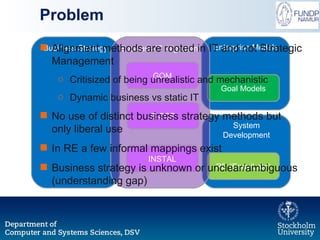
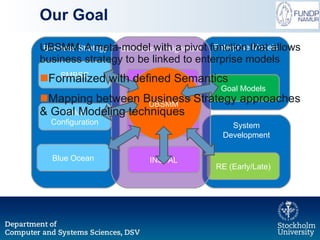
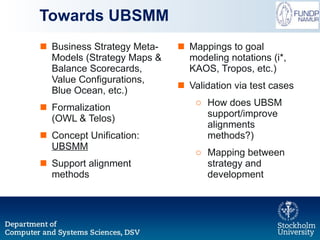
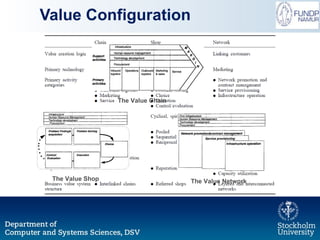
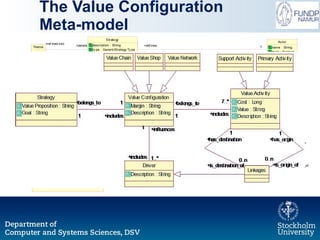
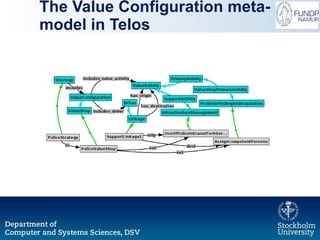
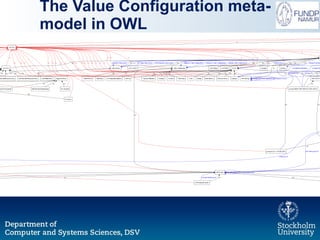
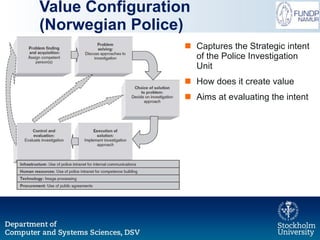
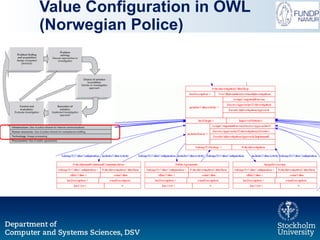
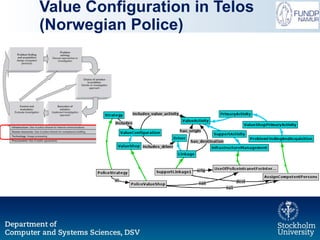
The document outlines a research initiative aimed at developing a Unified Business Strategy Meta-Model (UBSMM) to enhance business-IT alignment. It identifies existing gaps in the understanding and formalization of business strategies and proposes methods to integrate them with system requirements through various modeling techniques. Future work includes further formalization, validation, and mapping of UBSMM with existing business strategies to improve alignment methods.






![Questions? Constantinos Giannoulis [email_address] http://constantinos.blogs.dsv.su.se / Jelena Zdravkovic [email_address] http://jelena.blogs.dsv.su.se/ Micha ë l Petit [email_address] http://www.fundp.ac.be/universite/personnes/page_view/01002983/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/busital2011-110623061345-phpapp01/85/Modeling-Competition-driven-Business-Strategy-for-Business-IT-Alignment-19-320.jpg)