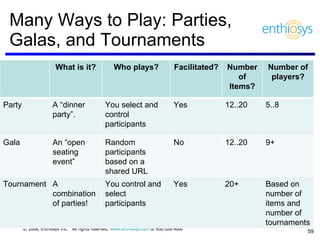
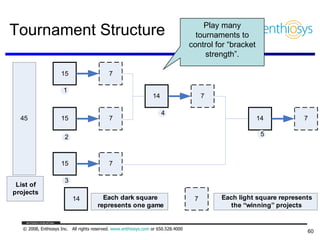
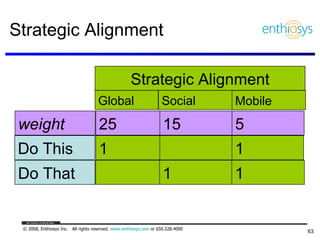
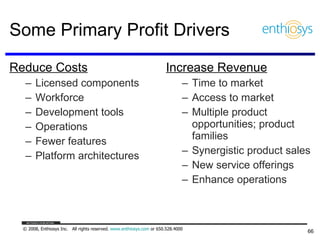
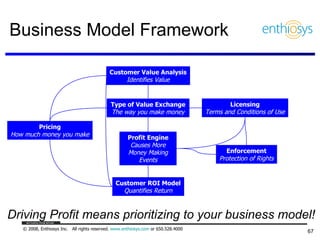
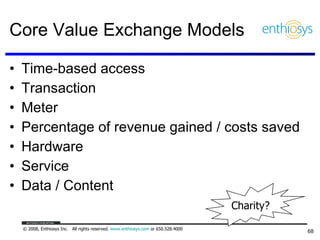
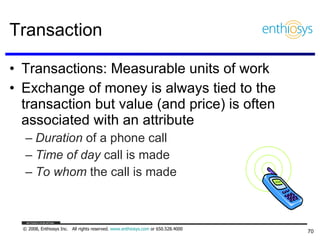
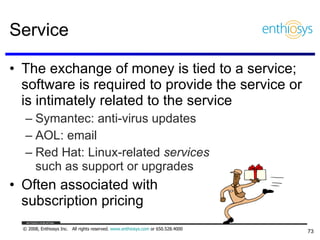
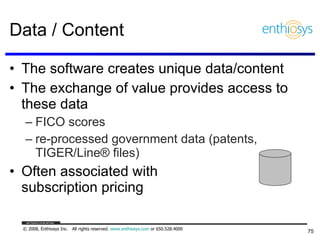
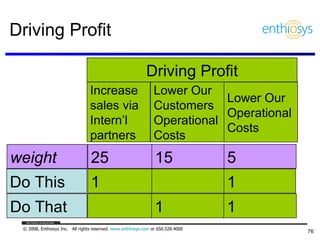
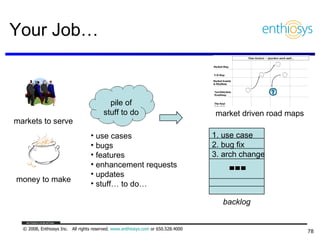
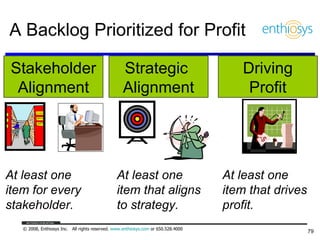
The document discusses prioritizing a product backlog for profit. It recommends considering three core groups when prioritizing: stakeholder alignment, strategic alignment, and driving profit. For stakeholder alignment, the backlog should include at least one item for each stakeholder group. For strategic alignment, it should include at least one item that aligns with the company's strategy. And to drive profit, it should include at least one item that generates revenue or reduces costs. The document provides various techniques for involving stakeholders, determining strategic priorities, and identifying profit drivers to create a holistically prioritized backlog.





































![Contact and Content Reach me at [email_address] More about agile and business models: agilePM blog and Product Bytes newsletter at http://www.enthiosys.com/insights-tools/ www.innovationgames.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agilepalooza-2009-prioritizingforprofit-090529163652-phpapp02/85/Prioritizing-for-Profit-from-AgilePalooza-80-320.jpg)